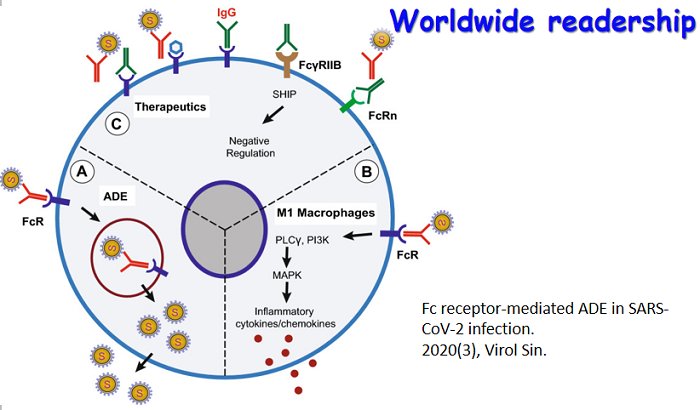
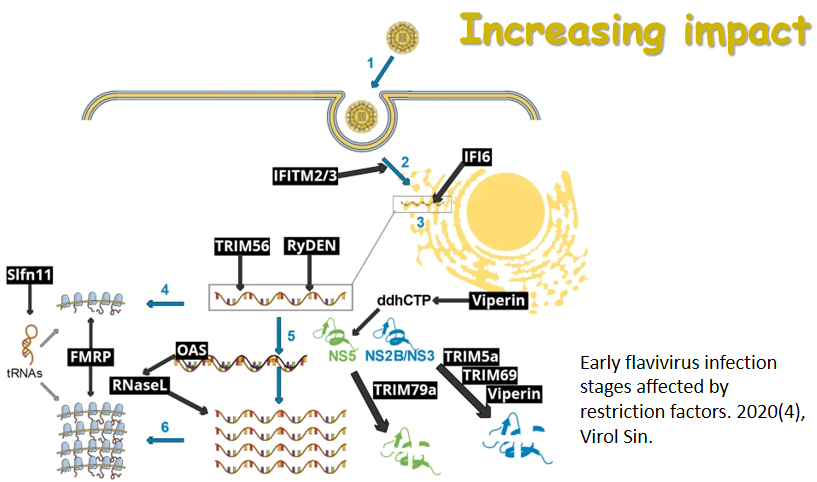
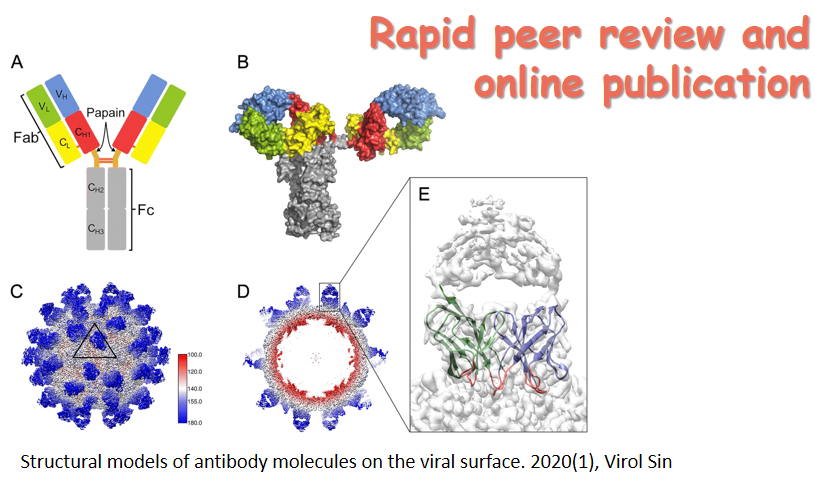
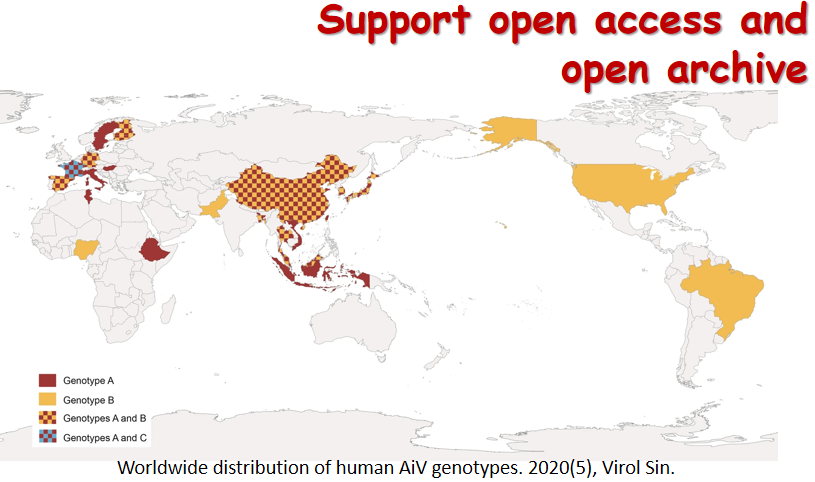
6月24日,国际学术期刊 Journal of Immunology在线发表了病毒学国家重点实验室朱应教授研究组的最新研究成果,论文题为NAC1 Potentiates Cellular Antiviral Signaling by Bridging MAVS andTBK1 (《NAC1通过桥接MAVS和TBK1增强细胞抗病毒信号通路》)。该工作揭示了在RNA病毒感染过程中,NAC1通过桥接MAVS和TBK1,诱导RIG-I样受体(RLR)介导的I型IFN表达的抗病毒机制。

细胞内病毒RNA被RIG-I样受体(RLR)识别,其通过线粒体抗病毒信号蛋白MAVS发出信号。MAVS募集并激活TBK1激酶,其进一步磷酸化和激活转录因子IRF3,诱导I型IFN和下游抗病毒基因的表达。研究人员鉴定了BTB / POZ家族成员中的人类伏隔核相关蛋白1(NAC1),其作为MAVS和TBK1的桥梁,正调节RLR介导的I型IFN的表达。NAC1的过表达或敲低可分别增强或降低仙台病毒引发的TBK1和IRF3的活化,以及IFN-β的表达。NAC1还显著增强针宿主对多种RNA病毒的抗病毒反应。在病毒感染后,NAC1能够与MAVS和TBK1相互作用。NAC1的BTB / POZ结构域(aa 1-133)与MAVS相互作用,其余部分与TBK1结合。此外,NAC1可以促进TBK1向MAVS的募集。相比之下,NAC1的敲低减弱了TBK1和MAVS之间的相互作用。总的来说,研究表明了NAC1是RLR介导的先天免疫反应的重要组成部分,并揭示了BTB / POZ家族蛋白质以前未被认识到的功能。
博士夏章传为该论文的第一作者,朱应教授为通讯作者。这项工作得到了国家自然科学基金和湖北省创新集团自然科学基金的研究资助。
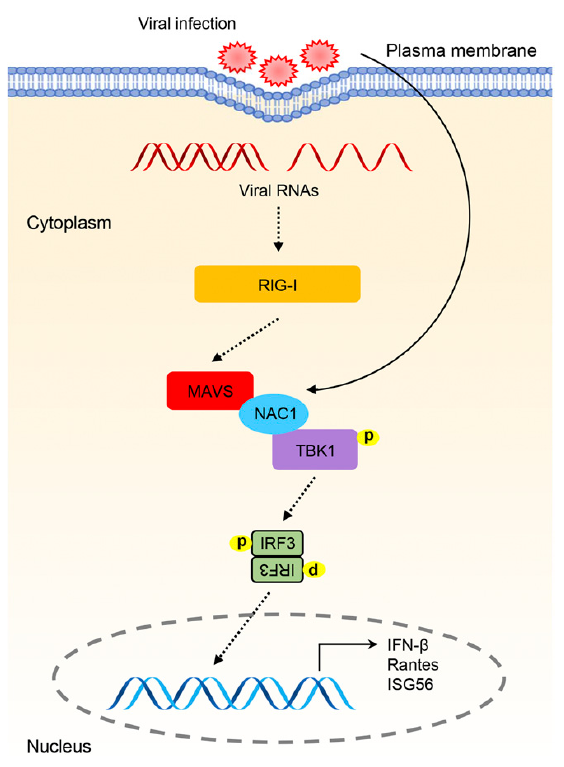
Abstract: Intracellular viral RNAs are recognized by the RIG-I–like receptors (RLRs), which signal through the mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS. MAVS recruits and activates TBK1 kinase, which further phosphorylates and activates the transcription factor IRF3, leading to the induction of type I IFN and downstream antiviral genes. We identified human nucleus accumbens-associated 1 (NAC1), a member of the BTB/POZ family, as a bridge for MAVS and TBK1 that positively regulates the RLR-mediated induction of type I IFN. Overexpression or knockdown of NAC1 could, respectively, enhance or impair Sendai virus–triggered activation of TBK1 and IRF3, as well as induction of IFN-β. NAC1 also significantly boosted host antiviral responses against multiple RNA viruses. NAC1 was able to interact with MAVS and TBK1 upon viral infection. The BTB/POZ domain (aa 1–133) of NAC1 interacted with MAVS, and the remainder of NAC1 bound to TBK1. Furthermore, NAC1 could promote the recruitment of TBK1 to MAVS. In contrast, knockdown of NAC1 attenuated the interaction between TBK1 and MAVS. Collectively, our study characterizes NAC1 as an important component of RLR-mediated innate immune responses and uncovers a previously unrecognized function of the BTB/POZ family proteins.