-
Duck viral enteritis is a disease of waterfowl (duck, goose, and swan) caused by duck enteritis virus (DEV), an alphaherpesvirus. DEV causes considerable economic losses to the commercial duck industry due to mortality and decreased egg production (12). In China, the virulence of DEV has increased in ducklings and geese, and recent reports indicate that the current DEV vaccine lacks long time efficacy. These findings suggest that DEV is constantly mutating (18).
The viral genome of DEV comprises a linear and double stranded DNA genome of approximately 180 kb with a structure similar to that of other alphaherpesviruses. Some glycoprotein genes of DEV have been previously characterized and studies of the gH, UL24, TK, gC, and UL5 genes suggest that DEV should be classified into the subfamily of Alphaherpesvirinae (13, 14, 17), and is more closely related to members of the Mardivirus genus than to other herpesviruses.
Among the herpesviruses, UL4 encodes a non-essential and non-structural protein that enhances virion formation and does not show apparent function in infected cells in culture or in experimental animal systems (2, 7, 10). In other studies, it was reported that UL4 was encoded by a 0.8 kb mRNA (19) and the product of the human herpesvirus 2 (HHV-2) UL4 gene was a very late (γ2) protein that accumulates in the cytoplasm of infected cells observed as punctate structures in the nucleus in late infection (23). It was also found that synthesis of the UL4 protein was blocked by phosphonoacetic acid, an inhibitor of DNA synthesis (6). However, there are no reports on nucleotide sequence and any function of the DEV UL4 gene. As a result, we could not clone the DEV UL4 gene based on previous studies. Entire genomic comparison revealed that the gene order UL6-UL5-UL4-UL3 is conserved amongst genomes of most alphaherpesviruses, in which UL4 is located between UL5 and UL3 genes (1, 3, 11). This genetic order made it possible for us to design a degenerate primer in a conserved region of the UL3 gene to amplify the DEV UL4 gene.
The objective of the present study was to clone and sequence the UL4 gene of the Chinese DEV vaccine strain by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using a specific primer and a degenerate oligonucleotide primer. The sequence obtained was compared with those of other herpesviruses. These data are useful for further study of molecular biology and accurate classification of DEV.
HTML
-
A vaccine DEV strain (No. 020318) was provided by Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences of China and deposited at our laboratory.
-
The virus was propagated in the allantoic membrane of 11-day-old non-immunized duck embryos by standard methods (22). The preparation of DEV DNA was performed as described by Hansen et al (9). Extracts of normal allantoic fluid were prepared and used as negative controls.
-
Primers SP1, DP1, P1 and P2 are shown in Table 1. Primer positions are indicated with arrows. (Fig. 1). The conserved sequence of DEV UL3 gene was shown in Table 2. All primers were synthesized by Invitrogen Co., Ltd. (Shanghai) and were suspended in double-distilled water to 50 pmol/μL concentration upon arrival.

Table 1. Primers used in PCR

Figure 1. The PCR amplification of the UL4 gene. The genomic structure scheme presented here is drawn according to human herpesvirus 1. Primer positions and amplification directions are indicated with arrows.

Table 2. The conserved region of herpesvirus UL3 genes that were used to design primers DP1
-
The primers SP1 and DP1 were used to amplify the sequence of the UL4 gene and partial sequence of the UL3 gene. PCR was performed in 50 μL volumes containing 5.0 μL of 10× PCR buffer (100 mmol/L Tris-HC1 (pH 8.3), 500 mmol/L KC1), 5 μL of 25 mmol/L MgCl2, 8 μL of 2.5 mmol/L dNTP mixture, 1 μL of SP1, 5 μL of DP1 and 0.5 μL of Ex Taq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa). The PCR parameters were 4 min at 95 ℃, and 30 cycles of 50 s at 94 ℃, 1 min at 50℃, 2 min at 72 ℃, and a final extension time of 10 min at 72 ℃. The PCR product was visualized on 1% agarose gel electrophoresis containing 0.8% μg/mL ethidium bromide. The negative control was performed under the same conditions.
-
The PCR product was purified using a Mini Gel kit (TaKaRa corp). Purified product was cloned into pMD18-T vector and transformed into Escherichia coli (E. coli) DH5α competent cells. The recombinant clones were selected by the Amp/IPTG/X-Gal agar plate. All reagents and vectors were purchased from TaKaRa corp. Sequencing reactions were performed by the Shanghai Invitrogen Co., Ltd. At least two recombinant plasmid sequences were 100% matching, so the nucleotide sequence of target fragment was finally confirmed.
-
The DNA sequences were analysed using the DNAStar sequence analysis software (version 7.0). One complete open reading frame (ORF) was found, hence P1 and P2 (Table 1) were used to amplify the only complete ORF of the DEV UL4 gene. The PCR product was cloned into pMD18-T as described above.
-
Comparison and phylogenetic analysis of the nucleotide sequences and deduced amino acids of the DEV UL4 gene with those of other herpesviruses (Table 3) were performed with DNAStar and BLAST. Phylogenetic analysis was performed using the MegAlign program in Lasergene (DNAStar 7.0) with Clustal Ⅴ multiple alignment and weight matrix PAM250 of sixteen reference strains of alphaherpesvirus (Table 3), reliability of the tree was assessed by bootstrap analysis with 1000 replicates.

Table 3. Reference sequences of alphaherpesviruses used for comparison and phylogenetic analyses
Virus strain
DNA extraction
Primers for PCR
PCR
Sequencing
Cloning of the UL4 complete ORF
Sequences analysis of the DEV UL4 gene
-
Primers SP1 and DP1 were predicted to amplify an approximately 2 000 bp product of DEV DNA. A 2.0 kb DNA product was observed after electrophoresis of the PCR products. The product was 2 086 bp in size and included a complete UL4 sequence which was determined to be 714 bp in size. The complete sequence of the DEV vaccine strain UL4 gene was submitted in the GenBank Database with accession number EF554397. Using primers P1 and P2, that were specific to UL4 gene of DEV, a PCR product of 714 bp was amplified and cloned into pMD18-T. The constructed recombinant plasmid, designated pMD18-T-UL4, was used as a template to determine the UL4 gene sequence.
-
Sequence analysis indicated that the nucleotide sequence of the entire UL4 gene ORF was 714 bases in length and had a base composition of 200 adenine (28.01%), 149 cytosine (20.87%), 165 guanine (23.11%), 200 thymine (28.01%), and a GC content of 43.93%. Sequence comparison with other herpesviruses revealed that the nucleotide sequence of the DEV UL4 gene was similar to those of other herpesviruses, having a homology of 25.1% with BHV-1, 27.7% with EHV-1, 26.5% with HSV-1, 21.0% with HHV-3, 35.3% with GaHV-2, 35.3% with MeHV-1, 23.3% with PRV, and 29.8% with ILTV. The DEV UL4 ORF was deduced to encode 237 amino acids. The encoded protein shared a 25.4% amino acid identity with BHV-1, 28.0% with EHV-1, 25.6% with HSV-1, 17.2% with HHV-3, 34.5% with GaHV-2, 33.9% with MeHV-1, 24.8% with PRV, and 25.3% with ILTV.
To analyze the phylogenetic relationships of UL4 with other herpesviruses (Table 3), we constructed a phylogenetic tree using the UL4 protein sequences. A representative minimal tree for the UL4 is shown in Fig. 2. The seventeen herpesviruses were classified into four major groups with each representing a genus.The Simplexvirus genus consisted of HSV-1, HHV-2, CeHV-1, CeHV-2 and CeHV-16. The Varicellovirus genus consisted of BHV-1, PRV, EHV-4, EHV-1, BHV-5 and HHV-3. The Mardivirus genus consisted of GaHV-2, GaHV-3, MeHV-1 and had the closest evolutionary relationship with DEV. The Iltovirus genus (ILTV) branched as an independent group.
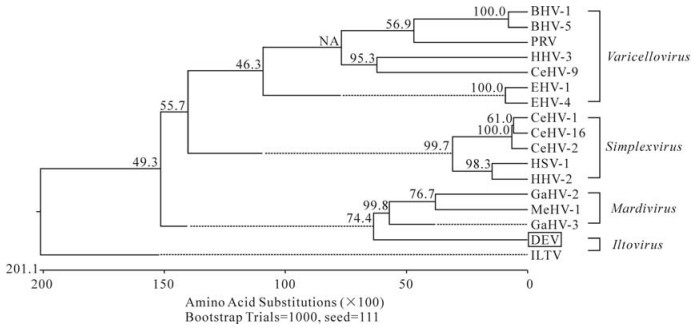
Figure 2. Phylogenetic relationships of the DEV UL4 proteins within the subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae. The phylogenetic relationships were estimated by using the Clustal Ⅴ method. Sequence distance indicated by the scale was calculated using the PAM250 matrix in Lasergene. Reliability of the tree was assessed by bootstrap analysis with 1000 replicates.
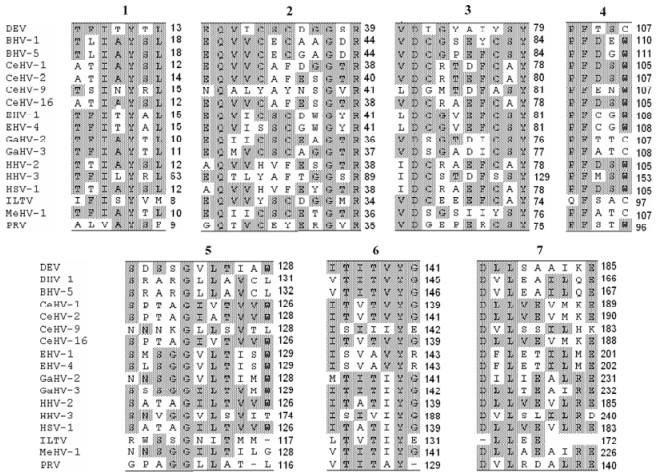
The UL4 amino acid sequence comparison of DEV with those of other alphaherpersviruses resulted in identification of ten highly conservative amino acid residues (Y11, Q29, G37, R39, D71, Y79, F104, G122, Y140, L206) in seven consensus regions of alphaherpesvirus UL4, although these regions have not been annotated functionally (Fig. 3).
Cloning of DEV UL4 gene
Sequence analysis
-
The presence of UL4 gene is reported in the genomes of a number of members of subfamily Alphaherpesvirinae (4, 5, 8, 16, 20, 21), but the corresponding gene in DEV has not yet been reported. The present study reported the characterization of the DEV UL4 gene from a DEV Chinese vaccine strain. In this study a method to clone the DEV UL4 gene was established and can be used as a more rapid and effective method to clone a new member of gene family in comparison with previous methods. The high fidelity of the Taq enzyme (TaKaRa Ex TaqTM) was also used to decrease the error rate of the PCR in this report.
Comparative analysis of viral protein sequences of alphaherpesvirus showed that the UL4 protein sequence is not highly conserved as the viruses evolve. The sequences of the UL4 proteins of DEV and GaHV-2 exhibit an identity of 34.5%, whereas the UL4 sequence identity to other alphaherpesviruses was much lower. Alignment of DEV UL4 protein sequence with other alphaherpesviruses showed that the C-terminal amino acids of UL4 is highly variable (Fig. 4), suggesting that it is likely related to host specificity of alphaherpesviruses and evolutionary relationship amongst the viruses. For example, Simplexvirus consists of CeHV-1, CeHV-2, CeHV-16, HSV-1, and HHV-2 which obviously differ from other alphaherpesviruses in C-terminal amino acids of UL4. Likewise, CeHV-1, CeHV-2, and CeHV-16 differ from HSV-1 and HHV-2 which infect cercopithecine and human, respectively. So the evolutionary relationship of UL4 could be used as an important basis for classification of alphaherpesviruses.
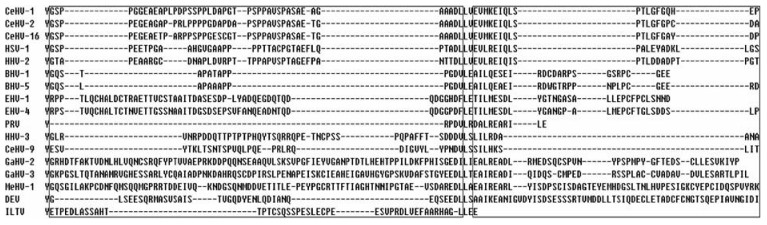
Figure 4. The diversity in the C-terminal amino acids of UL4 among 17 alphaherpesviruses. Highly variable regions were boxed. Alignment of UL4 protein sequences was performed using DNAStar 7.0.
Alphaherpesviruses are classified into four genera: Simplexvirus, Varicellovirus, Mardivirus, and Iltovirus (15). DEV is an alphaherpesvirus, and the genus it should belong to has not yet been determined. In this study its evolutionary relationship was analyzed by construction of a phylogenetic tree. The UL4 gene selected for the analysis formed four groups of evolutionarily related viruses. The UL4 of duck enteritis virus formed a separate cluster that branched from the group comprising GaHV-2, GaHV-3 and MeHV-1. This classification indicated that duck enteritis virus has a higher genetic relationship to members of the Mardivirus genus (GaHV-2, GaHV-3 and MeHV-1) than to other herpesviruses, and coincided with the fact that all these four viruses circulate naturally in avian species, suggesting that GaHV-2, GaHV-3, MeHV-1 and DEV may came from a common ancestor in the evolution.
In conclusion, the present study reports the initial characterization of the DEV UL4 gene of DEV and sequence analysis indicates that GaHV-2, GaHV-3, MeHV-1, and DEV are closely related. A more extensive study incorporating a broader set of gene sequences and more viral species need to be performed to achieve a more accurate DEV classification.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: