-
-
-

-
Classification Method Principle Accessibility Compiling environment Using experience Required data Limitation References Phylogenetic tree-based FluReF A bottom-up research Source code Written by C ++ on Linux system The test dataset containing 1050 strains spent 10 s in total Complete genome of influenza virus High computational complexity Yurovsky and Moret (2011) Villa et al. Core mutations Source code Written by both C++ and python on Linux system The mock test dataset containing 7477 strains with the 290 bp simulated genomic sequence took more than 5 days in total Complete HA and NA sequences Limited to the reassortment identification of the HA and NA segments Villa and Lassig (2017) FluResort Identities of predicted protein Web invalid Written with ANSI/ISO standard C ++ on both Windows or Linux systems Not available Viral protein sequences and mass spectral data of these proteins Limited to the HA, NA, NP and M1 proteins, and the mass spectral data with high-resolution was required Lun et al. (2012) Nagarajan et al. Enumerating maximal bicliques Not supported Not supported Not available Genomic segments of influenza virus High computational complexity Nagarajan and Kingsford (2008) GiRaF Graph theory Source code Written by C ++ on Linux, Mac or Windows systems The test dataset containing 35 strains took about 5 s in total Complete genome of influenza virus High computational complexity Nagarajan and Kingsford (2011) Suzuki et al. Topologies of quartet trees Not supported Not supported Not available Complete genome of influenza virus High computational complexity Suzuki (2010) Dong et al. Genotype profile IVEE soft Written by both C ++ and python on Windows system Each complete genome took 3 about seconds Complete genome and the genotype information It had limitations when inferring intra-subtype reassortments within the same host Dong et al. 2011) Phylogenetic tree independent Wan et al. Network module; MST Not supported Not supported Not available Genomic segments of influenza virus Not suitable for short sequences Wan et al.(2007a, 2007b, 2008) Rabadan et al. Hamming distance Not supported Not supported Not available Genomic segments of influenza virus The assumption of equal mutation rate among segments may not always hold Rabadan et al. (2008) Silva et al. Genetic distance Not supported Written by Ruby script using bioruby on a Debian Linux server system Not available Genomic segments of influenza virus The performance of this algorithm will be influenced by the sample bias significantly de Silva et al. (2012) HoPER Host tropism Not supported Not supported Not available The full-length amino acid sequences of all genomic segments It is difficult to identify the reassortments between different hosts Yin et al. (2020) Table 1. A brief review of the reassortment identification methods for the influenza viruses.
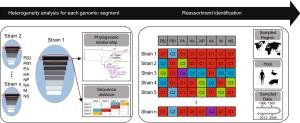
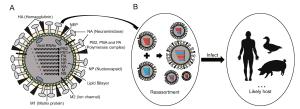
Figure 3 个
Table 1 个