HTML
-
2 billion people have been infected with hepatitis B virus (HBV) worldwide, of whom about 400 million developed chronic infection. Chronic HBV infection is a major public health problem. Every year, approximately 1 million patients die due to the acute or chronic consequences of hepatitis B, such as liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
HBV is a DNA virus which belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family. The viral particle is a spherical structure consisting of an outer envelope and an inner nucleocapsid. The host-derived outer envelope is composed of proteins (hepatitis B surface antigen, HBsAg), lipids and carbohydrates. The nucleocapsid is formed from hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg), within which is the double stranded DNA viral genome (Blum H E, et al., 1989). The HBV genome has four partially overlapping open reading frames encoding seven viral proteins: HBsAg (L, M, S), HBcAg, HBeAg, HBxAg and HBV polymerase (Dandri M, et al., 2012).
Exposure to HBV leads to either acute resolving HBV infection or chronic HBV infection. The chronic HBV infection is serologically defined as the presence of HBsAg in the serum for more than 6 months. 95% of infection acquired as adult result in spontaneous clearance, whereas more than 90% of infected neonates develop chronic infection (Ganem D, et al., 2004; Liang T J, 2009). The clearance of HBV relies on a potent and diverse T cell immune response, but how a favorable response is generated in an infected individual remains largely unknown (Chisari F V, et al., 2010).
The methods of chronic HBV infection treatment have been improved greatly over the past few decades. There are two types of antiviral therapies currently available for chronic HBV: (1) pegylated interferon alpha (PEG-IFNα) and (2) nucleot(s)ide analogues (NA), such as lamivudine and entecavir (ETV). However, treatment with PEG-IFNα is associated with side effects and leads to a sustained antiviral response in only about 30% patients. Although treatment with NA improves the clinical condition of chronic HBV patients, it is hampered by rebounding viremia after cessation of antiviral therapy and emergence of drug resistance mutations (Locarnini S, et al., 2006; Wu C, et al., 2012; Zoulim F, et al., 2009). Therefore, alternative strategies for the chronic HBV infection treatment are needed.
The immune responses of the host determine the outcome of HBV infection. A strong, multi-specific T cell response to HBV antigens is essential for the clearance of hepatitis B. Depletion of CD8 T cells in chimpanzees during acute HBV infection results in the persistence of the viremia (Thimme R, et al., 2003). In contrast, persistent HBV infection is associated with functional exhaustion of virus-specific CD8 T cells (Jung M C, et al., 1991; Penna A, et al., 1991; Rehermann B, et al., 2005; Yang P L, et al., 2010). Results of these studies gave the fundaments of the therapeutic vaccination trials that would elite the virus-specific immune responses and hence overcome the persistence of HBV. In this review, we would like to describe new therapeutic vaccination strategies to treat chronic hepatitis B which may be introduced for patient treatment in the future.
-
Most of the clinical trials of therapeutic vaccination for chronic HBV were designed based on using the conventional prophylactic HBsAg vaccines. Many of these trials achieved HBeAg seroconversion, induction of HBV-specific immune responses and decrease of viral load in patients. However, the antiviral effect of conventional HBsAg-based vaccine was only transient and could not lead to an effective control of viral replication (Couillin I, et al., 1999; Dikici B, et al., 2003; Jung M C, et al., 2002; Pol S, et al., 1994; Pol S, et al., 2001; Ren F, et al., 2003; Safadi R, et al., 2003; Yalcin K, et al., 2003).
The therapeutic vaccination based on immunogenic complexes (IC) which are composed of HBsAg and human anti-HBs was proposed by Wen et al. (Wen Y M, et al., 1995). IC can increase the uptake of HBsAg by APCs and thus stimulate robust T cell responses. It was demonstrated that IC vaccine led to HBeAg seroconversion, anti-HBs development and decrease of viral load in part of the HBeAg-positive patients (Yao X, et al., 2007). In a following phase Ⅱ B clinical trial, the IC-based vaccine led to HBeAg seroconversion in about 21.8% of treated patients (6 vaccinations). However, moderate levels of serum HBV DNA and HBsAg levels were still observed 24 weeks after treatment (Wang X Y, et al., 2010; Xu D Z, et al., 2008). Very recently, the results of phase Ⅲ clinical trial failed to show the therapeutic efficacy of IC-based vaccine when compared to the placebo control (alum). 12 injections of IC complex resulted in a decrease of the HBeAg seroconversion rate from 21.8% to 14.0%. Surprisingly, an increase of the HBeAg seroconversion rate from 9% to 21.9% was observed in the alum group (Xu D Z, et al., 2013).
Compared to the conventional vaccines, DNA vaccines can induce a wider range of immune response types. Therefore, several phase Ⅰ clinical studies were conducted to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of plasmid DNA vaccines expressing HBsAg in chronic HBV carriers. These studies showed evidences for the safety of HBV-DNA vaccination. They demonstrated that DNA vaccination can restore or elite T cell responses. However, DNA vaccines expressing only HBsAg did not result in significant suppression of viral replication (Mancini-Bourgine M, et al., 2006; Mancini-Bourgine M, et al., 2004).
According to the results of these studies, it seems that the therapeutic vaccination alone is not sufficient to achieve the control over HBV. High load of virus may be responsible for the immune tolerant status in the patients. Therefore, additional treatment such as nucleos(t)ide analogues treatment has been combined with vaccination to achieve better therapeutic efficacy.
-
Previous studies have already confirmed that the presence of high viremia may result in more profound inhibition of HBV-specific T cell function (Boni C, et al., 2007; Maini M K, et al., 2000; Webster G J, et al., 2004). Therefore, when viral load is high and T cell dysfunction is severe, therapeutic vaccination alone can not induce a strong HBV-specific T cell response. In line with this, studies have showed that lamivudine treatment could restore T cell responsiveness in chronic HBV patients (Boni C, et al., 1998; Boni C, et al., 2003). Thus, it is generally assumed that using antiviral treatments to reduce HBV viral load may facilitate the induction of HBV-specific immune responses by therapeutic vaccinetions.
-
Several studies in woodchuck hepatitis virus (WHV) infected woodchuck model have been conducted to examine the feasibility of combinating NA treatment and therapeutic vaccination. In a combination therapy of lamivudine treatment and serum-derived WHsAg vaccination, WHV-specific T-helper responses and Th0/Th1 cytokines production were induced in chronically WHV infected woodchucks. However, combination therapy showed no effect on viremia reduction or anti-WHs antibodies induction (Hervas-Stubbs S, et al., 2001). Our group also evaluated the efficacy of the combination therapy in the woodchuck model by combining lamivudine treatment, DNA vaccination and IC vaccination. In this study, lamivudine treated chronic WHV carriers were immunized with pWHsIm (plasmid expressing WHsAg) and WHsAg-anti-WHsAg complex. In comparison to control woodchucks (lamivudine treatment alone), woodchucks received additional vaccinations showed a further decrease of serum WHV DNA and WHsAg concentrations, and some of the vaccinated carriers developed anti-WHs antibodies (Lu M, et al., 2008). Further, we modified this protocol by using another antiviral drug ETV and increasing the number of the immunizations (Lu et al. unpublished results). Chronic WHV carriers were treated with ETV and then received six times of DNA vaccinations (plasmids expressing WHsAg and WHcAg). ETV potently suppressed WHV replication in the treated carriers, but the rebound of WHV viremia took place immediately after the cessation of ETV treatment. In contrast, a significant delay of the rebound of viremia was observed in woodchucks which received additional vaccination. This result indicated that combining therapeutic vaccination with potent antiviral drugs such as ETV may lead to a prolonged control of viral replication. In another study, chronic WHV carriers received a treatment of the potent antiviral drug clevudine in combination with an alum-adsorbed WHsAg vaccine. Combination treatment resulted in significant and sustained reduction of WHV DNA loads and WHsAg concentrations in most treated animals. Compared to vaccination alone, combination treatment induced more robust anti-WHs response (Menne S, et al., 2002; Menne S, et al., 2002). In addition, the combination therapy delayed the occurrence of disease progression. The results of these studies support the idea that the combination of NA treatment and vaccination is more effective in inducing virus-specific T cell responses than therapeutic vaccination alone.
-
However, the results of clinical trails of combining antiviral treatment and HBsAg vaccinations were somehow disappointing. In an open-labeled trial, chronic HBV patients received lamivudine treatment and 6 times of HBsAg vaccinations together with daily Interleukin-2 (IL-2) treatment. After the end of therapy, 7 of 9 vaccine/lamivudine and 2 of 5 vaccine/lamivudine/IL-2 patients showed no detectable HBV DNA. Combination therapy induced low frequencies of B cells producing anti-HBs and HBV specific T helper cells producing IFN-γ. Transient induction of HBV-specific cytotoxic T cells was also observed in some patients (Dahmen A, et al., 2002). In another clinical trail which enrolled 72 patients with chronic HBV infection, all patients received lamivudine treatment, and 15 of them (9 HBeAg+ and 6 HBeAg-) were also received an intradermal HBsAg vaccine (combination therapy). 12 months after the start of therapy, all HBeAg+ patients received combination therapy in contrast to 48% of HBeAg+ CHB patients received lamivudine monotherapy became serum HBV DNA negative. The rate of HBeAg seroconversion was also significantly increased in patients received combination therapy (56% combination therapy vs 16% lamivudine monotherapy). Moreover, no virological breakthrough of HBV was observed in any patient received combination therapy (Horiike N, et al., 2005). However, the results of another open label, controlled, randomized study which enrolled more patients were disappointing. In this study, 195 HBeAg+ patients were either received lamivudine monotherapy or combination therapy (lamivudine plus HBsAg vaccine). Although the combination therapy induced a vigorous HBsAg-specific lymphoproliferative response, this therapy did not improve the HBeAg seroconversion rate in the patients (Vandepapeliere P, et al., 2007).
Preclinical studies
Clinical trails
-
The results of previous therapeutic vaccination trials in animal models and patients indicate that the conventional prophylactic HBsAg vaccines can not elicit a functional antiviral T cell response. Therefore, strategies using more effective vaccines are needed. Vaccines using live attenuated virus have gained a great attention because of their ability to stimulate a broad and sustained immune response. Recombinant viral vectors that express heterologous antigens have been extensively investigated in the development of novel vaccines against many human infectious diseases (Paoletti E, 1996; Perkus M E, et al., 1985; Robinson H L, 2002; Tatsis N, et al., 2004). The possibility and efficacy of using these recombinant viral vaccines for chronic HBV infection treatment were also investigated by us and others.
Promising results were obtained from a study performed in the chimpanzee model (Sallberg M, et al., 1998). In this study, in total three chronically HBV-infected chimpanzees were immunized with recombinant retroviral vector expressing HBcAg and one of them showed HBeAg seroconversion and cleared the virus. Significant ALT elevation was observed in this chimpanzee, which indicated the restoration of HBV-specific cytotoxic T cell functions. Besides, the other two chimpanzees showed increasing anti-HBe titers after the vaccination and one of them developed HBcAg-specific cytotoxic T cell response. This study for the first time demonstrates the safety and the therapeutic benefits of using the recombinant viral vectors for the chronic HBV infection treatment in primates.
Very recently, our group has also examined whether potent and functional T-cell responses could be elicited with a DNA prime-recombinant adenoviruses (AdVs) boost vaccination strategy. By using a newly developed DNA plasmid (pCGWHc) which can more efficiently express WHcAg, we induced potent WHcAg-specific CD8 T-cell responses in mice. Moreover, boost immunization with recombinant AdVs expressing WHcAg resulted in more vigorous and functional T cell responses than immunization with pCGWHc alone. The pCGWHc plasmid or AdVs vaccination in woodchucks elicited a strong WHcAg-specific T cell response, which led to an effective control of WHV infection after virus challenge (Kosinska A D, et al., 2012). We also investigated the therapeutic effect of this prime-boost strategy in woodchucks with chronic WHV infection in combination with ETV treatment. The combination therapy elicited functional WHsAg-specific and WHcAg-specific T-cell responses and led to a prolonged suppression of WHV replication in treated woodchucks. Two of four woodchucks that received the combination therapy developed anti-WHs antibodies and cleared the virus (Kosinska A D, et al., 2012). This DNA prime-AdVs boost strategy has been further applied for the prevention of HDV infection, and we could demonstrate that the vaccination protected woodchucks from HDV infection in the setting of simultaneous challenge woodchucks with WHV and HDV (Fiedler M, et al., 2013). These results demonstrate that by using recombinant viral vectors, the prime-boost strategy can efficiently induce sustained and functional immune responses to control chronic WHV infection in woodchucks and may be a promising therapeutic strategy for chronic HBV patients.
-
Recent studies in chronic virus infection models indicate that the interaction between the inhibitory receptor programmed death-1 (PD-1) and its ligands plays a critical role in T cell exhaustion (Barber D L, et al., 2006; Finnefrock A C, et al., 2009; Maier H, et al., 2007; Velu V, et al., 2009). In many human chronic infections, including HBV, upregulation of PD-1 on virus-specific T cells was observed, and restoration of the T cell function has been achieved by blocking the PD-1/PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) interaction in vitro (Boni C, et al., 2007; Day C L, et al., 2006; Freeman G J, et al., 2006; Penna A, et al., 2007; Petrovas C, et al., 2006; Pilli M, et al., 2007; Trautmann L, et al., 2006). Moreover, in vivo blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in mice persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) successfully restored the antiviral function of exhausted virus-specific T cells, and hence improved the effect of the therapeutic vaccination (Barber D L, et al., 2006; Ha S J, et al., 2008).
In line with these findings, we designed a triple combination therapy strategy combined of antiviral treatment, therapeutic vaccination and PD-L1 antibody blocking to investigate whether in vivo blockade of the PD-1 pathway enhances virus-specific T cell immunity and leads to the resolution of chronic hepadnaviral infection in the woodchuck model. The antiviral drug ETV was administered for 28 weeks to suppress the WHV replication. Starting from week 12, animals received subsequently 12 intramuscular immunizations with DNA plasmids, expressing WHV core antigen (WHcAg) and surface antigen (WHsAg). For PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade, woodchucks were treated with rabbit polyclonal PD-L1 blocking antibody (αPD-L1) 3 times in week 24. In vivo blockade of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway on CD8 T cells, in combination with ETV treatment and DNA vaccination, synergistically enhanced the function of virus-specific T cells. Moreover, the combination therapy potently suppressed WHV replication, leading to sustained immunological control of viral infection, anti-WHs antibody development and complete viral clearance in some woodchucks (PLoS Pathgens, in press). Our results provide a new approach to improve T cell function in chronic hepatitis B infection, which may be used to design new immunotherapeutic strategies in patients.
The negative regulation of T-cell function involves numerous receptor and ligand interactions in separate cellular compartments at different phases of the immune response. Recent studies have suggested that multiple inhibitory receptors, such as CTLA-4 (Schurich A, et al., 2011), TIM-3 (Wu W, et al., 2012) and LAG-3 (Li F J, et al., 2013), have played important roles in T-cell exhaustion during persistent HBV infection. These observations suggest that there may be a synergy in blockade of various inhibitory pathways and encourage the examination of combinatorial strategies for treatment of woodchucks with chronic WHV or to later patients with chronic HBV in the future.
The current progress on therapeutic vaccination indicates the feasibility of this regimen for chronic HBV infection treatment. However, as more and more vaccine formulations become available, a crucial question is raised: what is the optimal scheme of the therapeutic strategy? According to the studies reviewed above, it seems the following steps should be taken to achieve a potent therapeutic vaccination: (1) Reducing viral load by antiviral treatment; (2) Inducing antiviral T cell and/or B cell responses by vaccinations; (3) Combining immunomodulation methods to amplify and maintain the T cell functions (Figure 1). In addition, proper design of antigens for vaccination is also important for the development of an effective regimen of immune therapy against HBV. It has been noticed that satisfactory therapeutic effects could not be documented in the studies using HBsAg-based prophylactic vaccines. In the mean time, evidence has supported that HBcAg-specific immunity is endowed with antiviral and liver protecting capacities in CHB patients and animal models. Therefore, which factors influence the effect of therapeutic vaccination remains to be investigated. Better understanding of these issues will be helpful for the translation of recent progress made on therapeutic vaccination for clinical applications.
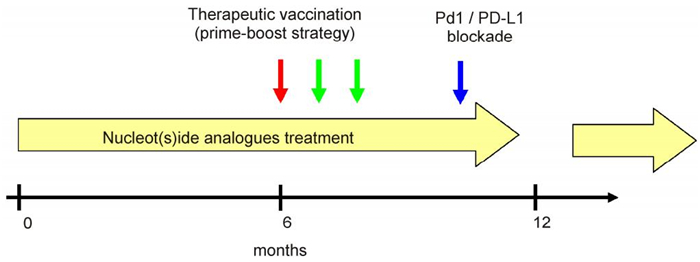
Figure 1. The perspective of an optimal scheme for the therapeutic vaccination in chronic HBV.This triple combination therapy strategy includes: (1) Administration of nucleot(s)ide analogues to suppress HBV replication (indicated by yellow arrows); (2) Performing therapeutic vaccination to induce antiviral immune responses at appropriate time points (indicated by red and green arrows); (3) Using immunomodulation methods such as PD-1/PD-L1 blockade to amplify and maintain the antiviral responses (indicated by blue arrow).
-
We thank the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (TRR60 and GK 1045/2), National Major Science and Technology Project for Infectious Diseases of China (2008ZX10002-011, 2012ZX10004503), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30271170, 30571646, 81101248) and the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2011DFA31030) for supporting some of the work in the review.
-
J Liu and M Roggendorf wrote the manuscript. A Kosinska and M Lu helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: