-
Human guanylate binding protein-1 (hGBP-1) is a member of the GTPase family which is induced by interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and interferon alpha/beta (IFN-α/β). It is not clear that whether hGBP-1 mediates the antiviral biologic activity of interferons. Anderson et al report that hGBP-1 inhibited Viscular stomatitis virus (VSV) and Encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) replication in Hela cells (1). To further investigate the antiviral effects of hGBP-1, we cloned the hGBP-1 gene and inserted it into the pcDNA3.1(-) eukayotic expression vector and analyzed the inhibition effect against Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Coxsackie virus B3 (CVB3).
HTML
-
Hind Ⅲ, EcoR Ⅰ BamH and Ⅰ NotⅠ restriction endonuclease were purchased from New England Biolabs Co., Pfu DNA polymerase and T4 DNA ligase were purchased from Promega Co., Dulbecco's modified Eagle (DMEM) medium, fetal bovine serum (FBS) and lipofectamine were purchased from Invitrogen Co., Anti-hGBP-1 polyclonal antibodies were kindly provided by Prof. Mengji Lu (Institute of Virology, Duisburg-Essen University).
-
TA cloning vector pCR2.1, eukayotic expression vector pcDNA3.1 (-) and competent cells TOP10 were purchased from Invitrogen Co., Hepatitis B virus replicon pHBV1.3 was previously constructed by Lu et al (10).
-
HepG2 cells and Hela cells were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle (DMEM) medium supplement with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Coxsackie virus B3 was stored in our laboratory and propagated on Hela cells.
-
Primers were designed based on nucleic acid sequence of hGBP-1 (GenBank accession number: M55542), P1 (-10~10) : 5'-CAGCCTGGACATGGCATCAG-3' and P2 (1779~1752): 5'-GCGGGCCCTTAGCTTATGGTACATGCCT-3' were designed for amplifying the complete coding sequence of the hGBP-1 gene; P3 (725~742): 5'-TTCACCGCAGGAAGCTTG-3' and P4(877~860): 5'-GTTGACCTGGATGCCTCCTG-3' were designed for amplifying partial sequence of the hGBP-1 gene.
-
HepG2 cells were stimulated with 400 U/ml recombinant human IFN-γ(rhIFN-γ)for 48 h, and total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent. hGBP-1 cDNAs were synthesized by incubating 1μg RNA with moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase and primer P2 at 42℃ for 60 min. cDNAs were used for PCR with primers P1 and P2. PCR was performed over 35 cycles of 94℃ 1min, 55℃ 1 min and 72℃ 90 sec, followed by an extension at 72℃ for 6 min. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining.
-
PCR product was inserted into pCR2.1 vector and then transformed into TOP10 competent cells. The recombinant plasmid harboring the correct length and direction of hGBP-1 gene were identified by EcoRⅠand Hind Ⅲ digestion and confirmed by sequencing. The hGBP-1 gene in the pCR2.1-GBP-1 plasmid was removed by BamHⅠand NotⅠdigestion and subcloned into pcDNA3.1 (-), the recombinant plasmid was named as pGBP-1.
-
6-well culture plates were seeded with 5×105/well Hela cells and HepG2 cells. 16h later, cells were transfected with 5μg of pGBP-1 plasmid using 5μL lipofectamine reagent according to the manufacturer's instruction. Culture media were changed 6h later and incubated for another 48h. Then intracellular hGBP-1 protein was characterized by Western blot analysis using rabbit anti-hGBP-1 polyclonal antibodies, and β-actin was analyzed using goat anti-actin antibody in parallel.
-
HepG2 cells were seeded in 6-well plates (5×105 cells/well) and cotransfected with 5μg of pGBP-1 plasmids and 1μg of pHBV1.3 plasmids. The level of HBsAg and HBeAg in supernatant was determined by ELISA everyday, and intracellular HBV replicative intermediates were analyzed by southern blot hybridi-zation 96 h post transfection.
-
5μg total DNA isolated from HepG2 cells contransfected with pGBP-1 and pHBV1.3 was separated on 1.5% agarose gels and transferred to nylon membranes by standard procedures and hybridized with a 32P-labeled HBV probe, the hybridization signal was quantified with PE hybridization analyzer.
-
Hela cells were transfected with 5μg of pGBP-1 and seeded in 24-well plates (5×104cells/well) 24 h later, then challenged with CVB3 at different TCID50(50% tissue culture infective dose). After incubation for 1 h, the cells were washed and incubated for additional 72 h. The cultures were refrozen and rethawed for three times and the virus yield were determined by TCID50 assay.
Reagents
Plasmids and bacteria
Virus and cells
Primers design
hGBP-1 gene amplification by RT-PCR
Construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid pGBP-1
Expression of hGBP-1
Replication of HBV
Southern blot analysis
Replication of CVB3
-
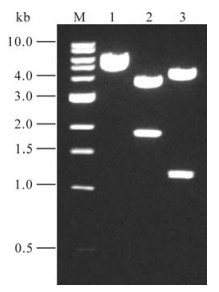
A 1790-bp fragment was obtained by long chain RT-PCR. This fragment was cloned into pCR2.1 vector by T/A method, and the inserted sequence was identified by restriction endonuclease cleavage (Fig. 1) and sequence analysis. After digestion with EcoRⅠor Hind Ⅲ, the fragments were 1.8/3.9kb and 1.11/ 4.60kb respectively, indicating that the hGBP-1 gene was inserted into pCR2.1 in the reverse direction. Sequence alignment indicated that the cloned hGBP-1 gene had 100% homology with the hGBP-1gene published in GenBank (Accession number: M55542). The hGBP-1 gene fragment was then subcloned into the pcDNA3.1(-) vector by digestion with BamHⅠ and NotⅠ, the recombinant plasmid was named as pGBP-1.
-
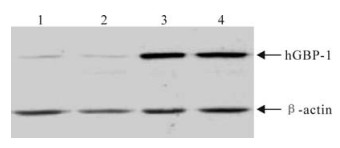
HepG2 and Hela cells were transfected with the pGBP-1 plasmid, the cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot. The hGBP-1 (about 67 kDa) protein was high level expression in pGBP-1 transfected cells, but was low level expression in the cells transfected with monk plasmid (Fig. 2).
-
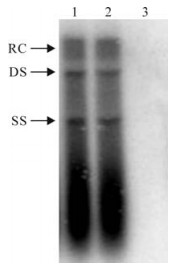
HBV replication in HepG2 cells contransfected with pGBP-1 and pHBV1.3 was studied by ELISA and Southern blot. The levels of HBsAg and HBeAg in supernatant were similar to that of the cells contransfected with pHBV1.3 and monk plasmid (Table 1). Furthermore, the levels of intracellular HBV replicative intermediates had no significant difference between the two groups (Fig. 3).

Table 1. The levels of HBsAg and HBeAg in supernatant after transfection (x±s)
-
CVB3 replication in Hela cells transiently transfected with hGBP-1 was studied by TCID50 assay. In brief, the viral products in the supernatant and cells were assessed by measuring the cytopathic effect (CPE) on Hela cells incubated with 0.1mL culture lysates. TCID50 of 0.1mL culture lysates was markedly reduced when compared with that of the Hela cells without hGBP-1 transfection, especially in Hela cells chal-lenged with lower doses of CVB3 (Table 2).

Table 2. Virus production in cultures after Hela cells challenged with CVB3 (TCID50/0.1mL)
Construction of eukaryotic expression plasmid pGBP-1
Expression of hGBP-1 gene in HepG2 cells and Hela cells
Effect of hGBP-1 against HBV replication in vitro
Inhibition of CVB3 replication by hGBP-1 in vitro
-
Interferons (IFNs) are capable of mediating an antiviral state, an antiproliferative effect, and an im-mune response after binding to cell surface receptors of responsive cells (15). The establishment of the antiviral effect by the IFNs is dependent on antiviral protein synthesis. While it is very clear about the effect of some antiviral proteins, such as RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR), 2'-5' oligoadenine sy nt he as e (2 '-5'OAS) an d M x pr ot ei n, t h e IFN-induced granulate binding proteins (GBPs) represent a family of proteins whose role in IFN-mediated biological effects is not understood. It has been reported that there are at least two forms of the IFN-induced GBPs in human and murine cells (GBP-1 and GBP-2). Recent studies on hGBP-1 were mainly focused on the function in inflammation, and hGBP-1 was regarded as the marker of the inflame-matory cytokine-activated phenotype of endothelial cells (11, 14). However, it is not very clear about the antiviral effect mediated by hGBP-1; Anderson et al. have found that interferon-induced hGBP-1 mediates an antiviral effect against vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) (1).
We have found that HepG2 cells stimulated with high concentration of recombinated human IFN-γ (rhIFN-γ) can produce abundant hGBP-1 protein (data not shown). Previous work showed that GBP-1 mRNA is induced in many kind of cells by cytokines, and IFN-γ was a strong inducer for hGBP-1 (13). So we can amplify the hGBP-1 gene using total RNA isolated from rhIFN-γ treated cells.
The GBP-1 protein belongs to the family of large GTPases. GTPases serve many different functions including playing key roles in such basic processes as signal transduction, vesicle transport and trans-plantation (2, 3, 7). Most GTPases contain the tripartite GTP-binding consensus motif GXXXXGKS, DXXG, and N/TXPG. The common feature of most GTPases is that they have functions in molecular switches, and GTP-and GDP-bound forms have different confor-mations which can influence their interactions with target proteins (12). Although GBP lack the N/TXPG consensus motif (4, 5), GBP-1 is characterized as GTPase by the high turnover of GTPase activity, with which it exhibits characteristically high binding affinities for GTP and GDP, and can efficiently hydrolyze GTP and release GDP (7, 9).
Mx proteins also belong to GTPase family, they are key components of the interferon-induced antiviral protein against RNA viruses, and their antiviral activity depends on GTPase activity (16). In particular, Mx proteins interfere with the intracellular transporttation of viral components. In the case of bunyaviruses, which have a cytoplasmic replication phase, MxA interferes with the transportation of viral nucleocapsid protein (N) to the Golgi compartment, which is the site for virus assembly. Association of MxA to the viral nucleocapsid protein leads to the sequestration of the viral protein into highly ordered perinuclear complexes and, as a consequence, to the inhibition of viral replication and formation of progeny viruses (6). In the case of orthomyxoviruses, the MxA protein prevents the incoming viral nucleocapsids from being transported into the nucleus, which is the site of viral transcription, by interacting with the ribonucle-oprotein complex of the virus (12). MxA is induced by IFN-α/β but not IFN-γ, however, GBP could be strongly induced by IFN-γ, perhaps due to the molecule differences between the IFN-α/β and IFN-γ receptors (15).
The results of our experiments indicated that hGBP-1 could inhibit CVB3 replication in Hela cells with high level of hGBP-1 expression, but hGBP-1 cannot inhibit HBV replication in HepG2 cells with high level of hGBP-1 expression. Guidotti et al reported that the antiviral activity of IFNs in HBV transgenic mice was not mediated by Mx protein, although HBV can replicate at higher levels in mice deficient in MxA protein when compared with the control mice (8). HBV belongs to the hepadnaviridae family, and the mechanisms of viral replication are markedly different from RNA viruses. MxA can selectively inhibit viral replication of RNA viruses. Similar results were obtained in our experiments about hGBP-1 against RNA viruses, suggesting that antiviral activity of hGBP-1 might be a consequence of the GTPase activity. Further studies on antiviral mechanism of hGBP-1 are necessary for clarification.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: