-
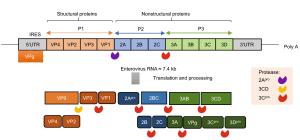
-
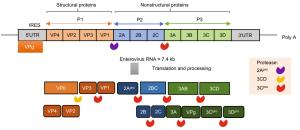
-
Organizations Sinovac Biotech Co., Ltd Beijing Vigoo Biological Co., Ltd Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences EV-A71 Strain H07 (C4) FY (C4) M01 (C4) Inactivation technique Formalin Formalin Formalin Cell substrate Vero cells Vero cells Human diploid KMB-17 cell Dosages 400 U, two-dose 320 U, two-dose 100 U, two-dose Adjuvant Aluminum hydroxide Aluminum hydroxide Aluminum hydroxide Population target Children (6–35 month) Children (6–35 month) Children (6–71 month) Enrollment 10, 077 10, 245 12, 000 References NCT01507857 NCT01508247 NCT01569581 Table 1. Official licensed inactivated EV-A71 vaccines by the Chinese Food and Drug Administration.
-
VLP-producing systems Yield capacity Properties Status Ref. Baculovirus-insect cell Moderate (64.3 mg/L) Moderate-yield; Relatively high cost; Large stocks (cell & viruses); Contamination risk of virus Lab (Chung et al. 2010) Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast Low (0.25 mg/L) Low-yield; Low cost; Ease in manipulation Lab (Li et al. 2013) Pichia pastoris yeast High (270 mg/L) High-yield; Low cost; Easy manipulation Clinical trial (CXSL1900022) (Yang et al. 2019) Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (rVSV) – Attenuated(ΔM51);
Replication-competent and may have adverse effectsLab (Yan et al. 2016) Recombinant adenovirus 5 (Ad-EVVLP) – Replication-incompetent(ΔE1/ΔE3); 3C-specific cellular immunity
Ad-EVVLPs from EV71 genes can protect against CVA16 infectionLab (Tsou et al. 2015) Table 2. The producing systems of enterovirus-related virus-like particle (VLP).
-
Vaccine
formatConformation Immunogenicity mAb
responsesLimitation Advantages Inactivated whole virus Natural virion with genome Strong (+++) High; Cross-genotype protection Low cross-serotypic protection Mature technology VLP Natural virion without genome Moderate (++) High; Cross-genotype protection Low cross-serotypic protection Safe; Low cost; Explicit composition; Easy large-scale production and quality control Synthetic peptide or recombinant subunit Linear epitope or antigen Relatively weak (+) Low; Cross-genotype protection Low cross-serotypic protection; Strong adjuvant requirement Safe; Inexpensive; Explicit composition; Easy large-scale production and quality control Novel chimeric vaccines Natural virion without genome or linear epitopes of antigens Relatively high (++/+++) High; Cross-genotype protection Required to know key neutralization domain and need to design the optimal chimeric strategy May induce cross-protection of serotypes Recombinant virus-vector vaccines Natural virion without genome of target viruses but vectors Relatively high (++/+++) High; Cross genotype protection Risk of vector replication May induce cross-protection of serotypes; Comprehensive T-cell immune response Table 3. The characteristics of the primary experimental enterovirus vaccine formats.
Figure 2 个
Table 3 个