-
Members of Circovirus family are all small, non-enveloped viruses with a circular single-stranded DNA genome. The family comprises two genera gyrovirus and circovirus (16, 18), and chicken infectious anemia virus (CIAV) is the only member of gyrovirus (11) amongst all known animal circoviruses, whereas many members of the circovirus genera have been discovered. Porcine circovirus type Ⅰ (PCV1) and porcine circovirus type Ⅱ (PCV2) (1), goose circovirus (GoCV) (17), pigeon circovirus (PiCV) (9) and duck circovirus (DuCV) (8) infect domestic animals and birds, while psittacine beak and feather disease virus (BFDV) (3) and cannary circovirus (CaCV) (10) have been isolated from wildfowls. Recently, the circovirus infection has been found in simultaneously Senegal doves (12), Finches (13), Ostrich (6) and Gull (19).
The remarkable feature of circovirus infection is that the lymphoid tissues are invaded and their function is corrupted with a result of immuno-suppression, growth retardation and an increased probability of secondary infections. CIAV was reported firstly by Yuasa in 1979 (20) and chickens infected with CIAV showed serious clinical anemia, effusing dermatitis and death in chicklings. Infection with PCV2 caused postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) which was firstly discovered in Canada (5), and later findings showed that the infection with PCV2 was also related to porcine dermatitis and nephropathy syndrome (PNDS), congenital tremors (CT), proliferative and necrotizing pneumonia (PNP) and reproductive disorders of pregnant sows etc. The infections of circoviruses had led to serious disruption of international husbandry of domestic animals and livestocks; however, so far only CIAV and PCV had been isolated and cultured in vitro successfully (15, 21).
Duck circovirus is the latest identification of circoviruses in sick ducks and first reported in 2003 (8) and the full length of its genome has been sequenced. Homology comparison of the genome showed that the circovirus was more similar to GoCV than to other circoviruses (8). Because there is no available in vitro cell system for the isolation of DuCV, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and nucleotide sequencing are often used for studies of DuCV(2, 4, 7). In this study, we report the epidemic survey of DuCV in flocks in Fujian Province of China. A pair of primers was designed for test for the presence of DuCV from samples of sick Muscovy ducks with infectious serositis and another 4 pairs of overlapping primers for amplifying the full length genome of the China isolate of DuCV according to the reported sequences.
HTML
-
Livers were collected from 43 sick Muscovy ducks with Riemerella anatipestifer from 12 rearing farms in Fujian Province in China in 2006. All liver samples were collected and kept at –80℃ until processing. The virus genomic DNA was extracted with the DNAEasy tissue kit (QIAGEN Hilden. Germany), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
-
Based on the published DuCV sequences (2, 4, 7), two primers were designed and desigated as P-9f: 5'-TATATTATTACCGGC GC(C/T)TG-3' and P115r: 5'-TCTTCAAAGGTAGGGTTATT-3'. The two primers amplified a 124 bp fragment from tissue homogenates containing DuCV. The PCR was carried out in a PCR system (Mastercycler personal; Eppendorf AG). The PCR mixture (25 µL) contained 17 µL water, 2.5 µL of 10 times buffer, 2 µL dNTP blend (2.5 mM each of four dNTPs), 1µL forward primer (25 picomole), 1 µL reverse primer (25 picomole), 1 µL template DNA and 0.2 µL of Taq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). The PCR condition was 1 cycle of 94℃ for 5 min, 32 cycles of 94℃ for 30 sec (denaturation), 50℃ for 30 sec (annealing) and 72℃ for 30 sec (extension), and 1 cycle of 72℃ for 5 min (final extension). Then the PCR product was subjected to electrophoresis on 0.8% agarose gels and stained with ethidium bromide.
-
Four pairs of primers were designed to amplify four overlapping fragments that covered the complete genome of DuCV. The sequences of the four pairs primers were P-2f: 5'-TTACCGGCGCTTGTACTC-3'/ P604r: 5'-TACTTGTTTTCGGCGGGA-3', and P509f: 5'-ACGCAACGTGATTGGAAG-3' / P1270r: 5'-CATTACGCCATGGGCATG-3', and P912f: 5'-CCAATAAACTACTGAGAC-3' /1908r: 5'-ATCGG CGTGCATATCGTG-3', and P1839f: 5'-CGTAGCC TTCGTCTTCTG-3' / P342r: 5'-GGTATGTCGACT CTTTGG-3'. Briefly, PCR was performed over 1 cycle of 94℃ for 5 min, 32 cycles of 94℃ for 30 sec (denaturation), 55℃ for 30 sec (annealing) and 72℃for 1 min (extension), and 1 cycle of 72℃ for 5 min (final extension). After amplification, the samples were examined by electrophoresis as above. The four fragments were then cloned into pMD18-T vector and sequenced from both directions by an automatic sequencer (ABI-377; PE Applied Biosystems).
-
The complete genome of DuCV FJ0601 was obtained by assembling sequences of the continuous over-lapping PCR products using EditSeq (DNAStar Inc., Madison, WI). Nucleotide and amino acid sequence alignments were performed by the Clustal W method with Megalin 5.08 (DNAStar Inc.), and Phylogenetic analyses were also performed. The complete DuCV FJ0601 sequence reported in this study was submitted to the GenBank database and the accession number was EF370476. The following DuCV sequences with their accession numbers were retrieved from the GenBank database for references and comparative pur-poses: 4 isolates from Taiwan TC1/2002 (AY394721), TC2/2002 (DQ166836), TC3/2002 (DQ166837) and TC4/2002 (DQ166838) (4), DQ166835-8 from Ger-many (AY228555) (14) and American strain 33753-52 (DQ166838) (2).
Viruses and DNA extraction
Detection of DuCV by PCR
PCR amplification and sequence analysis of the DuCV genome
Nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis of DuCV FJ0601
-
When PCR was performed using primers P-9f and P115r, DuCV DNA was detected in the tissue samples of 34 (79%) of the 43 sick ducks and 10 (83.3%) of the 12 farms (Fig. 1). The PCR-amplified products were subjected to sequence analysis. Sequence homology analyses based on the 6 already published DuCV sequences (TC1/2002, TC2/2002, TC3/2002 and TC4/2002: accession numbers DQ166835-8, German DuCV: AY228555, American DuCV 33753-52: NC-007220) showed that the PCR products were DuCV DNA, indicating that DuCV infection had been prevalent in mainland of China.
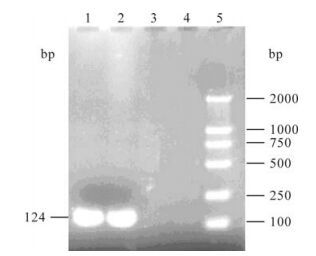
Figure 1. Analysis of PCR products of DuCV. 1 and 2, Positive samples of DuCV; 3 and 4, Negative samples of DuCV; 5. Marker DL2000.
A full length genome sequence of DuCV isolate FJ0601 (GenBank accession No. EF370476) was successfully obtained with the four overlapping primers (Fig. 2). Further analysis indicated that it consisted of 1988bp and possessed the common features of circoviruses including a potential replication-associated stem-loop structure and the Rep protein motifs. DuCV FJ0601 shared 97.3%~97.5% identities in genomic nucleotide sequence to the four Taiwan isolates TC1/2002, TC2/2002, TC3/2002 and TC4/2002, 82.9% to the America strain 33753-52 and 82.3% to the Germany isolate DQ166835-8. DuCV FJ0601 was located with the Taiwan isolates in the same branch of the predicted phylogenetic tree and distinct from the other strains, (Fig. 3), indicating that it is most closely related to the Taiwan isolates.
-
The result of bioinformatics analysis indicated that there were two open reading frames (ORFs) in the full length genome sequence of DuCV FJ0601; one was Rep, coding replicating proteins, and the other Cap, coding the capsid protein. Using by the Clustal W method in Megalin 5.08 (DNAStar Inc.), the deduced amino acid sequences alignment of the Rep and Cap proteins of DuCV FJ0601 and other DuCV isolates is displayed in Table 1. The Rep gene of FJ0601 encodes a 297 aa protein and starts at 33 nt, while the Rep for other strains are 292 aa long and start at 47 nt or 48 nt. The Cap gene of all isolates is 257 aa long, it starts at 1294 nt in FJ0601 and TC1-4/2002, and at 1928 nt and 1933 nt in 33753-52 and DQ166835-8 respectively. The intergenic region between Rep and Cap is 96 nt for FJ0601, while 110-111nt for all other strains.

Table 1. Genomic comparison of different DuCV isolates
Although there was some difference in the ORFs, there were some regions with high homology between the known DuCV strains. A stem-loop structure with a highly conserved sequence of nine nucleotides (TATTATTAC) (nt 1982-2) was found in the untrans-lated region (nt 1925-47) between the two ORFs of the FJ0601 genome. There were two reverse repeating sequences (nt 3-12 and nt 1969-1978] either side of this fragment, and beside the loop structure, another two conservative direct repeating seven-nucleotide sequences (Fig. 4) were found, which are probably for the rolling replication of the DuCV genome (8). A region (nt 25-47) with high mutations and deletions between the loop and the start codon of Rep was also found (Fig. 4).
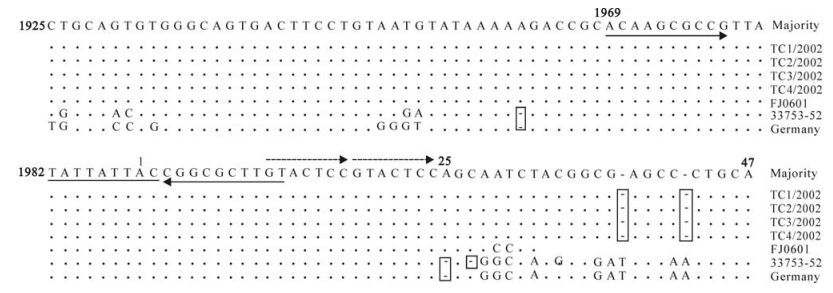
Figure 4. Sequence alignment of the intergenic region of DuCVs of different origin. The consensus (majority) sequences are shown on the top of the alignment. For each isolate, only sequences different from the consensus one are shown. The invert repeated sequences that form the potential stem-loop structure are indicated by arrows. Sequences of the conserved nucleotide motif are underlined, and sequences that form directed repeats are shown by dashed arrows. The deletions are boxed.
-
When Rep and Cap proteins are compared with other DuCV isolates the, FJ0601 did show some difference in amino acid sequence. The comparison with Clustal W indicated that the Rep protein of FJ0601 shared 98.2%~98.5% identity with that of the Taiwan isolates, while 87.3%~87.7% with that of the German and the American strains. The Cap protein of FJ0601 had a of 96.5%~97.3% identity with that of the Taiwan isolates, and 86%~86.4% with that of German and American strains.
PCR and sequence analysis
Genomic organization of DuCV FJ0601
Homology analysis for Rep and capsid proteins of DuCV FJ0601
-
In this study, the infection of DuCV in Muscovy ducks with breakout of infectious serositis was detected by PCR in Fujian province of P.R. China. Among the examined 43 liver samples from 12 farms, 34 (79.07%) samples from 10 farms (83.33%) were positive, which indicated that infection of DuCV in the ducks of Fujian province. The results indicate a common infection of DuCV in mainland China and a possible link between DuCV infection and Riemerella anatipestifer. It needs to be further studied whether the sickness of the ducks was due to the co-infection of various immune-suppressing pathogens or conversely that DuCV infection can worsen the pathogenicities of conventional pathogens such as duck plague virus, duck hepatitis virus, Riemerella anatipestifer, Escherichia coli, Pasteurella multocida, Salmonella and so on.
A full-length genome sequence of FJ0601, a Chinese DuCV isolate, was completed with four pairs of continuous overlapping primers. It was the first one from the mainland of China and has been submitted to GenBank. The genome of FJ0601 consisted of 1 988 nt which is the same length as the Taiwan isolates, (4), but shorter than that of the German isolate (1 996 nt) (14) and the American isolate (1 991 nt] (2). Homology analyses shown that FJ0601 contained a conserved replicating-relative stem-loop which was for transcribing the Cap protein. However, there was obvious differences in the Rep protein of FJ0601, which codes for 297 aa while other strains code for 292 aa, and interestingly it started at a different site in comparison to the other strains. Further work should be done to probe whether this difference can affect the DuCV biological characteristics, e.g. replication, trans-cription and pathogenicity. Meanwhile, the analysis for the amino acid sequences of Rep and Cap showed that there were two distinct groups located in two different branches of the estimated phylogenetic tree; one branch contained FJ0601 and the 4 Taiwanese with a homology of over 97.3%, while the other contained DQ166835-8 and 33753-52 with a homo-logy of over 98%. The homology in between of the two groups was only about 83.8%. Therefore, whether there was a certain relationship between the homology and their host species and the region in which the samples were isolated requires additional study since the 7 DuCV isolates came from different species in different regions.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: