-
Baculoviridae is a family of rod-shaped viruses with circular, covalently closed, double-stranded DNA genomes that range in size from 81.7 kb to 161 kb[11, 19, 20]. There are two genera, Nucleopolyhedroirus (NPV) and Granulovirus(GV), in this family[34]. NPV genes are subdivided into four groups: immediate early, delayed early, late, and very late [4]. Immediate early and delayed early genes are transcribed using host RNA polymerase Ⅱ after infection and some of them code for transcriptional transactivators of viral genes[7, 12, 14, 23, 32].
Baculovirus IE1 is a putative multifunctional protein coded by the viral immediate early 1(ie1) gene[1, 3, 37]. It was shown, in transient expression experiments, to be essential in viral DNA replication [16, 31]. Baculovirus IE1 can transactivate all known early genes and late genes of the virus [2]. Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus (BmNPV) IE1 transactivates a cell housekeeping gene promoter [22], Orgyia pseudotsugata multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (OpMNPV) and Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (AcMNPV) IE1 can self stimulate their expression[18, 33]. Furthermore, the baculovirus IE1 gene down regulates the expression of some other genes such as ie0, ie2[17] and pe38[21]. NPV genomes contain several regions of homologous DNA of 76 to 800 bp that are interspersed throughout the genome.The larger homologous regions (hrs) were shown to have the ability to cis-activate expression of the early generomoters. Recent studies showed that heterologous IE1 had a negative effect on late gene expression and truncated BmNPV IE1 strongly inhibited activation of the hr5-dependent p35 promoter[38]. These suggest that IE1 functions as a regulatory factor in different modes.
The functional domain of the baculovirus IE1 has been well characterized by mutant analysis. There is an acidic activation domain (AAD) which contains a virus specific domain for DNA replication, a highly conserved basic domain which is required for DNA binding and transactivation[29, 31], and a domain for possible second transactivation in the N-terminal region. An DNA binding domain and oligomerization domain are in the C-terminal region[9, 31].
The baculovirus IE1 was found to be functional in mammalian cells by transient expression assay. The viral early 39k promoter activated by the IE1 is dependent on the hr sequence in mammalian cells but is independent of the hr sequence in insect cells, which suggests that IE1 might exhibit different transcriptional modes[25]. Since BmNPV IE1 can transactivate several viral and heterologous core promoters this suggests that baculovirus IE1 has the potential to activate a core promoter in mammalian cells[24].
Phylogenetic analysis indicates that the nucleopolyhedroviruses are comprised of groupⅠand group Ⅱ NPV[6, 13]. Although the SeMNPV belong to group Ⅱ NPV, the amino acid sequence of SeMNPV IE1 has diverged considerably from others of group Ⅰ and group Ⅱ NPV IE1[15, 35, 36]. So far, the characterization of baculovirus IE1 had only been performed in group Ⅰ NPV. In this paper, we reported the function of SeMNPV IE1 in mammalian cells. This was first work for groupⅡ NPV IE1 function. By studying the expression of SeMNPV IE1-green fluorescent protein (IE1-EGFP) in HEK 293 cells, the IE1-EGFP fusion protein was localized in the nucleus of mammalian cells. SeMNPV IE1 could stimulate the F protein promoter but not affect the gp64 promoter in HEK 293 cells.
HTML
-
Human embryo kidney (HEK) 293 cells were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Invitrogen) in an incubator with 5% CO2 at 37℃.
-
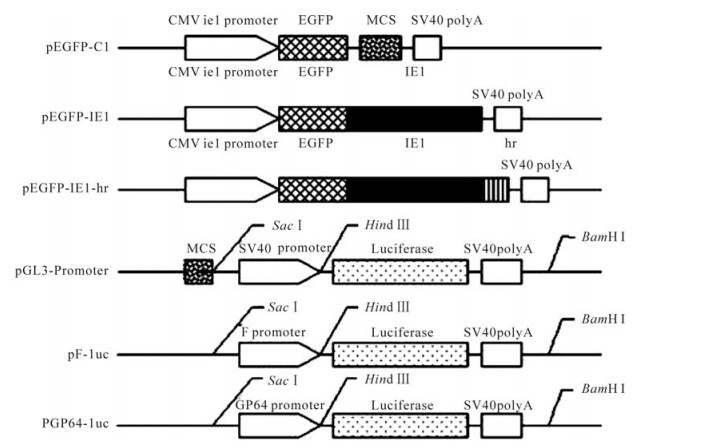
The structure of EGFP-IE1, EGFP-IE1-hr, pGL3-Promoter, pF-luc, and pGP64-luc constructors are shown in Fig. 1. For constructing the pEGFP-IE1 plasmid, SeMNPV ie1 ORF sequence was amplified by PCR using the SeMNPV genome as template with forward primer 5'-CTGAAGCTTCGATGCACACTCCGAGTCAC-3' and reverse primer 5'-GACGGATCCCTAATTGATAGATTTAGCATTC-3'. The PCR product was cloned in pMD18-T (Takara) and excised with Hind Ⅲ and BamH Ⅰ, then ligated with pEGFP-C1 (Clonetech) to produce pEGFP-IE1 plasmid.
For constructing the pEGFP-IE1-hr5, hr5 derived from SeMNPV was amplified by PCR with forward primer 5'-AACGGATCCCAATTTCAATACATGATC-3' and reverse primer 5'-CGAGGATCCACACAAACGAATCGT G-3'. The PCR product was cloned and digested with BamH Ⅰ, then the hr5 sequence was ligated with pEGFP-IE1 to construct pEGFP-IE1-hr5.
To construct pF-luc and pGP64-luc, the F promoter derived from SeMNPV was amplified with forward primer 5'-GGTGAGCTCTTTGGTCGTCGTCGTC-3' and reverse primer 5'-ACGAAGCTTATTTTGCTTGCGACT C-3', using SeNMPV genome as template; the gp64 promoter was amplified with forward primer 5'-GTGGAG CTCGTCGACTGAGCGTCCG-3' and reverse primer 5'-GCTAAGCTTCTTGCTTGTGTGTTCC-3', using AcMNPV genome as template. Sac Ⅰ-Hind Ⅲ digested F and gp64 promoter was ligated to pGL-3-Promoter vector digested with Sac Ⅰ and Hind Ⅲ (Promega) respectively to produce pF-luc and pGP64-luc. hr5 derived from SeMNPV was digested with BamH Ⅰ and inserted to pF-luc and pGP64-luc respectively to construct pF-luc-hr5 and pGP64-luc-hr5. pSV- -gal (Promega) was used as control vector.
-
For luciferase and -galactosidase assay, HEK 293 cells in six-well plates were left overnight to allow cell attachment. Cell number was about 3×105 to 5×105 per well. Cotransfection was performed by mixing 1µg PEGFP-IE1 with 0.5 µg reporter plasmid and 0.5µg pSV- -gal and Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen). Co-transfection of 0.5 µg reporter plasmid and 0.5µg pSV- -gal was performed for negative control. All co-transfections were done at least three times.
For nucleus staining, a disinfected 22×22mm coverslip was placed in a 35-mm cell culture dish and plated on HEK 293 cells overnight to allow cell attachment. The cell number was about 3×105 to 5×105 per dish. Then cells were transfected with 1µg pEGFP-IE1 or pEGFP-IE1-hr5 by mixing with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent and cultured with Opti-MEM medium containing reduced serum (Invitrogen). After 4 hours of incubation, cells were replaced with DMEM containing 10% FBS.
-
Transfected HEK 293 cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in 500µL reporter lysis buffer for 10 min at room temperature. The lysates were scraped off the dishes and centrifuged for 5 min at 10 000×g, 100µL luciferase assay reagent was added to 100µL supernatant and mixed by pipetting 2-3 times briefly. The tube was placed in the luminometer immediately to perform a 2-second measurement delay followed by a 10-second measurement for luciferase activity. The value of relative light unit (RLU) was recorded and luciferase values were normalized to -galactosidase activity by performing standard liquid O-nitrophenyl -galactopyranoside (ONPG, Sigma) assays.
-
HEK 293 cells were fixed with paraformaldehyde at 16-48 h post-transfection with pEGFP-IE1, rinsed with PBS and incubated with Hoechst 33342 dye (4µg/mL PBS). A drop of anti-fade mounting medium was added to each load slip and plate on the coverslip attached with cells. Confocal images were obtained with a laser confocal microscope (Leica TCSSP2, Germany) for GFP and Hoechst. Merged figures were obtained by overlapping single-channel images.
-
The HEK 293 cells were transfected with pEGFP-C1 and pEGFP-IE1 respectively. The transfected cells were harvested at 48 h post-transfection. Cells were washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH6.2) and lysed with sodium dodecylsulfate lysis buffer. Equal volumes of lysates were resolved by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Millipore). The membrane was immunolabeled with 1:1 000 dilution of anti-GFP polyclonal antibody. The immune complexes were detected with ECL.
Cell culture
Plasmid constructions
Plasmid transfections
Reporter assays
Confocal microscopy
Western blot analysis
-
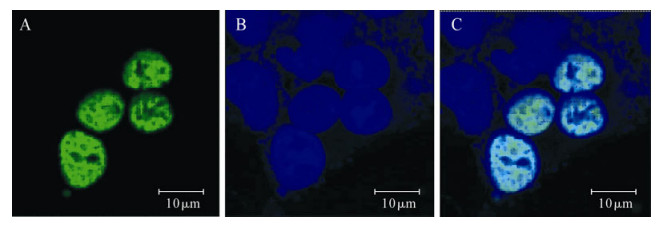
To investigate the intracellular localization of SeMNPV IE1 in mammalian cells, we expressed IE1 fused to the C-terminal of GFP under the control of the CMV (cytomega virus) ie1 promoter (Fig. 2). To confirm the expression of GFP-IE1 in mammalian cells, Western blot analysis with anti-GFP antibody was performed (Fig. 3). We found that GFP-IE1fusion protein was distributed within the nucleus of the mammalian cells (Fig. 4). The GFP-IE1 cis-linked to SeMNPV hr5 (GFP-IE1-hr5) didn't show any differences to the GFP-IE1. In our experiment, the negative control (pEGFP-C1) showed that GFP protein was distributed in cytoplasm.
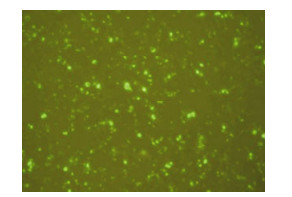
Figure 2. Visualization of EGFP-IE1 expression. Transfection of HEK 293 cells with plasmid pEGFP-IE1. Cells were analyzed directly by fluorescence microscopy at 24 h post-transfection. The GFP-IE1 fusion protein expressed in the cells was showed.

Figure 3. Western blot detection of EGFP-IE1. HEK293 cells plated on 35-mm cell culture dishes were transfected with 2 mg pEGFP-C1 and pEGFP-IE1 respectively. Cells were harvested 24h post-transfection and cell extracts were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membrane. EGFP alone and EGFP-IE1 fusion was detected as indicated above.
-
Recent studies, proved that SeMNPV IE1 stimulated late and early gene expression in insect cells, and the activating function was dependent on the baculovirus hr sequence[2]. The NPV can be subdivided into groups Ⅰ and Ⅱ, according to the size, shape and similarity of the genes. The group Ⅰ NPV possess the membrane protein GP64. The GP64 protein is expressed both in early and late stage of infection and is transported to and incorporated into the cell membrane. Group Ⅱ is characterized by the F protein instead of GP64 protein functioning in membrane fusion[5, 22, 39]. In our experiments, the gp64 and F promoters were used. When the reporter plasmid containing the gp64/F promoter was transfected alone, a certain amount of luciferase expression was detected, and the activity of the gp64 promoter was higher than that of F promoter. To examine the transactivation function on different promoters, pEGFP-IE1 was co-transfected with pF-Luc/pGP64-Luc. The results showed that the ie1-gp64 promoter was not significantly different from that of gp64 promoter alone, but the activity of the ie1-F promoter was about 3 folds higher than that of F promoter alone (Fig. 5).
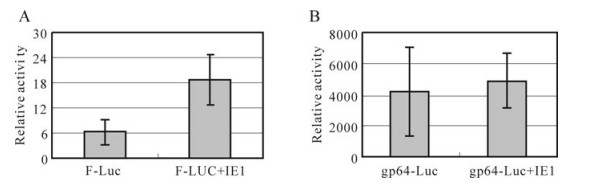
Figure 5. Transactivation effect of IE1 on SeMNPV F protein promoter and AcMNPV gp64 promoter. A HEK293 cells were transfected with pF-Luc alone or cotransfected with pEGFP-IE1. Cells were lysed 24h post-transfection and lysates were assayed for luciferase and -galactopyranoside activity according to standard procedure. Relative activity = relative light units/ OD420. B HEK293 cells were transfected with pGP64-Luc alone or cotransfected with pEGFP-IE1. Cells were analyzed at the same time and then analyzed with the same method. Bars above each column represent standard error.
SeMNPV-IE1 localizes in the nucleus of HEK293 cells
F promoter shows activity in mammalian cells
-
Mutation analysis has shown that a dimeric nucleus localization element is a prerequisite for IE1 localization and transactivation[30]. After the entry into nucleus, baculovirus IE1 binds the hr sequences and then locates at the virogenic stroma where the viral DNA replicates and the nucleocapsid is assembled[10, 26, 21, 28]. In insect cells, IE1-GFP exhibited the same dynamic localization as untagged IE1 and could be used as a reporter gene to track IE1 localization in insect cells[28]. In our study, pEGFP-C1, pEGFP-IE1 and pGFP-IE1-hr5 were transfected respectively and fluorescence microscopy showed that GFP alone was distributed in the cytoplasm, while EGFP-IE1 was transported to the nucleus of mammalian cells. Thus our reports showed that EGFP-IE1 also localizes in the nucleus of mammalian cells, and the IE1 form focal distribution didn't depend on the hr sequence. Although baculovirus IE1 could bind to hr in the absence of insect cell factors[8], SeMNPV IE1 didn't bind to hr sequence in mammalian cells. This suggested that the formation of IE1 focus might need other specific factor(s) in mammalian cells. The further detail of IE1 localization in mammalian cell lines may disclose the binding and localization mechanism of SeMNPV IE1.
SeMNPV IE1 showed a moderate similarity of 35%–40% to other IE1 proteins. This value is much lower than the IE1 similarities of AcMNPV, BmNPV, OpMNPV and Choristoneura fumiferana multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (CfMNPV), but equal in comparison to Lymantria dispar multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus(LdMNPV) and Helicoverpa zea single nucleopolyhedrovirus (HzSNPV). This supports the view that SeMNPV is distinct from the other baculoviruses[35]. The SeMNPV IE1 protein, encompassing 714 amino acids, is larger than any of the other baculovirus IE1 proteins. The amino acid sequence alignment showed that most of the extra length of the SeMNPV IE1 protein could be accounted for by additional amino acids at the N-terminus. There is no evidence that similar duplications do occur and are responsible for the additional length of the N-terminus of the SeMNPV IE1. Two domains with different functions have been identified in the AcMNPV IE1 protein. The N-terminal part was responsible for transactivation and the C-terminal part for DNA binding and inhibitory activities. In the latter part a consensus single-stranded DNA binding motif consisting of basic and aromatic amino acid residues was found. This motif in the SeMNPV IE1 sequence could extend beyond the consensus due to a high content of basic and aromatic amino acids of the C-terminal region. The conservation of the C-terminal DNA binding region in SeMNPV IE1, combined with the similarity with transactivators, suggests that SeMNPV IE1 has a similar role in transactivation of gene expression and/or viral DNA replication as AcMNPV and OpMNPV IE1. The diversity in the N-terminal part and possible differences in phosphorylation SeMNPV IE1 may play a role in the specificity of SeMNPV[35, 36]. A recent study of chimeric IE1 revealed that the stimulation function of SeMNPV IE1 might be dependent on the whole structure of the protein [2]. The study also showed that SeMNPV IE1 appeared to be more dependent on SeMNPV-derived sequences than AcMNPV IE1. The AcMNPV and BmNPV IEs showed hr dependent and independent activation in mammalian cells[24, 39]. The acidic activation domains of AcMNPV and OpMNPV IE1s were functional in multiple mammalian cell types and showed significantly different activity in different cell lines[27]. Here, we reported that the group Ⅱ NPV IE1 had transactivation function in mammalian cell line. In transient expression, IE1 showed different impacts on the F protein promoter and the GP64 promoter in HEK293 cells. In the absence of hr, SeMNPV IE1 stimulated the F protein promoter but not the GP64 promoter which suggests that IE1 of group Ⅱ NPV also has a transactivation function. This indicates that the IE1 transactivates gene expression in multiple selective mammalian cell lines and the IE1 may bind to transcriptional factors of a certain structure. Whether the IE1 in group Ⅱ NPV has other special function (s) remains to be studied.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: