HTML
-
Grass carp reovirus (GCRV), a member of the genus Aquareovirus in the family Reoviridae (Attoui H, et al, 2002), is one of the most virulent aquareoviruses identified so far, leading to high fatality rates (up to 85%) of fingerlings and yearlings of grass carp (Fang Q, et al, 2007). No commercial vaccines against GCRV infection have been developed as yet.
Baculovirus has been extensively used as a vector for expression of exogenous genes in a wide range of cell types, including mammalian and fish cells, due to its efficient transduction. A recent study reported that VP6 expressed by the baculovirus vector in silkworm evoked antibody responses in grass carp (Xue R, et al, 2013). Previously, our group demonstrated efficient transduction of recombinant baculovirus containing the cytomegalovirus-immediate early (CMV-IE) promoter in several fish cell lines (Huang F, et al, 2011). Several investigators have validated the utility of baculovirus as a potential vector for gene therapy and vaccine development. The GCR virion is nonenveloped and icosahedral with VP6 in its inner capsid. The VP6 protein is encoded by RNA segment 8 and plays a vital role in virus assembly.
In the present study, baculovirus was employed as a vaccine vector to generate a recombinant virus expressing GCRV VP6 protein under control of the CMV-IE promoter. GCRV-specific neutralizing antibodies were successfully induced in grass carp via immunization with recombinant Bac-CMV-VP6. Simultaneously, two innate immune response genes, IFN-regulatory factor-7 (IRF-7) and IFN-1, were upregulated.
Firstly, we constructed recombinant baculovirus containing the GCRV VP6 gene under control of the CMV-IE promoter (Figure 1A). To examine whether the promoter of CMV-IE can effectively drive foreign gene expression in insect and fish cells, sf9, EPC and CIK cells were infected with Bac-CMV-VP6 and Bac-CMVEGFP at an MOI of 50. At 3 days post-infection, red fluorescence was observed in Bac-CMV-VP6-infected cells with the immunofluorescence assay using mouse anti-His tagged antibody, followed by Alexa Fluor 555 goat anti-mouse IgG (Figure 1B). These results were consistent with our previous observation that the recombinant baculovirus not only enhances transduction efficiency in fish cells but also mediates expression of the transgene VP6 in sf9 cells, thus facilitating VP6 protein expression in grass carp immunized with recombinant baculoviruses.
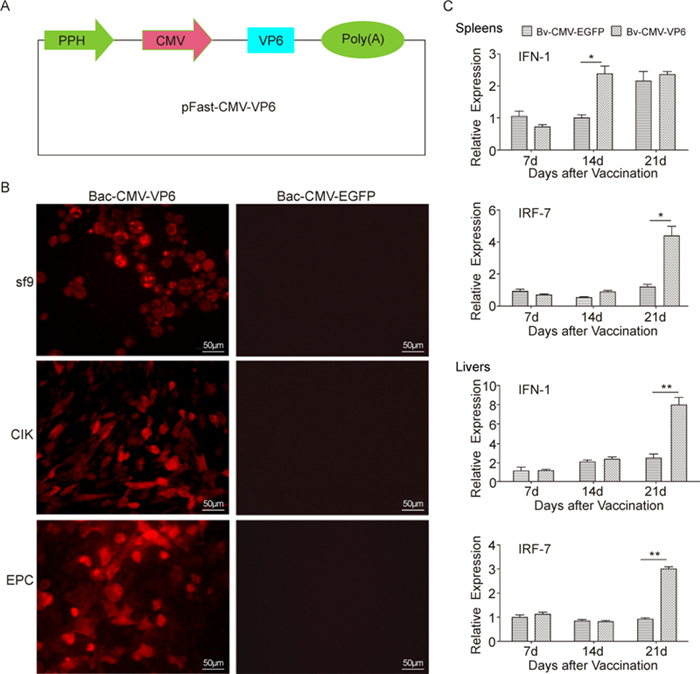
Figure 1. The detection of recombinant baculovirus expressing the VP6 protein in some cells, and genes expression analysis in liver and spleen of fish immunizated with the baculoviruses. A: Map of the baculovirus transfer plasmid, pFast-CMV-VP6. The baculovirus transfer plasmid was constructed on the basis of pFastBac1, as described in Materials and Methods. Expression of the GCRV VP6 gene was driven by the cytomegalovirus immediate-early promoter. PPH, polyhedrin promoter of baculovirus; Poly (A), polyadenylation signal. B: Immunofluorescence analysis of VP6 expression in SF9, CIK and EPC cells. Briefly, cells were infected and transduced with the recombinant baculoviruses, Bac-CMVVP6 and Bac-CMV-EGFP, at 50 MOI. At 72 h post-infection, the immunofluorescence assay was performed using monoclonal antibodies against His-tag, followed by Alexa Fluor 555 goat anti-mouse IgG. Images were obtained with a fluorescence microscope, Scale Bar=50 μm. C: Gene expression analysis in liver and spleen of fish vaccinated with recombinant baculoviruses. At 7, 14 and 21 days post-immunization, fish (n=3/group) were sampled for qRT-PCR analysis of total RNA in spleens and livers to detect IRF-7 and IFN-1 expression. The β-actin gene was used as an internal reference. Data represent mean values ± S.D. of three individuals (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01)
In fish, neutralizing antibodies play a central role in adaptive immunity against viral infection. Accordingly, the neutralization assay was performed to evaluate the neutralization activity of sera from fish vaccinated with recombinant baculoviruses. Neutralization titers of the three sera are shown in Table 1. The 50% neutralization titer (EC50) of Bac-CMV-VP6 against GCRV of 1/160 was significantly higher than those of the two control groups, Bac-CMV-EGFP and PBS. Moreover, in fish treated with Bac-CMV-EGFP (EC50 of 1/25), the neutralization titer was similar to that with phosphate buffer solution (PBS) (EC50 of 1/40), suggesting that the baculovirus has no influence on antibody production.
Viruses Serum samples Serum dilution Percentage of CPEa 50% Neutralization titer CCV PBS 1/20
/40
1/8083%
83%
100%— Bac-CMV-EGFP 1/20 100% — Bac-CMV-VP6 1/20 100% — SVCV PBS 1/20
1/40
1/8067%
83%
100%— Bac-CMV-EGFP 1/20 100% — Bac-CMV-VP6 1/20 100% — GCRV PBS 1/20
1/40
1/8017%
50%
100%1/40 Bac-CMV-EGFP 1/20
1/40
1/8033%
83%
100%1/25 Bac-CMV-VP6 1/80
1/160
1/320
1/64033%
50%
83%
100%1/160 a: CPE, cytopathogenic effect Table 1. Neutralizing titers of tested sera CPE
To further ascertain whether the neutralizing activity of fish sera is GCRV-specific, SVCV and CCV viruses were included to test the neutralizing capacity of sera from grass carp immunized with Bac-CMV-VP6. The effects of protection were not significant, clearly suggesting that the recombinant baculovirus vaccine is able to specifically neutralize GCRV virions. Although the neutralization titer of the Bac-CMV-VP6-immunized group remained relatively low, the value obtained in this study is similar to those reported with other vaccines based on baculovirus expression systems, and requires further optimization (Lu L, et al, 2007).
Baculovirus alone has been reported to elicit innate immunity that confers a certain level of protection in mice infected with influenza A and encephalomyocarditis virus (Abe T, et al, 2003). In cases of fish infection by specific viruses, type 1 interferon (IFN) is triggered, which plays a vital role in non-specific immunity and provides a close association between innate and adaptive immune responses (Workenhe S T, et al, 2010). Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF-7) is considered a major regulator of type 1 interferon-dependent immune response (Honda K, et al, 2005). To elucidate whether Bac-CMV-VP6 elicits the innate immune response in carp grass, the relative expression profiles of two immune-related genes, IRF-7 and IFN-1, were detected using quantitative real-time PCR in liver and spleen tissues from immunized fish (Figure 1C). Notably, fish immunized with Bac-CMVVP6 produced significantly higher levels of IRF-7 and IFN-1 mRNA in the spleen than those immunized with the control virus (Bac-CMV-EGFP) (P < 0.05). In liver, IRF-7 and IFN-1 mRNA production was not significant in both Bac-CMV-VP6-and Bac-CMV-EGFP-inoculated groups at days 7 and 14. However, expression levels of both transcripts were dramatically upregulated at 21 days post-vaccination in the Bac-CMV-VP6-vaccinated group (P < 0.01), signifying that innate immune responses are stimulated in fish vaccinated with Bac-CMV-VP6.
In conclusion, our study demonstrates that Bac-CMVVP6 not only triggers the production of neutralizing antibody against GCRV in grass carp but also induces IFN-1-related non-specific immunity responses, supporting its utility as a promising vaccine against GCRV infection. Further research is warranted to optimize the conditions for effective use of Bac-CMV-VP6 against GCRV infection.
-
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (30901118, 31172433), National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2012BAD25B06) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2011PY121, 2011QC029, 2013PY069, 2013PY70, 2013PY071). The authors thank Professor Qin Fang (Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for providing the GCRV-873 strain. All authors declare they have no competing interests.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: