-
Among neurotropic viruses, RABV is a deadly pathogen that primarily invades the host through motor nerve endings and transports in a retrograde fashion to the central nervous system (Jackson, 2016). The RABV follows clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway, but the later intracellular transport kinetics remain partially unclear (Piccinotti et al, 2011; Weir et al, 2014). The nature and type of host cells predict the internalization of the virus (McMahon and Boucrot, 2011). After entry, viruses hijack the cellular and immune machinery of the host cells for their own transcription and replication. Early events involve the interaction with early and late endosomes that decide the fate of the viral genome in the cytosol (Vidiricaire et al, 2005; Macovei et al, 2013). RabGTPases (there are 60 known GTPases in humans) exclusively regulate vesicle docking and fusion with these viruses (Seabra et al, 2002); they are versatile endosomal proteins present on the phagosomes, early endosomes and late endosomes (Vidiricaire et al, 2005). Different types of Rab proteins also recruit motor proteins to lysosomes and endosomes (Caviston and Holzbaur, 2006). Among these, Rab5 and Rab7 are the most important GTPases, and regulate the overall intracellular signaling pathways involving different RabGTPases. Rab5 is an important hub for crosstalk between trafficking and signaling. It is also involved in the integrated setup of clathrin pits and clathrin-mediated endocytosis at the plasma membrane for the endocytosis of transferrin receptor (McLauchlan et al, 1998; Stenmark, 2009). This endosomal protein is also localized to caveosomes and phagosomes (Seabra et al, 2002), and controls the tethering of vesicles to different recipient membranes (Rubino et al, 2000) and microtubules (Nielsen et al, 1999). Early endosome antigen-1 (EEA1) is a sub-domain antigen for the early endosomes that coordinates their sorting and docking in diverse cell lines (Wilson et al, 2000), while lysosomal-associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP1) is usually transported from the trans-Golgi network to the late endosomes or lysosomes, but before this happens, LAMP1 is first translocated to the early vesicles (Cook et al, 2004). However, Rab7 ensures maturation of late endosomes and phagosomes, and regulates signaling between late endosomal pathways and the lysosome (Verhoeven et al, 2003; Vidricaire and Tremblay, 2005). It also interacts with the lysosomal proteins to recruit the dynein complex for intracellular transport (Deinhardt et al, 2006). Therefore, markers or antibodies for Rab5/EEA1 and Rab7/LAMP1 are generally used to investigate possible colocalization with different viruses to explain the route of infection in neuronal, endothelial and SH-SY5Y cells (Deinhardt et al, 2006; Macovei et al, 2013; Liu et al, 2014).
In fixed neuronal cells, dynamic viral interaction withRab5 and Rab7 in vesicle transport has been described in several studies using live imaging and immunofluorescence (Schmieg et al, 2013; Vidricaire and Tremblay, 2005; Macovei et al, 2013; Liu et al, 2014). However, very few studies have depicted the crucial interaction of these endosomal proteins with RABV in the SH-SY5Y and host nerve cells that have been extensively used to study neurodegenerative diseases, neurotoxicity and the dynamic cytoskeleton (Pierrea et al, 2011). Therefore, the experiments presented here were conducted to investigate early events after the endocytosis of RABV in fixed neuronal cells using specific markers directed against corresponding proteins of early and late endosomes.
-
Pregnant female rats were purchased from Changchun Animal Center and acclimatized before the start of experiments. All the procedures regarding animal handling and care were carried out in accordance with the Institutional Animal Welfare Act. Baby hamster kidney (BHK) cells and a human-based cell line (SH-SY5Y) were maintained in the laboratory, while the challenge virus strain (CVS-11) was kindly given to us by the Changchun Veterinary Research Institute, OIE Rabies Reference Laboratory. The following antibodies were utilized: Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC-labeled) mouse anti-RABV nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody, anti-Rab7 monoclonal antibody, anti-EEA1 monoclonal antibody, anti-Rab5 monoclonal antibody, anti-LAMP1 polyclonal antibody, Alexa594 fluorescence-labeled goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody and Tetramethyl Rhodamine Iso-Thiocyanate (TRITC-labeled) goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies.
-
Gene sequences for mouse Rab5 (GenBank: M28215) and Rab7 (GenBank: AF050175) were used for the synthesis and design of three pairs of siRNA primers.siRab5-sense, CCAGUUCAAACUAGUACUUTT; siRab5-anti-sense, AAGUACUAGUUUGAACUGGTT; siRab7-sense, CUAGAUAGCUGGAGAGAUGUU; siRab7-anti-sense, UCCUAUUGUGGCUUUGUACUU. Negative control siRNA sequence (5′–3′): NC-sense, UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT; NC-anti-sense, ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT.
-
The 15 to 18 days pregnant rats were anesthetized with ether and sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The primary cortical neuronal cells were isolated and cultured according to a previously described protocol (Song et al, 2013).In a similar way, SH-SY5Y cells in the loga- rithmic growth phase were resuspended, and 3 × 105 cells were seeded, with cover slips, in each well of a 24-well plate. When the cell density reached about 60%, the medium was replaced and each well was infected with 104TCID50 of CVS-11. The 24-well plate was incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator for 1 h. In the meantime, the plate was gently shaken 2 to 3 times. Finally, the medium was discarded, and the plate wells were washed twice with Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM).
-
The cell culture medium was discarded from the 24-well plate, which was washed with normal phosphate buffer, and the cortical cells were fixed with 4% paraformalde- hyde, as described in a previous article (Song et al, 2013). In brief, the cortical cells were blocked with 500 μL of 3% goat serum and then incubated for 2 h at 37 °C with anti-EEA1 monoclonal antibody, anti-Rab7 monoclonal antibody, anti-Rab5 monoclonal antibody and anti-LAMP1 polyclonal antibody (1:200) separately for different cell slides. Then, the cell slides were washed three times with 500 μL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C with TRITC-fluorescence-labeled goat anti-mouse secondary antibody and Alexa 594-fluorescence-labeled goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1:200) diluted in blocking buffer. FITC-labeled mouse anti-rabies nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody was applied under similar conditions. Finally, the cortical cells were stained with Hoechst and observed under a laser confocal microscope.
-
Preparation of slices from samples of fixed mice brains for pathological examination was carried out according to a previous report (Flannigan and Zewail, 2012). In brief, about 2 mm3 of brain sample for Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) was immersed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde buffer (pH 7.4 with 0.1 mol/L sodium phosphate), kept at 4 °C for more than 24 h and washed three times in cold sodium phosphate buffer. Then, the brain tissues were post-fixed in 1% osmium tetroxide solution for 2 h at 4 °C. Following that, the fixed tissues were dehydrated in an increasing ethanol gradient series, sunk into propylene oxide for 60 min and embedded using an embedding agent SPI-PON812 kit (SPI supplies, USA) for 12 h according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dilution of Rab5 and Rab7 antibody was performed in blocking buffer in a ratio of 1:200. Thin sections were immersed in a humid chamber at 37 °C for 2 h and subsequently rinsed with PBS 5 times. Colloidal gold-labeled secondary antibodies were diluted 1:40 in blocking solution, and the ultrathin sections were immersed in the secondary antibodies in a humid chamber at 37 °C for 1 h. The sections were rinsed three times with PBS and finally washed twice with ultrapure water. Ultrathin sections were sliced using an Ultramicrotome (EM UC7; LEICA, Germany) and stained with uranyl acetate. The ultrastructure of the mice brains was observed by TEM (H-7650; HITACHI, Japan) at 80 kV.
-
For RNA interference, SH-SY5Y cells were resuspended with Opti-MEM medium and 3 × 105 cells/well were employed in a 24-well plate. When the SH-SY5Y cells grew into a monolayer, Lipofectamine RNAiMAX transfection reagent was mixed with a final concentration of 100 nmol/L siRNA (containing SH-SY5Y transfected with Homo-siRab5 and Homo-siRab7), and then the mixture was added into each well. After 36 h of interference, all cells were infected with 104TCID50 of CVS-11 per well. Normal control-siRNA was setup for com- parison with the results from the experimental group.
-
The samples of cells were lysed with cold sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) to collect the protein. The concentration of SDS was maintained at 2% with loading buffer and the mixture was incubated at 100 °C for 15 min. The protein lysates were separated using SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and transferred to a poly- vinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane of 0.45 μm pore size. The non-specific blocking of primary and secondary antibodies was carried out with 5% (w/v) skimmed milk in tris-buffered saline (TBS) with 0.45% Tween for 2 h. The primary antibodies against Rab5, Rab7, N and β-actin antibody were labeled and incubated at room temperature for 2 h. The membranes were washed thrice with TBS for 3–5 min in each interval in order to remove excessive antibodies. The corresponding horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies were incubated at room temperature for 2 h. Again, the membranes were washed with TBS for 3–5 min. The detection substrate, chemiluminescent HRP substrate, was added for the final acquisition of the images.
-
Virus fluorescent signal intensity was interpreted using Image J software, and whole fields of images were measured in three replicates. Fluorescence analysis and TCID50 results were obtained using SPSS software, while ANOVA results were obtained with
$\bar {\rm X}$ ± SD representation; P < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference. -
Fixed cortical neurons were incubated at different time intervals (0, 12, 24, 48 h) with primary and secondary antibodies against specific markers of early and late endosomes. The results depicted that RABV successfully colocalized with these markers at 24 h and 48 h post-infection. The infection time was directly proportional with the fluorescence intensity of colocalization in the fixed neuronal cells. At 0 h and 12 h post-infection, no apparent intensity of colocalization was observed. However, a minute intensity of yellow fluorescence was seen for Rab5, Rab7, EEA1 and LAMP1 markers at 24 h that was an indication of colocalization with RABV. Numerous yellow fluorescent signals near the cell body, as well as along the entire projected axons, could be seen in Rab5-and EEA1-stained fixed neuronal cells (Figure 1). Close observation revealed few fluorescent signals near the cell body in the case of 24 h post-infection compared with 48 h. Hence, the extension in post-infection time probably facilitates the initial viral entry with respect to Rab5 and EEA1 of early endosomes in clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Similar kinds of phenomena were observed with Rab7 and LAMP1 in fixed neuronal cells following similar time intervals (Figure 1). These findings led us to propose that RABV infection perhaps requires early and late endosomes for the clathrin-mediated initial entry into the nerve cells.
-
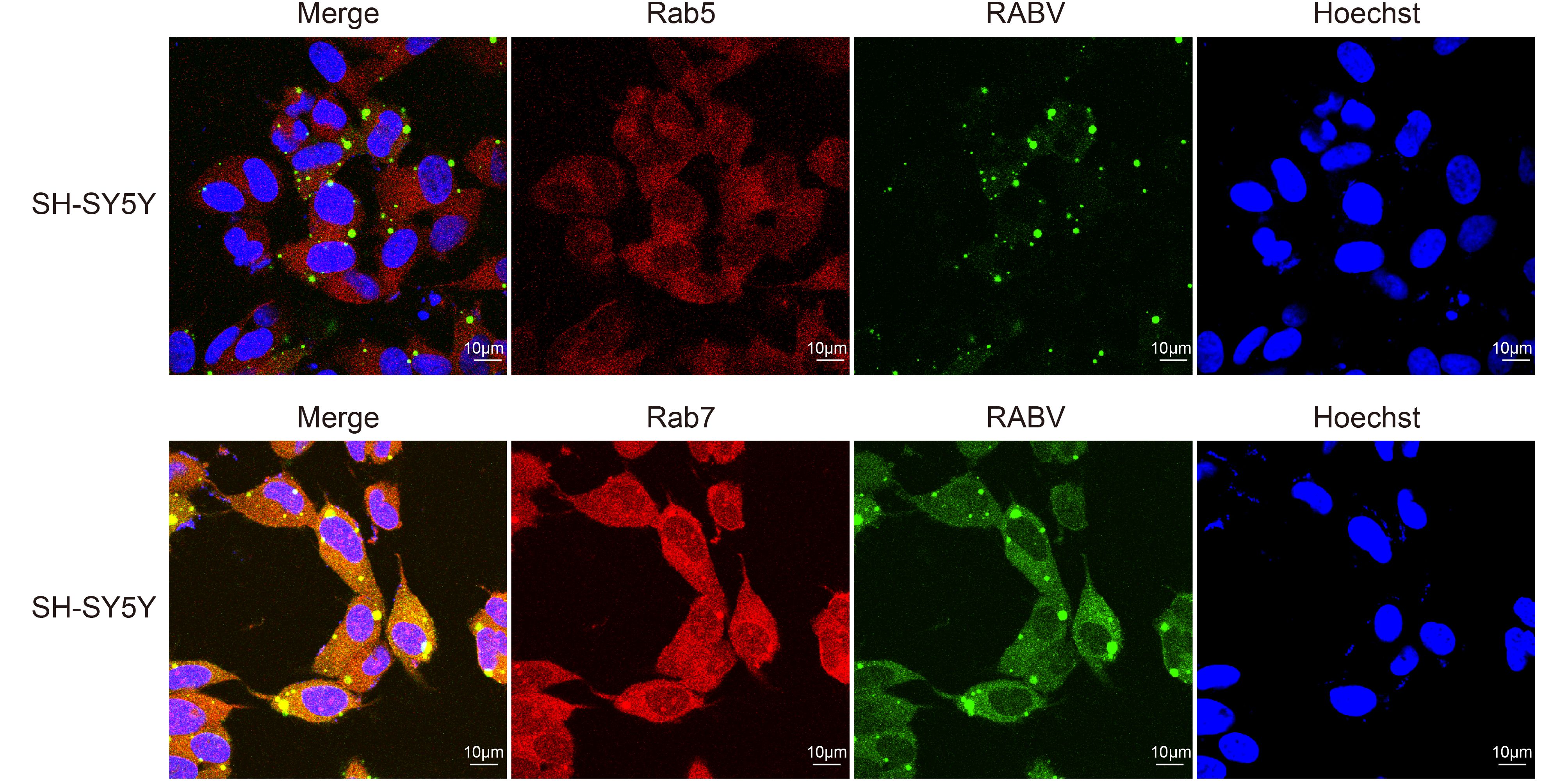
At 24 h post-infection, immunofluorescence staining of SH-SY5Y cells showed significant results. The majority of cells (67.5% ± 0.05) were detected in the periphery of the section. The SH-SY5Y cells also provided verification that RABV can colocalize with markers of early (Rab5) and late (Rab7) endosomes in host nerve cells. The N-specific anti-RABV green fluorescent signals were scattered in the peripheral domain of the cells. The red fluorescence showed that the Rab5 and Rab7 were efficiently stained during the post-inoculation period, while the merged images showed yellow fluorescent signals, indicating the co-localization of green and red fluorescent intensity. Thus, RABV had also a similar route for infection of SH-SY5Y cells using these markers of early and late endosomes (Figure 2).
-
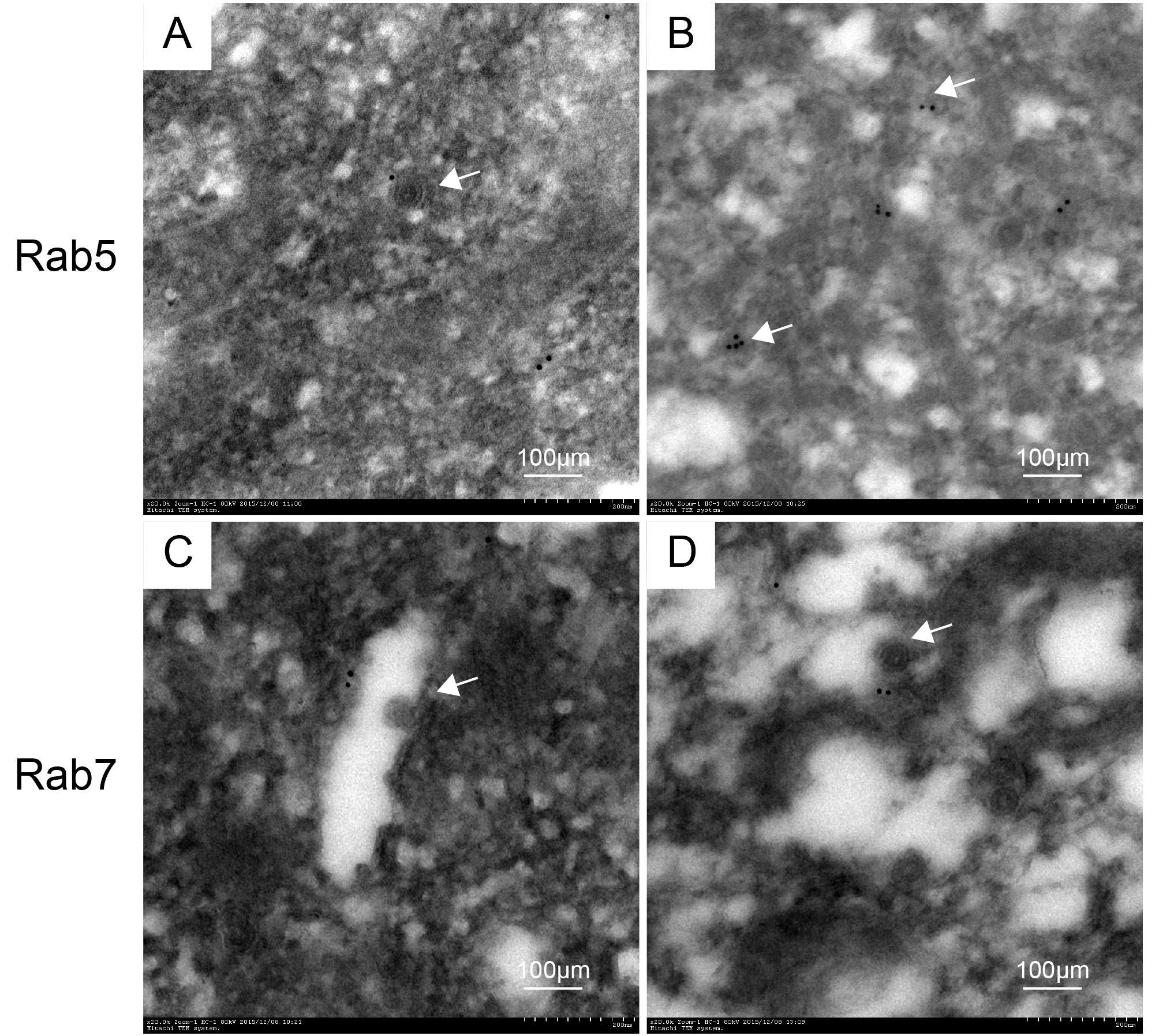
The CVS-11 virus infected ultrathin neuron sections were processed through immunogold labeling experiments, where the RABV particles were observed in the cell to verify the cytological changes. In Figure 3, the white arrows indicate the RABV, and there is an apparent clear spot in the colloidal gold particles surrounding RABV in a membrane. Moreover, the early endosomes of Rab5 were labeled significantly less than Rab7. These findings again justify the proposed idea that RABV probably merges with Rab proteins to complete the initial kinetics right after internalization into the host nerve cells.
-
The proportions of cells positive for RABV infection were significantly reduced (17.5% ± 0.06) by RNA interference of Rab5 and Rab7, which proved the fact that siRNA of Rab7 and Rab5 can significantly reduce early RABV infection. During the interference with Rab5, the RABV mainly localized near the cell membrane (indicated by arrows in Figure 4A). The results were indicative that the RABV perhaps fuses with the Rab5 receptors of the early endosome, and later joins Rab7 or LAMP1 for onward virus transport to late endosomes or lysosomes. Moreover, siRNA of the Rab5 and Rab7 resulted in a significant reduction in the green fluorescence of RABV. The reduction was found to be statistically significant, P < 0.011 (Figure 4B).
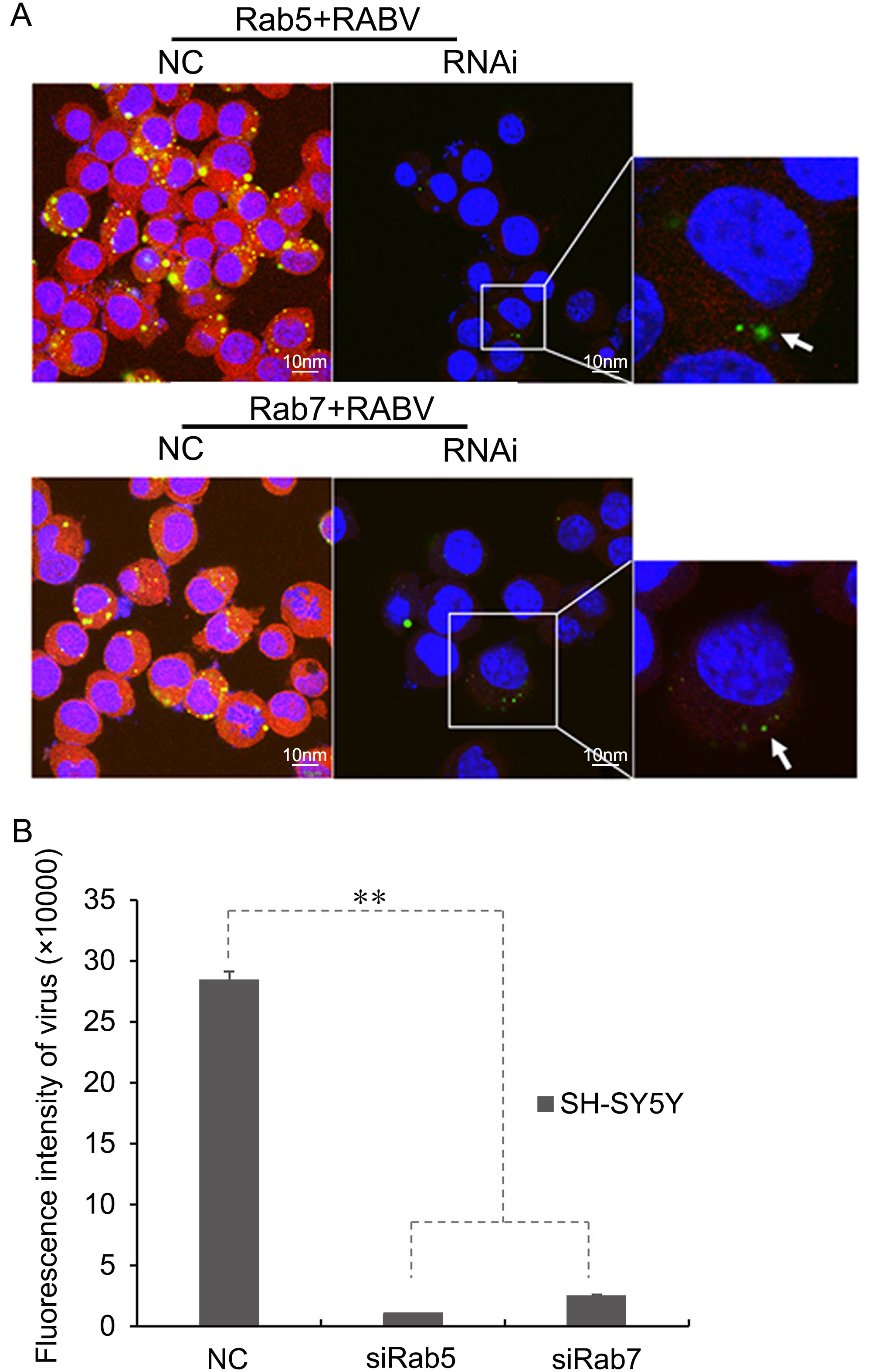
Figure 4. (A) RNA interference for Rab5 and Rab7 showing the reduction in RABV infection in SH-SY5Y cells at 24 h post-infection (shown magnified in the inset images of RNAi for Rab5 and Rab7). Green fluorescent dots indicate RABV, while Rab5 and Rab7 appear as red fluorescence. RABV localized near the cell membrane is indicated by arrows. NC, normal control images showing colocalization of RABV with Rab5 and Rab7 in SH-SY5Y cell lines at 24 h post-infection as previously described. (B) Fluorescent intensity analysis of siRab5 and siRab7, as compared with a normal control (NC), in SH-SY5Y cells at 24 h post-infection. **, P < 0.011.
-
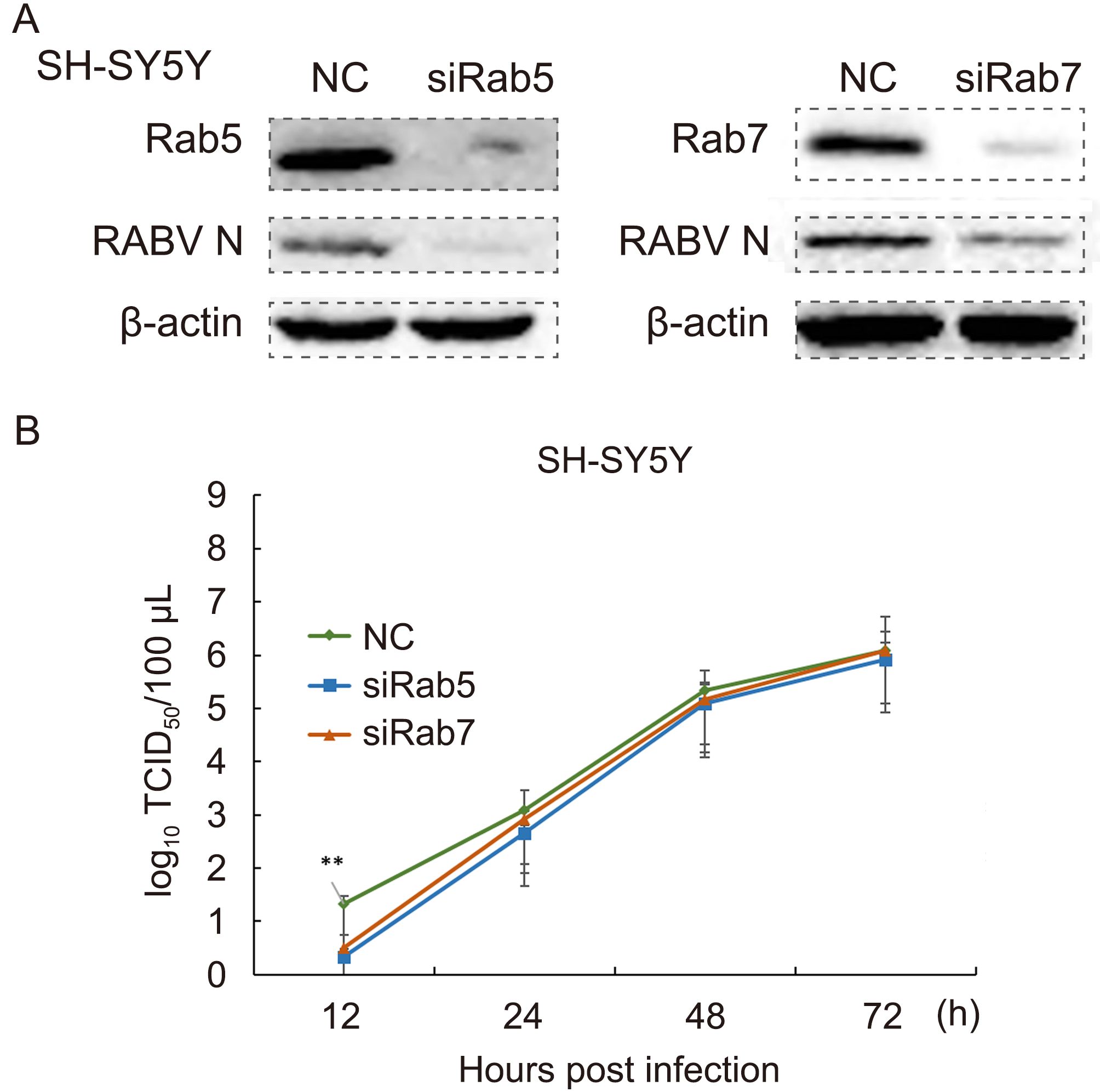
The protein samples of RNAi and control groups were processed through western blotting. It was clearly evident that siRNA for Rab5 and Rab7 down-regulated the expression of these two proteins in SH-SY5Y cells, as compared with the normal control group (Figure 5A). The down-regulation of Rab5 and Rab7 may have reduced the productive infection of RABV. The cellular supernatants collected at 12 h, 24 h, 48 h and 72 h were measured for their TCID50 on BHK cells. An infectivity graph for these 3 parameters rose from 12 h to 72 h post-infection. The line graph showed higher values for the normal control, but down-regulation of Rab5 and Rab7 decreased the RABV infection as compared with the control group. The virus titer was also significantly lower (101.13 times, P < 0.02), as shown in the graph (Figure 5B).
-
RabGTPases are a unique class of proteins that perform essential functions, such as identification of membrane-bounded organelles, uncoating, budding and ultimate fusion with the help of effector proteins and tethering factors (Vidricaire and Tremblay, 2005; Stenmark, 2009). They also play a role in the integration and accomplishment of transport events, and sort them within the soma through guidance cues in mammalian and yeast cells (Pereira and Seabra, 2001; Seabra et al, 2002; Stenmark, 2009). Rab5 participates in the homotypic fusion of early endosomes, because a Rab5 deficient experiment yielded giant early endosomes (Stenmark et al, 1994; Rubino et al, 2000). The activation of epi- dermal growth factor results in the release of an active GTP-bound form of Rab5, which is involved in receptor signaling in an early endocytic pathway (Barbieri et al, 2000).Furthermore, these GTPases also facilitate the retrograde transport of the viruses in an extrinsic neuronal culture medium (Bucci et al, 1992; Deinhardt et al, 2006; Weir et al, 2014; Macovei et al, 2013; Liu et al, 2014). Despite the existence of several RabGTPases, only Rab5 and Rab7 are vital for regulating overall vesicle transport and population of GTPases (Stenmark, 2009).The effectors for Rab proteins mediate vesicle tethering and bring about changes in the biological activity of the GTPases or cell signaling. These effectors carry different binding sites for different GTPases. Rab5 holds the coordination between these effectors to regulate the mechanism of vesicle fusion and docking (Rubino et al, 2000). EEA1 is an effector or tethering factor that interacts with the bound form of Rab5 in mediating membrane fusion with early endosomes (Callaghan et al, 1999). It forms coiled dimers and contains both amino- and carboxy-terminal binding sites for Rab5GTPase. These features make it a perfect candidate to act as a tethering factor between Rab5 and the corresponding transport vesicle (Simonsen et al, 1998).
Like other enveloped viruses, RABV usually requires acidic pH to fuse with the endosomal compartment in the endothelial cells (Marsh and Helenius, 2006). The colocalization experiments with Rab5/EEA1 and Rab7/ LAMP1 revealed that RABV might have followed the degradation pathway, starting from fusion with early endosomes to the recycling of endosomes and lysosomes. Right after entry, the RABV is taken up by the early endosome, which then encapsulates the virus, and at a later stage matures into late endosome through a Rab-switch (Huotari and Helenius, 2011; Rink et al, 2005). Previous studies have shown that Rab7 controls the transport of the captured cargo (for example RABV) through microtubules (Nielsen et al, 1999).
Various studies strongly correspond with the results of the present study, including the colocalization of RABV with fluorescent tracers of early and late endosomes in an extrinsic culture of hippocampal neurons (Lewis and Lentz, 1998). Hepatitis B virus follows a similar entry mechanism involving early and late endosomal proteins (Vidiricaire et al, 2005; Deinhardt et al, 2006; Macovei et al, 2013). The pseudo-typed glycoprotein lentiviral vector was transported through the action of Rab5 and Rab7 (Hislop et al, 2014). In a much similar way, Rab5 is essentially required for the internalization of dengue and West Nile viruses in HeLa cell lines (Krishnan et al, 2007). The Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus colocalized with Rab5 and Rab7 in an acidified environment (Colpitts et al, 2007), and adenovirus serotype 7 was also colocalized with recycling endosomes (Miyazawa et al, 2001). However, down-regulation of Rab7 reduced the productive infection of Pichinde virus up to 80% (Vela et al, 2008), and the movement kinetics of epidermal growth factor-receptor complex via early endosomes to late endosomes did not change in HeLa cells, but Rab7 deficiency did affect the kinetics of cargo from late endosomes to lysosomes (Vanlandingham and Ceresa, 2009). Similarly, the surface proteins of RABV efficiently colocalized with a monoclonal antibody marker and followed earlyendosomes, late endosomes and ultimately lysosomes right after internalization (Pierrea et al, 2011). Based on these endosomal protein colocalization experiments, different therapeutic agents for the possible counteraction of known viral pathways can be envisaged (Kaspar et al, 2007). The biological significance of these RabGTPases is also indicated by the fact that mutations in Rab7 have resulted in neurological disorders and misguided transport behaviors leading to neurodegenerative diseases (Verhoeven et al, 2003). To our knowledge, few studies have documented the molecular interactions of Rab5, Rab7 and their tethering factors or effectors with RABV in nerve or neuro-2a cells (Pierrea et al, 2011).
Keeping in this context, several controversial reports have described that Rab7 either coordinates trafficking between early and late endosomes, or between late endosomes and lysosomes (Ceresa and Bahr, 2006; Luzio et al, 2007). For example, vesicular stomatitis virus and Semliki Forest virus are dependent and independent of early and late endosomes, respectively (Schmieg et al, 2013). Our results led us to deduce that Rab5/EEA1 and Rab7/LAMP1 both colocalized with RABV at different time intervals of infection in neuronal and SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, down-regulation of these proteins through siRNA significantly inhibited the initial trafficking or kinetic pathways of RABV. The study led us to speculate that the reduced levels of N are simply a measure of a productive infection by the virus. Down-regulation of Rab proteins did not block the N expression, but it prevented productive infection of RABV via blocking the normal trafficking and kinetics of RABV inside host cells. The negative results for immunofluorescence during 0 h and 12 h post-infection could be due to the incubation time that RABV usually take to replicate itself or it could be due to variations in the optimum conditions of infection in fixed nerve cells. Hence, this study broadens our view regarding the manipulation of host endosomal pathways, and the ideas can be propagated by using different cell lines to study the mechanism of RABV entry with respect to different Rab proteins of early and late endosomes. In addition, the onward intracellular trafficking of RABV in relation to other Rab proteins of endosomes, the microtubule-cytoskeleton and motor proteins must be explored to delineate the RABV mechanism of infection more precisely.
-
The study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 216YFD0500402) and Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 31272579 and 31472208).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The guidelines pertaining to care and welfare of laboratory animals were fully abided by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Jilin University.
-
WA, YYL, YDG, and XYW performed the experiments. MD and ZHG designed the study plan, performed image analysis. ZSL and MLZ performed statistical analysis and drafted the article. WA and YYL critically revised the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rabies virus co-localizes with early (Rab5) and late (Rab7) endosomal proteins in neuronal and SH-SY5Y cells
- Received Date: 04 March 2017
- Accepted Date: 09 May 2017
- Published Date: 16 June 2017
Abstract: Rabies virus (RABV) is a highly neurotropic virus that follows clathrin-mediated endocytosis and pH-dependent pathway for trafficking and invasion into endothelial cells.Early (Rab5,EEA1) and late (Rab7,LAMP1) endosomal proteins play critical roles in endosomal sorting,maturity and targeting various molecular cargoes,but their precise functions in the early stage of RABV neuronal infection remain elusive.In this study,the relationship between enigmatic entry of RABV with these endosomal proteins into neuronal and SH-SY5Y cells was investigated. Immunofluorescence,TCID50 titers,electron microscopy and western blotting were carried out to determine the molecular interaction of the nucleoprotein (N) of RABV with early or late endosomal proteins in these cell lines.The expression of N was also determined by down-regulating Rab5 and Rab7 in both cell lines through RNA interference.The results were indicative that N proficiently colocalized with Rab5/EEA1 and Rab7/LAMP1 in both cell lines at 24 and 48 h post-infection,while N titers significantly decreased in early infection of RABV.Down-regulation of Rab5 and Rab7 did not inhibit N expression,but it prevented productive infection via blocking the normal trafficking of RABV in a low pH environment.Ultrathin sections of cells studied by electron microscope also verified the close association of RABV with Rab5 and Rab7 in neurons.From the data it was concluded that primary entry of RABV strongly correlates with the kinetics of Rab-proteins present on early and late vesicles,which provides helpful clues to explain the early events of RABV in nerve cells.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: