HTML
-
Undoubtedly, vaccination is the best way to prevent infectious diseases. However, purified or recombinant subunit vaccines are often poorly immunogenic and require additional components to help to stimulate the protective immunity based on antibodies and effector T-cell functions. These additional components, termed adjuvants, enhance the immunogenicity of vaccine antigens (Coffman R L, et al., 2010; Harandi A M, et al., 2010; Mbow M L, et al., 2010). However, recent data suggest that most adjuvants enhance T-and B-cell responses by engaging components of the innate immune system, rather than by direct effects on the lymphocytes themselves (Coffman R L, et al., 2010).
Flagellin is a major structural protein of the flagella filaments of bacteria, and a type of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) (Demento S L, et al., 2011; Miao E A, et al., 2007). Responses to PAMPs are mediated by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) which can be divided into subfamilies, first according to the ligands they recognize, e.g. lipopolysaccharides (LPS), lipopeptides, virus-associated nucleic acids (CpG or Poly(I:C)) or flagellin, and second according to their cellular localization, expressed either on the cell surface or in intracellular compartments (Epand R M, et al., 1999; Klinman D M, et al., 2009; Krishnamachari Y, et al., 2009; Wischke C, et al., 2009). Flagellin can be recognized by TLR5 on the cell surface which leads to a rapid induction of an innate immune response by the secretion of cytokines and chemokines, and thus the modulation of an adaptive immune response (Honko A N, et al., 2005; Mizel S B, et al., 2010). After entering the cytosol of macrophages, flagellin can be recognized inside the cell by the Nod-like receptor C4 (NLRC4) that activates caspase-1 by inducing the formation of an Naip5/NRLC4 inflammasome (Franchi L, et al., 2012; Liu F, et al., 2010). As both TLR5 and NLRC4 signal pathways play an important role in immunomodulation, flagellin is regarded as a potential adjuvant candidate (Sun Y, et al., 2012; Vijay-Kumar M, et al., 2010).
Our previous results demonstrated that flagellin is potentially beneficial for inducing mucosal IgA and IgG generation (Amicizia D, et al., 2013; Shi W, et al., 2012; Sun Y, et al., 2012; Yang J, et al., 2013). We have also demonstrated that calcium phosphate nanoparticles are efficient carriers for different biomolecules, like DNA, RNA, peptides and proteins across the cell membrane (Sokolova V, et al., 2012), associated with a good biocompatibility and biodegradability (Dorozhkin S V, et al., 2002; Neumann S, et al., 2009). They can also be used for a selective stimulation of the immune system, if loaded with CpG and an antigen (Knuschke T, et al., 2013; Sokolova V, et al., 2011; Sokolova V, et al., 2010; Sokolova V, et al., 2013). Therefore, we combined flagellin with calcium phosphate nanoparticles to further activate the innate immune system and to generate a more efficient adjuvant candidate. Here we report on the physicochemical properties and the immunomodulating effect of this delivery system, both by in vitro and in vivo experiments.
-
The preparation of protein-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles was carried out as reported earlier (Kozlova D, et al., 2012). Calcium phosphate nanoparticles were stabilised with poly (ethyleneimine) (PEI; MW=25 kDa) and loaded with SF, a full-length recombinant flagellin (fliC derived from Salmonella enterica subsp., GenBank Accession No. 1070204; 55 kDa). As control, the particles were loaded with ΔL, a flagellin mutant that stimulates neither the TLR5 pathway nor the NLRC4 pathway (54 kDa). Aqueous solutions of calcium lactate (18 mmol/L, pH=10, p.a., Merck), diammonium hydrogen phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 (10.8 mmol/L, pH=10, p.a., Merck), and PEI (2 g/L; Aldrich) were simultaneously pumped in a volume ratio of 5 mL : 5 mL : 7 mL into a stirred glass vessel containing 20 mL of ultrapure water during 1 min. After 20 min stirring, 3.6 mL of the cationic calcium phosphate/PEI nanoparticle dispersion was mixed with 400 µL of solutions of either SF or ΔL (1 mg/mL) under stirring, followed by stirring for 30 min at room temperature.
For coating the nanoparticles with a shell of silica, 4 mL of either SF- or ΔL-loaded or of unloaded calcium phosphate/PEI nanoparticles (i.e. without protein) were added to a mixture of 16 mL ethanol, 20 µL tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS; Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany) and 11 µL aqueous ammonia solution (30-33%). The reaction mixture was then stirred for 16 h at room temperature. The particles were isolated by ultracentrifugation at 66, 000 g for 30 min and redispersed in the original volume of water (4 mL) under ultrasonication (UP50H, Hielscher, Ultrasound Technology; sonotrode 7, cycle 0.8, amplitude 70%, 20 s). By this method, unreacted synthesis parent compounds and byproducts were removed, including dissolved excess protein. Assuming an incorporation efficiency of 50% of protein into the nanoparticles in accordance to our earlier studies (Sokolova V, et al., 2011), the protein concentration was 50 µg/mL in the dispersion, i.e. 0.91 µmol/L for SF and 0.93 µmol/L for △L.
Ultrapure water (Purelab ultra instrument from ELGA) was used for all preparations. All formulations were prepared and analysed at room temperature. The morphological characteristics of the particles were obtained by scanning electron microscopy (ESEM Quanta 400) with palladium-sputtered samples. Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential determinations were performed with a Zetasizer nanoseries instrument (Malvern Nano-ZS, λ = 532 nm). The particle size data refer to scattering intensity distributions (z-average).
-
Human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells were grown in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS (Gibco, Darmstadt, Germany) and 100 U mL-1 of penicillin/streptomycin at 37 ℃ in 5% CO2 atmosphere. Caco-2 cells were seeded at a density of 1×105 per well into 48-well polystyrene plates (Costar, Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany) and cultured for 5 days. After an overnight culture in medium without FBS, the cells were stimulated either with SF-loaded nanoparticles or with ΔL-loaded nanoparticles or with dissolved SF (as positive control) or with dissolved △L (as negative control) in medium without FBS for 6 h. The total volume of the stimulation system was 300 µL. The supernatants were collected and stored at -70 ℃ for IL-8 measurement by ELISA.
-
Primary bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were prepared from the femurs of C57BL/6 mice and cultured in RPMI 1640 containing 10% fetal bovine serum with the addition of 15% L929 supernatant and non-essential amino acids. After 7 days of induction, the macrophages were seeded at a density of 8×104 cells per well in 96-well plates and cultured for another 24 h. The macrophages were pre-treated with LPS at a concentration of 50 ng/mL for 3 h and washed three times with RPMI 1640. Then the cells were stimulated with SF or ΔL (alone and with nanoparticles), and with the same concentration of unloaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles. 6 hours later, the supernatants were collected and stored at -70 ℃ for IL-1β detection by ELISA.
As control, the cells were transfected with SF with DOTAP (Roche Diagnostics, Freiburg i.Br., Germany) as positive control and △L with DOTAP as a negative control, as described previously (Yang J, et al., 2013).
-
Female C57BL/6 mice (6 to 8 weeks old) were obtained from the Beijing Laboratory Animal Research Center and housed under specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions in the Animal Center of the Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Animal studies were performed according to the Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals in China (1988), and all protocols were reviewed and approved by the Laboratory Animal Care and Use Committee of the Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
-
200 μL of serially diluted (0.9% normal saline as dilution and control) SF- or ΔL-loaded nanoparticles (corresponding to 0.1 μg, 1 μg, 10 μg SF or ΔL per mouse) or the same dilution of unloaded nanoparticles or the same concentration of the dissolved proteins SF or ΔL were intraperitoneally injected into C57BL/6 mice. Four hours after injection, blood was taken from mice and serum was prepared and stored at -70 ℃ until ELISA detection of IL-6. The mice were sacrificed after bleeding and the abdominal cavity was lavaged with 1 mL 0.9% NaCl solution. After centrifugation at 2, 000 rpm for 10 min at 4 ℃, the supernatant of the lavage liquid was collected and stored at -70 ℃ until detection of IL-6 by ELISA.
-
IL-6, IL-8 and IL-1β in cell supernatant, mouse serum or peritoneal lavage fluid were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). ELISA kits were obtained from BD Biosciences.
Preparation of flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles
Activation of TLR5 signal pathway in Caco-2 cells
Preparation of macrophages and stimulation of the inflammasome pathway
Mice
Innate immune response to flagellin-Functiona-lized nanoparticles in vivo
Determination of cytokines by ELISA
-
Polyethylenimine-stabilized calcium phosphate nanoparticles with flagellin-cargo were coated with a silica shell to protect the protein inside (Figure 1). The morphology and the particle size distribution of unloaded and flagellin-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles were determined by dynamic light scattering (Table 1) and scanning electron microscopy.
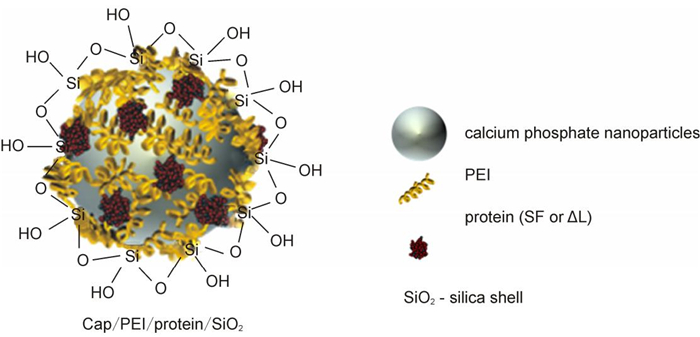
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the structure of calcium phosphate nanoparticles, loaded with flagellin (SF) or an inactive flagellin mutant (ΔL).
Protein PDI Average size (DLS)/nm Zeta potential/mV none 0.147 194 22±5 SF 0.211 330 9±4 ΔL 0.260 385 10±4 PDI=Polydispersity index from dynamic light scattering; DLS=Dynamic light scattering. Table 1. Colloid-chemical data of protein-functionalized calcium phosphate nanoparticles (standard deviations given after the average in parentheses).
The average hydrodynamic diameter was around 190 nm for unloaded nanoparticles and 330-380 nm for protein-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles, indicating some agglomeration in the latter case. Representative DLS curves of functionalized nanoparticles are shown in Figure 2. The unloaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles had a positive zeta potential of +22 mV. The protein-loaded nanoparticles had a zeta potential of +10 mV. In Figure 3, scanning electron micrographs of the protein-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles are shown. The particles had a spherical morphology with a diameter between 60 and 100 nm.

Figure 2. Dynamic light scattering data of calcium phosphate nanoparticles without and with flagellin (SF) or an inactive flagellin mutant (ΔL).
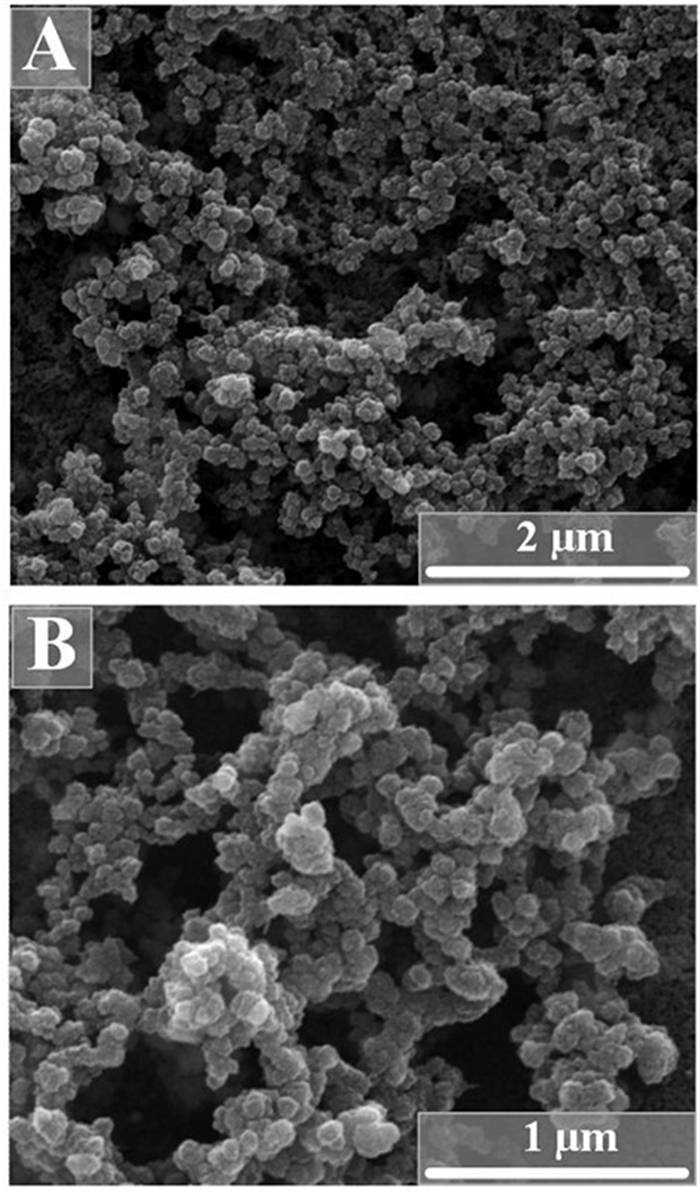

Figure 3. Scanning electron micrographs of calcium phosphate nanoparticles, loaded with either flagellin (SF) (A) or an inactive flagellin mutant (ΔL) (B). Note that the particles are agglomerated due to the drying process in the electron microscope. The primary particle size is between 60 and 100 nm.
-
To test the immunomodulating function of flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles, we tested whether they stimulated reagent DOTAP, SF induced the production of IL-1β by macrophages to a small extent. When SF was incorporated into nanoparticles, it induced IL-1β much more efficiently (Figure 4). However, it is remarkable that the unloaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles and the △L-loaded nanoparticles also led to a significant expression of IL-1β. This points to some general effect of stimulation, possibly by dissolved calcium ions after uptake or by the stabilizing agent poly (ethyleneimine).
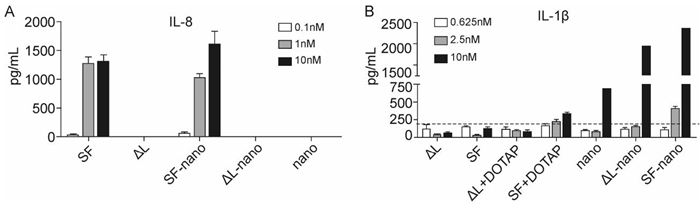
Figure 4. Flagellin-loaded nanoparticles induced the production of proinflammatory cytokines in vitro. A: Human Caco-2 cells were stimulated with flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles or purified flagellin for 6 hours and supernatants were collected for IL-8 detection. B: Mice bone marrow-derived macrophages were pretreated with 50 ng mL-1 LPS for 3 hours and then stimulated with flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles or purified flagellin for 6 h, and supernatants were collected for IL-1β detection. The dashed line represents the control. SF = flagellin; ΔL = inactive flagellin mutant; SF-nano = nanoparticles, loaded with SF; △L-nano = nanoparticles, loaded with ΔL; SF+DOTAP = flagellin + transfection agent DOTAP; ΔL = inactive flagellin mutant + transfection agent DOTAP; nano = nanoparticles without protein.
The effects of flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles on innate immunity were further tested in vivo using IL-6 as the indicator. C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneal immunized, and the serum and peritoneal lavage fluids (PLFs) were collected as described above. The contents of IL-6 in PLFs and serum were determined by ELISA. SF-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles more efficiently induced the production of IL-6 in serum in comparison to the dissolved SF protein alone. The only other system that led to an increased concentration of IL-6 in the serum was △L-loaded nanoparticles (Figure 5). Surprisingly, there were no significant differences between the levels of IL-6 in PLFs of mice treated with SF-loaded nanoparticles and that mice treated with △L-loaded nanoparticles. In the PLF, the nanoparticles alone also led to an increase in the IL-6 production, again pointing to a hitherto not understood effect of the nanoparticles alone.
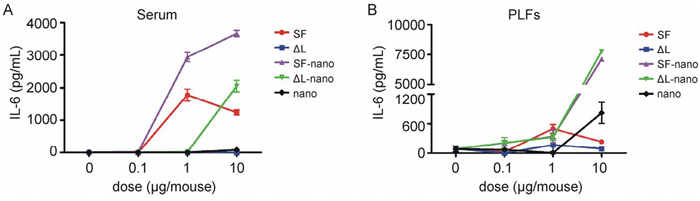
Figure 5. Flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles induced proinflammatory cytokine productions in vivo. C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally immunized, and the serum and peritoneal lavage fluids (PLFs) were collected as described in materials and methods. The contents of IL-6 in serum (A) and PLFs (B) were determined by ELISA. SF = flagellin; ΔL = inactive flagellin mutant; SF-nano = nanoparticles, loaded with SF; ΔL-nano = nanoparticles, loaded with ΔL; nano = nanoparticles without protein.
Characterization of flagellin-functionalized calcium phosphate nanoparticles
Flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles activated innate immune response efficiently
-
Taken together, these in vitro and in vivo data demonstrate that flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles are capable to inducing the production of proinflammatory cytokines very well and in all cases significantly stronger than the dissolved proteins at the same concentration. Therefore, flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles can efficiently stimulate the innate immune response.
It is well accepted that some proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-8 and IL-6 are important bridges of innate and adaptive immunity (Frisdal E, et al., 2011).
During the immune activation phage, these cytokines are mostly secreted by antigen presenting cells (APCs) and thereafter help to further activate T- or B-lymphocytes. In our previous study, we demonstrated that flagellin activates TLR5 and induces the production of cytokines like IL-8, IL-6, IFN-γ. Based on the activation of TLR5, flagellin can be considered as a potential novel adjuvant candidate. The most important advantage is the induction of mucosal IgA, which is an important factor for protection against local virus infections of mucosal surfaces (Blutt S E, et al., 2012; Yan H, et al., 2002). With the combination with nanoparticles, the flagellin adjuvant produced broader cytokine profiles, comprising the intracellular inflammasome cytokine family. The typical cytokine we detected by in vitro stimulation in this family was IL-1β. IL-1β is a powerful immune modulator, and was reported to be an adjuvant target in the past decades. Some other cytokines from the family are IL-18 and IL-33 that tend to enhance Th1 type CTL response. Thus, SF-loaded nanoparticles provide a potential new adjuvant with the simultaneous application of both flagellin and nanoparticles, especially if loaded with an antigen (Knuschke T, et al., 2013; Sokolova V, et al., 2010) and targeted at specific antigen-presenting cells (Kozlova D, et al., 2012).
We have demonstrated how colloidally stable flagellin-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles can be prepared and how they can act on the innate immune system. In this context, we have examined the efficiency of flagellin-loaded calcium phosphate nanoparticles in vitro and in vivo. Flagellin-functionalized calcium phosphate nanoparticles were able to enhance the IL-6 pro duction in caco-2 cells and the IL-1β production in mice bone marrow-derived macrophages in vitro. IL-8 production was detected after intraperitoneal immunization of C57BL/6 mice with flagellin-functionalized nanoparticles. Thus, flagellin is well suited as adjuvant in future nanoparticle-based formulations to stimulate the immune response.
-
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungs-gemeinschaft (SFB/Transregio 60) to A.M.W., J.B. and M.E and grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81302609 and 81202312).
-
Diana Kozlova, Viktoriya Sokolova, Maohua Zhong, Ejuan Zhang, Jingyi Yang, Wei Li and Yi Yang have synthesized the nanoparticles and carried out the cell-biological and animal experiments. Jan Buer, Astrid Maria Westendorf, Matthias Epple and Huimin Yan have designed the study, supervised the data evaluation, and wrote the manuscript.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: