-
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs), which are thought to have arisen from germ-line infections by their exogenous ancestors during primate evolution, account for about 8%–12% of the human genome (Belshaw et al., 2004). Based on sequence relationships, HERVs are classified into three general classes: class I (gamma (like) retroviruses), class II (beta (like) retroviruses) and class III (spuma (like) retroviruses) (Blikstad et al., 2008; Mullins and Linnebacher, 2012; Romanish et al., 2010).
The HERV-W family is a representative of class II HERVs. Further investigations interestingly showed that a HERV-W envelope (HERV-W env) is localized on chromosome 7q21, which retains a complete env open reading frame (Blond et al., 1999) and encodes a functional protein, called Syncytin-1 (Grandi et al., 2016).
HERV-W env has been found to be associated with several human diseases, including neuropsychiatric disease (Perron et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2011; Huang et al., 2006), some cancers (Li and Karlsson, 2016) and various autoimmune disorders (Clausen, 2003; Perron et al., 2012). For example, it could be detected in both the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) (Karlsson et al., 2001) and blood (Perron et al., 2008) of schizophrenia patients. HERV-W env was also found to be overexpressed in the urothelium cell carcinoma tissues of the bladder (Yu et al., 2014). Some evidence has showed that the expression of HERV-W env protein is increased in the brain (van Horssen et al., 2016), CSF (Sotgiu et al., 2010) and blood (Mameli et al., 2009) of individuals with the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS). Recent studies showed that HERV-W env plays an important role in neuropsychiatric disease by triggering schizophrenia-associated genes (Huang et al., 2011; Li et al., 2013; Qin et al., 2016). Further studies showed that HERV-W env might act as an autoantigen (Drexhage et al., 2011) or superantigen (Shen et al., 2010) with the potential to induce immune reactions.
In general, cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) play a major role in immune reaction, especially in virus infection. Cytotoxic T cells kill targets mainly in two ways: directly inducing apoptosis or causing death of the target through the release of cytokines. Recognition of the target by T lymphocytes depends on high-affinity T cell receptors for specific peptides presented in the context of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC).
Human leukemia antigen (HLA) plays an important role in T cell recognition. HLA-A*02 is the most prevalent HLA class I allele among the Chinese Han population, and has been associated with the control of many viral infections (Shen et al., 2010).
Many pieces of evidence have demonstrated that people with neuropsychiatric diseases have aberrant immunological responses. HERV-W env is associated with neurological disease, and it has the potential to induce immune reactions. However, it is worth noting that whether or not HLA-A*0201+-restricted HERV-W env peptides cause an immune response in people with neuropsychiatric diseases has not been reported so far. This study was undertaken to identify the immunological potential of the HLA-A*0201-restricted epitopes of HERV-W env by using a reverse immunology approach. First and foremost, the HLA-A*0201+-restricted CTL peptides of HERV-W env were predicted. Five peptides were chosen and synthesized. The functional avidity and activity of the candidate peptide-specific CTLs was evaluated using enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISpot) assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and cytotoxicity assay. Our research might provide the experimental foundation for a peptide vaccine of HERV-W env and also contribute a new insight into the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases.
-
HLA-A*0201 binding peptides within HERV-W env (Chromosome 7 - NC_000006.12) were screened by using two types of T cell epitope prediction tool: SYFEPITHI (http://www.syfpeithi.de/), and BIMAS (https://www-bimas.cit.nih.gov) (Imahashi et al., 2013; Seyed et al., 2011). Peptides were selected only when they matched both the cut-off score > 20 for SYFPEITHI and T 1/2 > 10 for BIMAS. The known HbcAg-derived HLA-A*2402-restricted peptide HbcAg117e125 (EYLVSFGVW) was used as a negative-control peptide ( Guo et al., 2010). All the peptides were synthesized by the Synpeptide Company (Shanghai, China). They were of > 95% purity as determined by high-performance liquid chromatography and their identity was confirmed by mass spectrometry. The powder of these lyophilized peptides was dissolved according to the manufacturer’s instructions in ultrapure water, diluted in phosphate-buffered saline to a final concentration of 20 μg/mL and stored at –80 °C until used.
-
The blood samples of healthy people were obtained at Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University (China). Samples were collected with consent agreements, and were approved by the Institutional Review Board of Wuhan University, School of Medicine in Human Production. The genomic DNA from whole blood was extracted using a Blood Genomic DNA Mini kit (CW2087A; Cwbiotech China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCRs were performed as follows: 95 °C for 5 min; 40 cycles of 96 °C for 40 s, 63.7 °C for 50 s, 72 °C for 50 s. The primers for HLA-A*0201 were: sense 5′-TCCTGGTCCCCAGGCTCT-3′, anti-sense 5′-G TGGCCCCTGGTACGT-3′ ( Liang et al., 2006). The product of HLA-A*0201+ was about 813 bp; positive samples were selected for the following experiment.
-
PBMCs were isolated from heparinized whole blood of HLA-A*0201+ donors by Ficoll-Paque density gradient separation (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) according to the manufacturer’s directions. PBMCs were cultured in RPMI 1640 media (GIBCO BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, 2 mmol/L L-glutamine, 1% penicillin-streptomycin and 2 ng/mL IL-2. PBMCs were stimulated with peptides (20 μg/mL) separately and 3 μg/mL β2-micro globulin (M4890; Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) every 48 h, and constantly stimulated three times, the peptide-specific T cells were harvested as effector cells for future study.
Human glioma cell lines U251 and A172 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection and cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (GIBCO BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (GIBCO BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and penicillin-streptomycin (100 U/mL).
-
Plasmid pCMV-env was obtained in our laboratory as previously described (Li et al., 2013). U251 (HLA-A*0201+) and A172 (HLA-A*0201–) cells were transfected with 2.0 μg pCMV-env and 4 μL of Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions; pCMV was used as a control. These cells were inoculated in 12-well plates and incubated for 48 h at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 as target cells, followed by further analysis.
-
To assess the binding affinity of each candidate peptide to the HLA-A*0201 molecule, a classic T2 peptide-binding assay was carried out as previously described (Dervillez et al., 2013), with certain modifications. Briefly, T2 cells were incubated overnight with peptides (final concentration 20 μg/mL) in RPMI 1640 serum-free medium (GIBCO BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) containing human β2-micro globulin (3 μg/mL) at 37 °C, 5% CO 2. Cells were collected by gently transferring them into a centrifuge tube and centrifuging at 200 g for 5 min. Subsequently, cells were washed twice, then stained with anti-HLA-A*0201 monoclonal antibody conjugated to FITC for 30 min at 4 °C and analyzed by Elite flow cytometry (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, USA). Experiments were replicated three times. The fluorescence index (FI) = [MFI sample – MFI background]/MFI background, where MFI, mean fluorescence intensity, FI > 1.5 indicated a high affinity; 1.0 < FI < 1.5 indicated a moderate affinity and 0.5 < FI < 1.0 indicated a low affinity.
-
PBMCs were distributed in 96-well plates at a density of 6 × 10 4 T cells/well in 100 μL media. Peptides were added at a final concentration of 20 μg/mL. T cells were harvested every 24 h. Vital T cells were then tested by CCK-8 (zp-328-2; Zoman Biotechnology Company, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Absorbance at 570 nm was read using a Multiskan FC plate reader (Thermo Scientific, Asheville, NC, USA).
-
The frequency of peptide-specific stimulation was analyzed by IFN-γ ELISpot assays (DKE22-1000-096s; Dakewe Biotechnology Company, Shanghai, China). In brief, 2 × 10 5 PBMCs/well were constantly stimulated with peptides at a final concentration of 20 μg/mL every 48 h, three times. The PBMCs were harvested for IFN-γ-ELISpot assay and the culture supernatant was harvested for ELISA assay. The operations were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After 60 min, the reaction was stopped by washing with water. When the plates were dried, spot-forming cells (SFCs) were counted by the Dakewe Biotechnology Company (Shanghai, China).
Culture supernatants and intracellular fluid were harvested by centrifugation at 400 g for 5 min and preserved at –80 °C. A human IFN-γ ELISA kit (DRE 10184; Daocell Biotechnology, Germany) was used for detection of human IFN-γ. Experiments were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
-
Cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes was measured using a LDH Cytotoxicity Assay kit (C0016; Beyotime, China). For this, a constant number of target cells (5 × 10 3 cells/well) was added to the effective cells at a ratio of 50:1 (effective cells to target cells), and at the same time, a control was set according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The percentage cytotoxicity was determined using the following formula: Cytotoxicity (%) = [(Experimental Spontaneous – Effector Spontaneous – Target Spontaneous)/(Target Maximum – Target Spontaneous)] × 100.
-
PBMCs were cultured with the env peptides (20 μg/mL) and β2-micro globulin (3 μg/mL)at 37 °C, 5% CO 2. After stimulation for 16 h, peptide-specific T cells were harvested as effective cells; after transfection with pCMV-env for 48 h, U251 (HLA-A*0201+) and A172 (HLA-A*0201–) were used as target cells. Peptide-specific T cells and target cells were co-cultured for 6 h at a ratio of 50:1 (effective cells to target cells). Then, the cells were processed with an Annexin V-FITC/PI apoptosis detection kit (Promega, USA), following the manufacturer’s protocol, and the cells were analyzed via flow cytometry. The apoptosis rate of the cells was measured by a Beckman Coulter Epics Altra with Expo32 software (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, USA).
-
Experiments for each group were repeated at least three times. Data were analyzed using SPSS22.0. Statistical analysis among experimental groups was performed by analysis of variance (ANOVA). One-way ANOVA was used only for comparing differences between groups. A P value < 0.05 was regarded as being statistically significant.
-
MHC-I peptides with HLA-A*0201 binding motifs were predicted according to the amino acid sequence of HERV-W env using SYFPEITHI and BIMAS. There were 17 peptides that matched the cut-off score > 20 for SYFPEITHI, and 20 peptides matched the T 1/2 > 10 for BIMAS. Seventeen peptides matched both criteria. Among them, five epitope peptides ( Figure 1) that had a higher SYFPEITHI score were chosen (Table 1).
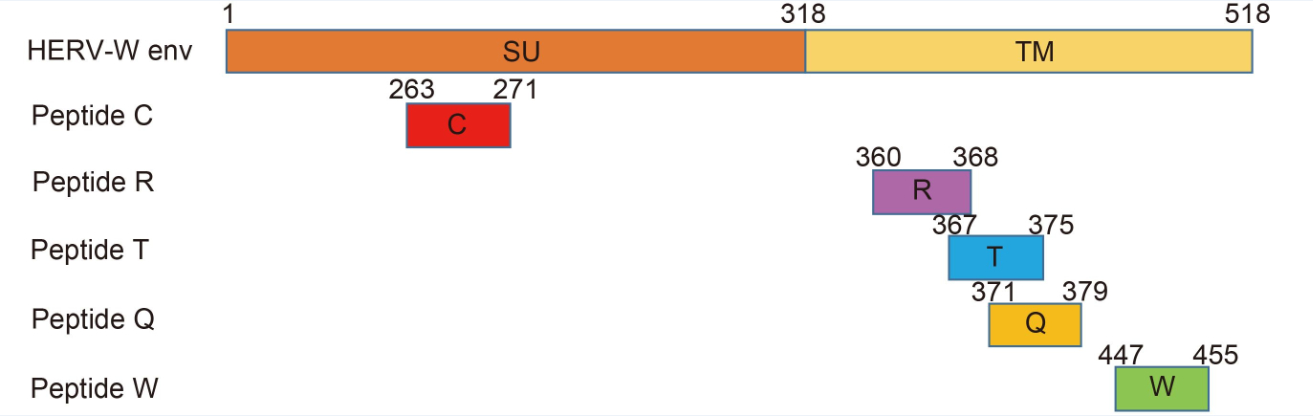
Figure 1. The positions of the five predicted epitope peptides of HERV-W env. The HERV-W env protein has the characteristics of a typical retroviral envelope protein, including a cleavage site that separates the surface (SU) and transmembrane (TM) proteins which form a heterodimer
Peptide Score Starta Sequence Name SYFEPITHIb BIMASc 263 C L P S G I F F V C 26 5103.03 360 R V A D S L V T L R 25 28.516 367 T L Q D Q L N S L T 28 201.447 371 Q L N S L A A V V Q 24 17.627 447 W I L P F L G P L W 27 56.802 HBc117e125 E Y L V S F G V W E – – Note: aAmino acid start position in the protein; bposition binding scores to HLA-A2.1; cselection criteria: T 1/2 > 10. Table 1. CTL epitopes restricted by the HLA-A2.1 allele and control peptides
-
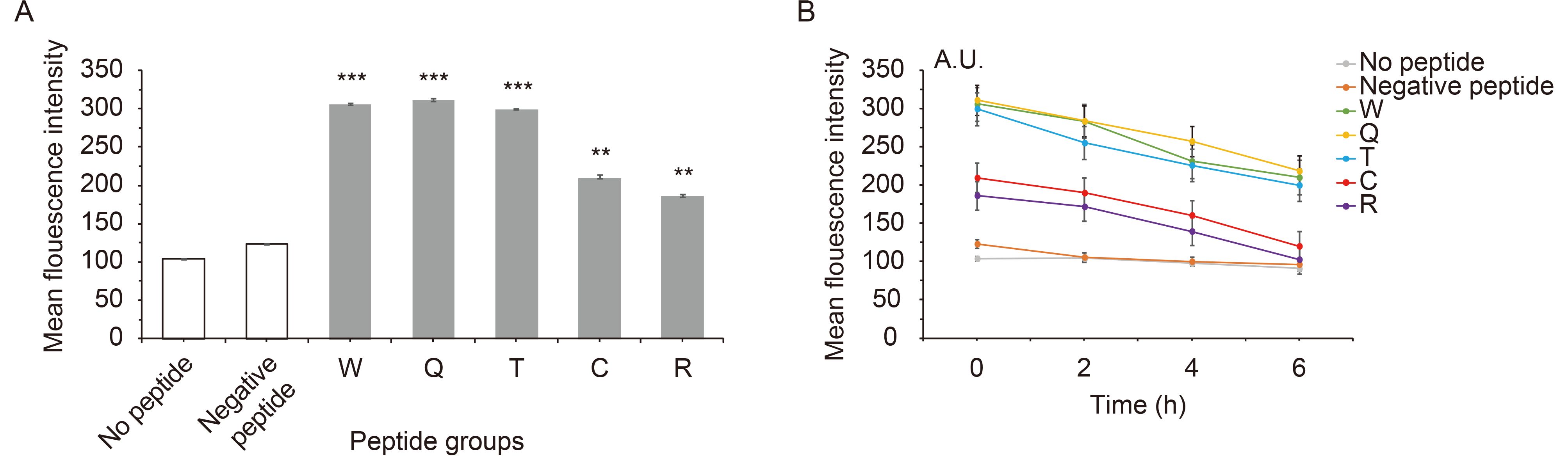
Evidence indicated that peptide affinity to MHC molecules is often correlated with its immunogenicity (Paul et al., 2013). Therefore, the transporter-associated antigen processing (TAP)-deficient and HLA-A*0201+ cell line T2 was used to detect peptide affinity for the HLA-A*0201 molecule. When the peptides were added, the MFI of T2 cells increased significantly (Figure 2A). Of the five candidate peptides, peptides W and Q had the highest affinity to HLA-A*0201, with MFIs of 306 and 314, and FIs of 1.94 and 2.02. For peptide T, the MFI was 299, and the FI was 1.875, and for the peptides C and R, the MFI values were 213 and 188, and their FIs were 1.04 and 0.81, respectively, indicating moderate affinity for the HLA-A*0201 molecule (P < 0.001). The FI of the negative control was only 0.192. From the results, peptides W and Q have the highest affinity, and no weak-affinity peptides were found in the five candidate peptides according to the definition of peptide affinity for the HLA-A*0201 molecule. With increasing time, the MFI of T2 cells in each group decreased, the longer the time, the less stable the complex. Complex stability of peptide W, Q and T were highest. And peptide C and R have a lower stability ( Figure 2B).
-
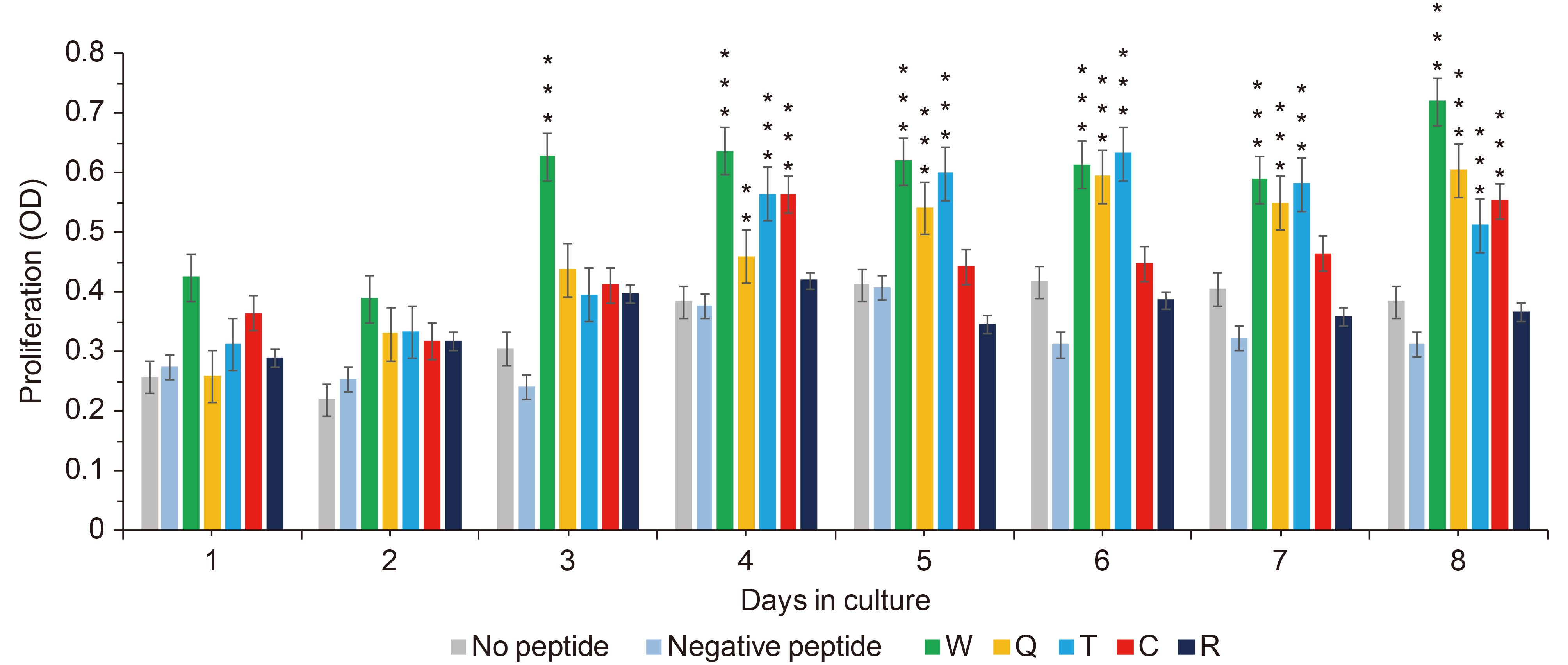
The feasibility of induction and antigen recognition of peptide-specific CTLs was investigated. T cell proliferation rates were measured daily by CCK-8 assay. The T cells stimulated with peptide W started proliferating on the third day. And Q, T group started proliferating on the fourth day. T cells stimulated with the peptides R or without any peptide did not result in proliferation, and had no statistical significance compared with the negative control (Figure 3). On the eighth day, the proliferation of T cells stimulated with peptide W had the highest increase rate, by 2.2 times (P ≤ 0.001), and peptides Q and T had increased by nearly 1.8 times (P ≤ 0.001), compared to the negative control. In conclusion, T cells would proliferate when stimulated with peptides W, Q and T, but peptides C and R would not induce T cell proliferation.
-
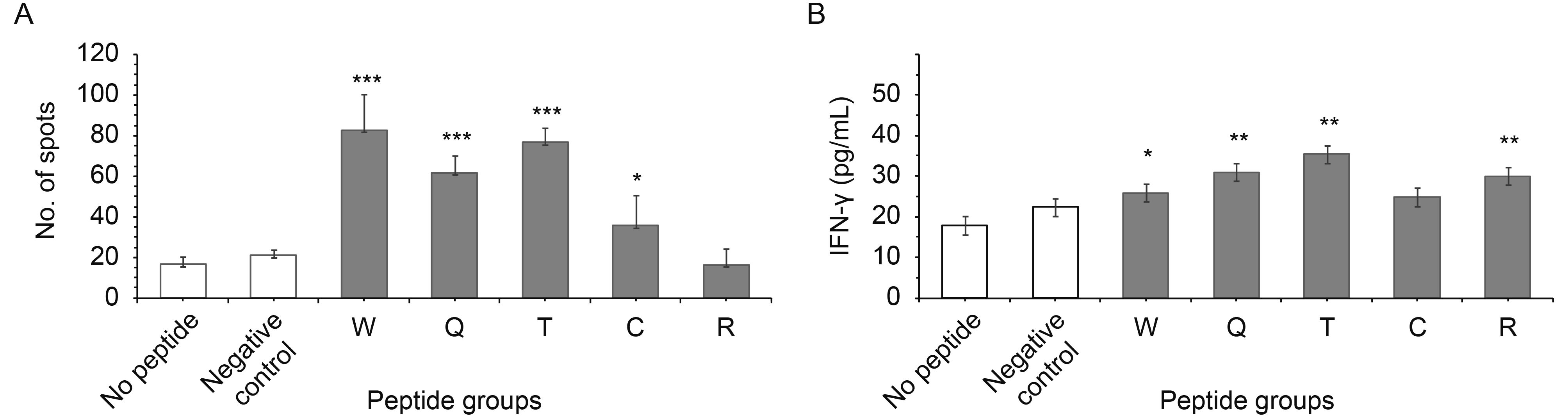
To determine the immunogenicity of the peptides, PBMCs were stimulated as indicated in the Materials and Methods section. The potential of CTLs for IFN-γ production was detected by IFN-γ ELISpot and ELISA. The SFC stimulation with peptides of W, Q and T was about 82, 66 and 41 peptide-specific spots, whereas the spots for negative peptide were about 20, showing statistically significant increases of 4, 3 and 2 times compared with negative peptide, P ≤ 0.0001 (Figure 4A); while stimulation with peptides C and R showed no significant differences compared with the negative control.
The T cell specifically secreted IFN-γ from the supernatant was determined by ELISA (Figure 4B). In this, for stimulation with peptide W the IFN-γ rose nearly one time, P ≤ 0.05, for stimulation with peptide Q the IFN-γ rose 2.2 times, P ≤ 0.001, and for stimulation with peptide T the IFN-γ increased 1.8 times, P ≤ 0.001, which were all statistically significant values; but peptides C and R had no statistically significant change compared with the negative control.
The number of SFCs increased markedly after stimulation with peptides W, Q, T and C; the T cell specifically secreted IFN-γ also increased after stimulation with peptides W, Q and C, compared with the negative control. The SFCs were tested by ELISpot, which only detected the intracellular IFN-γ, whereas ELISA detected the IFN-γ in the supernatant.
-
Only when both T cell antigen receptor complex and MHC recognize the antigen in the target cell surface, can T cells kill the target cells. Many reports have shown that T cells can kill target cells through two processes: (1) effector T cells damage the target cell membranes and cause target cell lysis by secreting perforin; (2) effector T cells via FasL-Fas, induce target cells apoptosis.
The ability to kill target cells is the ultimate goal of each reverse immunology approach. The potential of specific CTLs to attack human glioma cell lines was analyzed. The death rate increased by 2.2 ± 0.2 times compared with pCMV, P ≤ 0.0001 (Figure 5A). In addition, for peptides W, T and C the rate increased by 2.2 ± 0.2 times compared with negative peptide, P ≤ 0.0001 (Figure 5A). But the control cell line (A172) was just marginally affected and showed no significant difference (Figure 5B). CTL stimulation with peptides W, Q and T caused approximately 40%–60% specific lysis of U251.
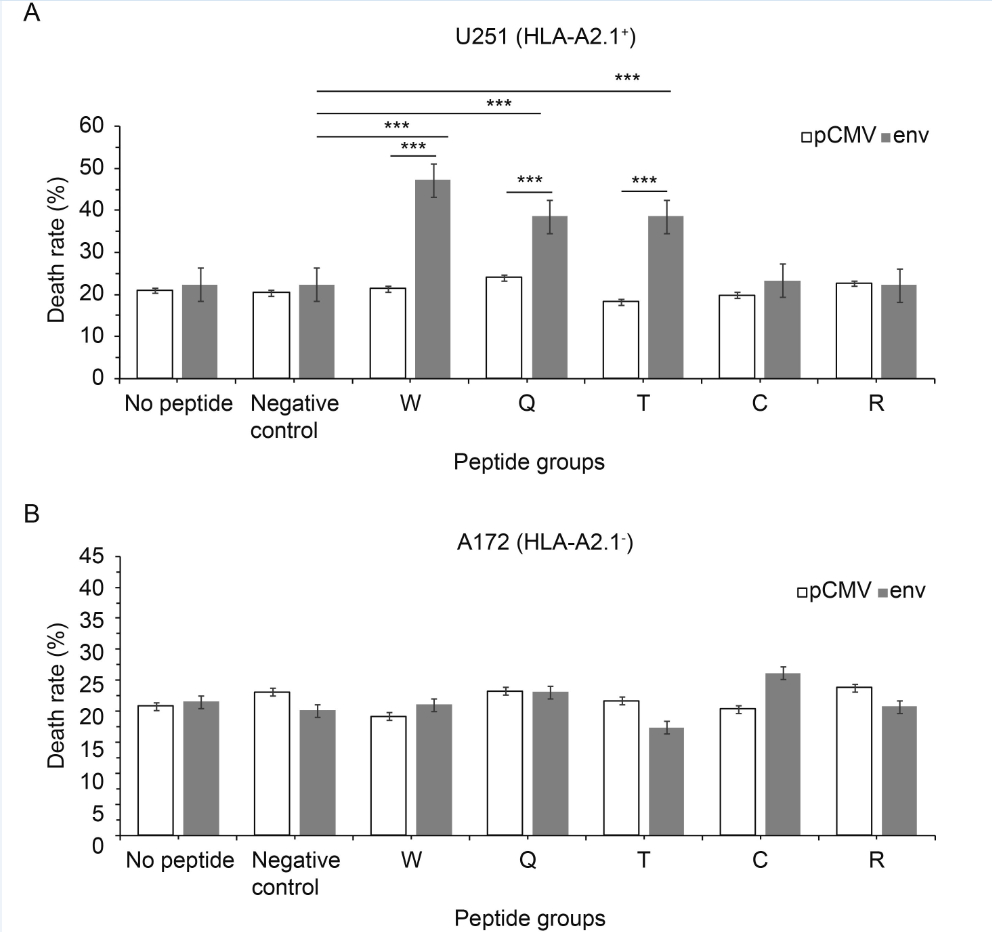
Figure 5. Functional characterization of candidate-epitope-specific CTLs. LDH release assays were used at a ratio of effectors to targets of 50:1. (A) U251 (HLA-A2.1+) cell line and (B) A172 (HLA-A2.1-) cell line. Values are expressed as the mean±standard deviation of LDH release. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001 compared with pCMV or the negative peptide control
As preliminary studies showed some promising results, we tried to find out whether the increase in cytotoxicity was related to apoptosis. When transfected with plasmid pCMV-env, the apoptosis of the target cells (U251) stimulated with peptides W, Q and T increased 2.2 ± 0.2 times compared with cells with plasmid pCMV, P ≤ 0.0001 (Figure 6A). For peptides W, T and C, apoptosis increased by 2.2 ± 0.2 times compared with negative peptide, P ≤ 0.0001 (Figure 6A). All showed statistically significant differences. In addition, there were no significant changes in A172 stimulated with any peptides and transfected with any plasmid (Figure 6B). Peptide W- Q- and T-specific CTLs could cause env+ U251 cell apoptosis in a HLA-A* 0201 background, but not env– U251 or A172 cell apoptosis.
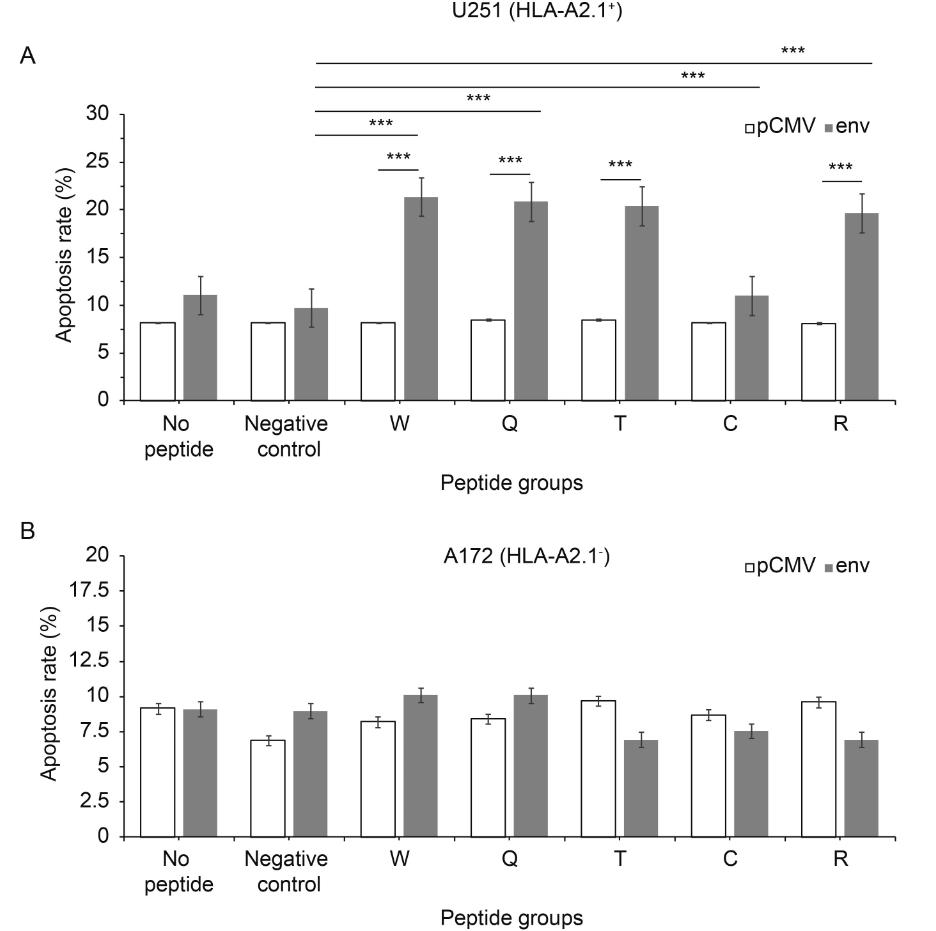
Figure 6. Peptides induce apoptosis. The apoptosis rate of the U251 (HLA-A2.1+) cell line was more than that of the A172 (HLA-A2.1-) cell line. Apoptosis assays were used at a ratio of effectors to targets of 50:1. (A) U251 (HLA-A2.1+) cell line and (B) A172 (HLA-A2.1-) cell line. Each data point represents the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001 compared with pCMV or the negative peptide control
In conclusion, peptides W, Q and T were HERV-W env antigenic epitopes, and they have both antigenicity and immunogenicity, so that they could cause strong T cell immune responses. From these results, we suspect that HERV-W env may act as an autoantigen inducing autoimmunity in people with neuropsychiatric disease.
-
In the late 1980s, HERV-W env was first reported to be associated with MS, and named as multiple sclerosis-associated retrovirus (MSRV) (Perron et al., 1989). HERV-W env has been specifically associated with MS (Christensen, 2005). The HERV-W-encoded env is up-regulated in glial cells in active lesions. A recent study of blood samples (serum), showed 47%–49% of patients with schizophrenia were positive for HERV-W env, with 3%–4% positive in the controls (Perron et al., 2008).
In addition, HERV-W env also plays a role in various autoimmune disorders. HERV-W env protein has been shown to induce potent activation of innate immunity through Toll-like receptor (TLR-4) initial agonist effect (Rolland et al., 2006). It also could induce autoimmunity (Perron et al., 2013)
T lymphocytes and monocytes have been found to be increased in schizophrenia (Duperray et al., 2015). In addition, centrally produced factors can also access the CNS through multiple humoral pathways that act in parallel. Immune information is also transmitted to the brain through rapid neural pathways that activate primary afferent nerve fibers in response to peripheral cytokine release (Dantzer et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2002). In short, people with schizophrenia demonstrate a distinct profile of immunological responses to immunogenic peptides.
HLA-A2 is the most frequently expressed class I HLA molecule (> 50% in Chinese people) (Liang et al., 2006). The structure, function and peptide binding motifs of the HLA-A*0201 molecule, the major HLA-A2 subtype, have been characterized and have been useful in identifying antigenic peptides recognized by HLA-A2-restricted T cells (Hickel et al., 1991). A main function of HLA class I molecules is to present antigens to CD+ T cells; thus, starting the immune complex processing that creates cytotoxic T cells to attack specific targets.
HERV-W env is associated with neuropsychiatric diseases, such as schizophrenia (Qin et al., 2016) and MS, and people with neuropsychiatric diseases often are found to have autoimmune responses. Moreover, HERV-W env could induce an immune response. However, there were no reports about whether or not HLA-A*0201 restriction is involved in the immune response that is caused by HERV-W env. Furthermore, the polypeptides recognized by CTLs are bound to MHC on antigen presenting cell surfaces. So, we combined SYFPEITHI and BIMAS analysis to predict peptides that could significantly save time by narrowing the validation scope (Tang et al., 2015) (Table 1).
The predicted peptides are not always true binders, and several false-positive peptides may be selected (Kessler et al., 2003); therefore, experiments were carried out to validate their immunogenicity. Peptide affinity to HLA molecules is one of the key events, and a correlation between HLA binding and immunogenicity is often observed (Assarsson et al., 2007) (Figure 2).
PBMCs separated from healthy people have been commonly used to evaluate the immunogenicity of a peptide. Peptide-specific CTLs were induced by immunizing the PBMCs of three rounds of stimulation with peptides W, Q and T and a positive control, the number of peptide-specific CTLs was sufficiently increased (Figure 3).
Following successful induction of specific CTLs, IFN-γ ELISpot and ELISA assays were used to quantify the occurrence of T lymphocyte cells secreting IFN-γ after stimulation with peptides. It was found that stimulation by peptides W and T resulted in production of more SFCs, while the maximum secretion of IFN-γ seemed to be induced by peptide T (Figure 4). We thought the reason for this was that SFCs were used to detect the intracellular IFN-γ (Figure 4A), while ELISA detected the IFN-γ in supernatants (Figure 4B).
Finally, as already mentioned, there are two ways that the T cells induce the target cell’s death. First, activation of the target cell surface FasL-Fas induces apoptosis; second, T cells can secrete granulysin and perforin, which cause cell lysis. T cells kill the target cells after recognition of the antigen in the target cell surface by both the T cell antigen receptor complex and MHC. The recognition efficiency of peptide-specific CTLs for target cells was evaluated using apoptosis and LDH assays. When the target cells were transfected with pCMV-env, peptide-specific CTLs could only dissolve U251 cells (HLA-A*0201+) (Figure 5A), but not HLA-A*0201– cells (A172) (Figure 5B). The apoptosis results were similar to those for the LDH assays (Figure 6). This indicated that the cytotoxicity was HLA-A*0201 restricted. Peptides W, Q and T could dissolve the HLA-A*0201+ cells significantly compared with negative peptide. Together with the ELISpot and ELISA results, this demonstrated that the W, Q and T predicted epitopes were naturally presented, and that they were CTL epitopes of HERV-W env.
T cells proliferated when stimulated with peptides W, Q and T; the T cell specifically secreted IFN-γ was also increased by stimulating with peptides W, Q and C, compared with the negative control. The CTL stimulation with peptides W, Q and T caused approximately 40%–60% specific lysis of U251 transfected with plasmid pCMV-env, expressing the complete protein comprising the studied peptides; the peptides W, Q and T specific CTLs could cause env+ U251 cell apoptosis in a HLA-A*0201 background. In conclusion, peptides W, Q and T, which were HERV-W env antigenic epitopes, had both antigenicity and immunogenicity, and could cause strong CTL responses. From these results, we suspect that HERV-W env may promote autoantigen-induced autoimmunity in neuropsychiatric diseases, such as MS and schizophrenia. Our research might provide an experimental foundation for a peptide vaccine for HERV-W env and also contribute a new insight into the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases.
-
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (no. 31470264, no. 81271820, no. 30870789 and no. 30300117), the Key Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (no. 2014CFA078), the Stanley Foundation from the Stanley Medical Research Institute (SMRI), USA (no. 06R-1366), for Dr. F Zhu, and the Scientific Innovation Team Project of Hubei Province of China (no. 2015CFA009).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Wuhan University School of Medicine.
-
FZ designed the experiments. XNT, SL and RX carried out the experiments. LJZ provided the blood samples. XLW analyzed the date. XNT prepared the figures and/or tables and drafted the manuscript. FZ finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Human leukemia antigen-A*0201-restricted epitopes of human endogenous retrovirus W family envelope (HERV-W env) induce strong cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses
- Received Date: 24 March 2017
- Accepted Date: 20 July 2017
- Published Date: 22 August 2017
Abstract: Human endogenous retrovirus W family (HERV-W) envelope (env) has been reported to be related to several human diseases,including autoimmune disorders,and it could activate innate immunity. However,there are no reports investigating whether human leukemia antigen (HLA)-A*0201+ restriction is involved in the immune response caused by HERV-W env in neuropsychiatric diseases.In the present study,HERV-W env-derived epitopes presented by HLA-A*0201 are described with the potential for use in adoptive immunotherapy.Five peptides displaying HLAA*0201-binding motifs were predicted using SYFEPITHI and BIMAS,and synthesized.A CCK-8 assay showed peptides W,Q and T promoted lymphocyte proliferation.Stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HLA-A*0201+ donors with each of these peptides induced peptidespecific CD8+ T cells.High numbers of IFN-γ-secreting T cells were also detectable after several weekly stimulations with W,Q and T.Besides lysis of HERV-W env-loaded target cells,specific apoptosis was also observed.These data demonstrate that human T cells can be sensitized toward HERV-W env peptides (W,Q and T) and,moreover,pose a high killing potential toward HERV-W env-expressing U251 cells.In conclusion,peptides W Q and T,which are HERV-W env antigenic epitopes,have both antigenicity and immunogenicity,and can cause strong T cell immune responses.Our data strengthen the view that HERV-W env should be considered as an autoantigen that can induce autoimmunity in neuropsychiatric diseases,such as multiple sclerosis and schizophrenia.These data might provide an experimental foundation for a HERV-W env peptide vaccine and new insight into the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: