-
-
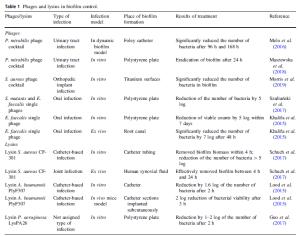
Phages/lysins Type of infection Infection model Place of biofilm formation Results of treatment Reference Phages P. mirabilis phage cocktail Urinary tract infection In dynamic biofilm model Foley catheter Significantly reduced the number of bacteria after 96 h and 168 h Melo et al.(2016) P. mirabilis phage cocktail Urinary tract infection In vitro Polystyrene plate Eradication of biofilm after 24 h Maszewska et al. (2018) S. aureus phage cocktail Orthopedic implant infection In vitro Titanium surfaces Significantly reduced the number of bacteria in biofilm Morris et al. (2019) S. mutants and E. faecalis single phages Oral infection In vitro Polystyrene plate Reduction of the number of bacteria by 5 log Szafrański et al.(2017) E. faecalis single phage Oral infection In vitro Polystyrene plate Reduction of viable counts by 5 log within 7 days Khalifa et al. (2015) E. faecalis single phage Oral infection Ex vivo Root canal Significantly reduced the number of bacteria by 7 log after 48 h Khalifa et al. (2015) Lysins Lysin S. aureus CF-301 Catheter-based infection In vitro Catheter tubing Removed biofilm biomass within 4 h; reduction of the number of bacteria > 5 log Schuch et al.(2017) Lysin S. aureus CF-301 Joint infection Ex vivo Human synovial fluid Effectively removed biofilm between 4 h and 24 h Schuch et al.(2017) Lysin A. baumannii PlyF307 Catheter-based infection In vitro Catheter Reduction by 1.6 log of the number of bacteria after 2 h Lood et al. (2015) Lysin A. baumannii PlyF307 Catheter-based infection In vivo mice model Catheter sections implanted subcutaneously 2 log reduction of bacterial viability after 3 h Lood et al.(2015) Lysin P. aeruginosa LysPA26 Not assigned type of infection In vitro Polystyrene plate Reduction by 1–2 log of the number of bacteria after 2 h Guo et al.(2017) Table 1. Phages and lysins in biofilm control.
Figure 1 个
Table 1 个