HTML
-
Eukaryotic cells are exposed to many environmental conditions that can elicit severe stress, including damage to the genetic material. DNA damage includes a wide variety of lesions, including but not limited to: oxidation, single-nucleotide mismatches, single-stranded breaks(SSBs), double stranded breaks(DSBs), and stalled replication forks which can lead to DNA damage(Luftig, 2014). DNA damage can be caused by external factors such as irradiation and chemotoxins as well as internal factors such as errors during DNA replication or cellular metabolism. Each cell is estimated to undergo 104 spontaneous DNA lesions per day(Hoeijmakers, 2009), but fortunately, multiple mechanisms are in place to rectify different types of DNA damage: mismatch repair(MMR) for nucleotide mismatches; base excision repair(BER) to remove chemically damaged nucleotides; nucleotide excision repair (NER) for the removal of more severe chemical modifications such as crosslinks; non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) and homologous recombination(HR) to repair DSBs(Ciccia and Elledge, 2010). Repairing DNA damage through these different mechanisms first requires the recognition of damage and activation of the DNA damage response(DDR) pathways.
DDR pathways have evolved to alleviate the cell of DNA damage and allow continued replication and cell survival or to target the cell for apoptosis or senescence if the damage is irreparable. DDR is coordinated by two major phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinases(PIKKs): ataxia telangiectasia mutated(ATM) and ATM-and Rad3-related(ATR). Different types of DNA damage are recognized by various DNA binding proteins that signal the appropriate PIKK(Figure 1). DSBs, for instance, are recognized by the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1(MRN) complex, which in turn recruits ATM. Single-str and lesions are recognized by replication protein A(RPA), which recruits ATR-interacting protein(ATRIP) and ATR(Ciccia and Elledge, 2010). Although the ATR and ATM pathways are activated by different proteins, some of the downstream kinases and cellular proteins are shared amongst these two PIKK pathways. For example, both ATM and ATR can tar-get checkpoint proteins(such as Chk1 and Chk2) and p53 (Figure 1). DDR pathways contain both unique and overlapping members including numerous binding proteins, signaling proteins, and repair enzymes.
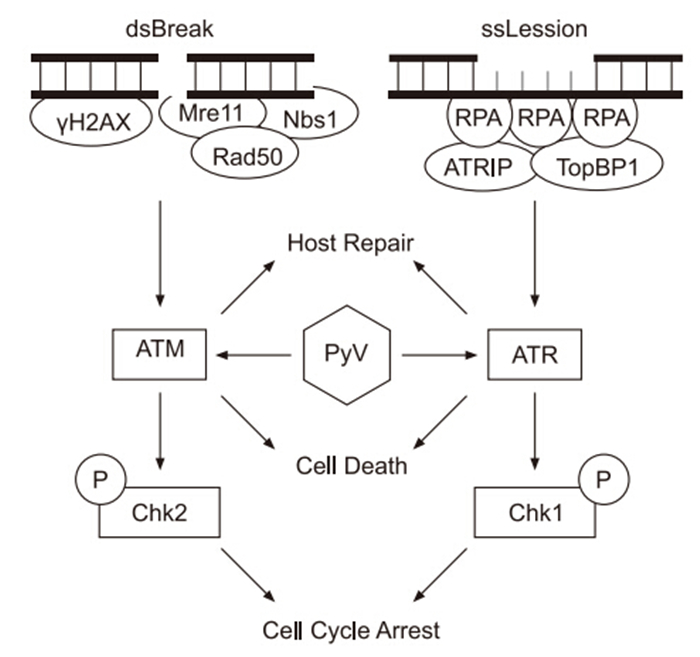
Figure 1. Simplified concept map of ATM and ATR DNA damage response. ATM is recruited to DSBs sensed by the MRN complex(Mre11, Nbs1, Rad50) and marked with γH2AX. ATM then mediates DNA repair while activating Chk2, which arrest the cell cycle. ATR is activated by RPA coated ssDNA lesions by accessory factors. Once activated it mediates DNA repair while simultaneously arresting the cell cycle through Chk1. Both ATM and ATR can, in the event of ineffective repair, induce cell death. PyV infection activates both ATM and ATR, although the mechanism and downstream consequences of this activation are under investigation.
In 2002 it was reported that adenovirus early protein E4 disrupts the ATM pathway by degrading or reorganizing the MRN complex(Stracker et al., 2002). When both of E4 open reading frames 3 and 6 are deleted or mutated, the linear viral DNA is recognized as damaged DNA by the MRN complex and is repaired to form viral DNA concatemers that are too large to be packaged into virions. This discovery led to a new direction in studying the host DDRs in the context of viral replication. For many viruses, it was already known that viral genome replication and propagation is dependent on the host cell. However, until the adenovirus discovery it was uncertain that the DDR pathways were also involved in viral genome integrity and viral replication.
Now, it is well established that the DDR pathways are crucial especially for DNA virus replication. For some DNA viruses such as adenovirus, DDR proteins would intrinsically sense viral DNA as damaged DNA and attempt to repair the damage, which must be overcome to allow for virus propagation. For other viruses including herpesviruses and parvoviruses, viral DNA can activate DDRs as well as recruit DDR proteins including ATM and ATR to replication centers(Lilley et al., 2011; Luo and Qiu, 2013). Activation of DDRs also leads to cell cycle arrest or apoptosis; however, viruses have come up with multiple ways to circumvent the cell cycle checkpoints and utilize DDRs for both replication and genome maintenance(Luftig, 2014). For example, many viruses have evolved to target p53 for degradation(human papillomavirus(HPV), hepatitis B virus(HBV), adenovirus) (Luftig, 2014) or to inactivate p53(polyomavirus)(An et al., 2012) to prevent apoptosis before completion of viral replication. Furthermore, the activation of DDRs by virus infection and replication has led to many avenues of research in order to gain understanding of virus-host interactions as well as host and viral DNA replication. In this review the focus will be the interactions of PyVs and the host, specifically the DDRs.
-
Polyomaviruses(PyVs) are non-enveloped viruses composed of small, circular genomes of approximately 5 kb. The genome is separated into three regions: non-coding control region(NCCR), late region(expressing capsid proteins VP1, VP2, VP3), and the early region (expressing T antigens). The late coding region has also been found to express a multi-functional agno protein in some PyVs and /or VP4 which is suspected to act as a viroporin(Raghava et al., 2011; DeCaprio and Garcea, 2013). There are at least 13 human PyVs with the expectation of more to be discovered(Yu et al., 2012; Moens et al., 2014). The best characterized human polyomaviruses include BK polyomavirus(BKPyV), JC polyomavirus(JCPyV), and Merkel Cell polyomavirus(MCPyV) (DeCaprio and Garcea, 2013; Pinto and Dobson, 2014). BKPyV and JCPyV are found in the majority of the adult population as latent infections acquired in childhood and reside in the genitourinary tract(BKPyV and JCPyV) and bone marrow and brain(JCPyV)(Pinto and Dobson, 2014). For healthy individuals, the latent infection typically does not present itself clinically. However, both viruses can transition from a latent to a lytic infection. This transition occurs for BKPyV when a patient becomes immunosuppressed and can cause severe disease including hemorrhagic cystitis in bone marrow transplant recipients and polyomavirus-associated nephropathy(PVAN) in kidney transplant patients. JCPyV is also associated with immunosuppressed patients, such as those with HIV/AIDS and those with autoimmune diseases undergoing certain immunosuppressive therapies. JCPyV reactivation into the lytic phase can give rise to progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy(PML), a fatal demyelinating disease. Although PyVs are considered oncogenic due to the transformation properties of the large T antigen(TAg), a multifunctional protein encoded by the early region of PyVs, thus far only MCPyV is clearly associated with human cancer(Gjoerup and Chang, 2010; Li et al., 2013). Over 80% of Merkel Cell Carcinomas (MCC) contains the MCPyV genome integrated into the host genome(Feng et al., 2008; Kassem et al., 2008). Similarly though, MCPyV has a latent stage wherein it is considered part of the healthy epithelial microbial population. The transition from latent to lytic stage of the PyV life cycle is not well understood. Therefore the research done to further underst and the host-virus interactions, particularly in terms of DNA replication, is of necessity.
Much of the understanding of PyV replication comes from work that has been done with the simian virus 40 (SV40). SV40 was first identified and discovered as a contaminant in polio vaccines(Sweet and Hilleman, 1960; Garcea and Imperiale, 2003) and since has been used to study both virus and host DNA replication and other cellular processes, yielding a greater understanding of many aspects of current molecular biology. The replication forks of SV40 contain many host proteins that are also found at replication forks of the host(Sowd et al., 2013). In addition to being a good model for DNA replication, SV40 shares approximately 70% of genome homology with human PyVs therefore yielding a general model for PyV replication(Pinto and Dobson, 2014). In this review, we will focus on the PyV activation and interactions with host DDRs with an emphasis on the ATM and ATR pathways.
-
Evidence for a significant role of the ATM-and ATRmediated DDRs during PyV infection exists across the family. One of the first indications that ATM may be a factor during infection is mouse polyomavirus(mPyV) induced phosphorylation of p53 at Ser15, which is normally associated with ATM kinase activity(Dey et al., 2002). Similarly, a role for the ATR kinase was first implied by observing that SV40 infection induces Chk1 phosphorylation, which is downstream of ATR activation, and subsequent G2 arrest(Okubo et al., 2003). Continued research into these host-pathogen interactions has revealed that members of the family Polyomaviridae universally activate the ATM and ATR DDRs(Okubo et al., 2003; Dahl et al., 2005; Shi et al., 2005; Hein et al., 2009; Boichuk et al., 2010; Orba et al., 2010; Rohaly et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Sowd et al., 2013; Tsang et al., 2014).
Exactly how PyVs induce host DDR is currently under investigation. Upon infection, TAg, the major viral regulatory protein, binds to the tumor suppressor protein Retinoblastoma(pRb)(Dey et al., 2002). TAg binding to pRb relieves pRb inhibition of the G1/S transition and S-phase-associated transcription factor, E2F. This allows E2F to induce expression of proteins needed for replication(including proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), DNA polymerase α and δ) as well as DDR proteins such as ATR, ATM and associated factors(Bracken et al., 2004). Thus, PyV begins to modulate the host environment and interact with host DDRs at the level of transcriptional upregulation. Supporting this, microarray analysis reports an upregulation of DDR protein expression in primary human renal epithelial cells infected with BKPyV(Abend et al., 2010)
Deregulation of host protein expression, particularly regarding DDR, is important for engineering a host environment favorable for PyV infection; however, upregulation of DDR proteins alone does not explain their activation during PyV infection. In the context of PyV infection, three possibilities arise that may contribute to DDR activation: 1) interaction of viral proteins with host proteins, 2) interaction of viral proteins with viral or host DNA or 3) viral replication itself. It appears that expression of TAg alone is sufficient to activate ATM-and ATR-mediated DDRs—at least in the case of SV40(Hein et al., 2009), JCPyV(Orba et al., 2010), and MCPyV(Tsang et al., 2014). In SV40 it was found that activation of the ATM-and ATR-mediated DDRs is dependent upon TAg binding to Bub1, a spindle assembly checkpoint kinase(Hein et al., 2009). In addition, it seems that TAg interaction with DNA, be it viral or host, also contributes to DDR activation. TAg contains three primary domains that interact with DNA: 1) a viral origin of replication(ori) binding domain, 2) a helicase domain and 3) a non-specific DNA binding domain. Mutagenesis of the JCPyV TAg designed to increase TAg ssDNA binding affinity greatly enhances its ability to induce cell cycle arrest and to trigger DDR through ATM and ATR(Orba et al., 2010). Consistently, DNA binding deficient TAg mutations attenuated DDR activation and G2 arrest(Orba et al., 2010; Verhalen et al., 2015). These data suggest that PyV TAg interaction with DNA is important for DDR activation. Several cases have also been made supporting that viral DNA replication is essential for host DDR activation. MCPyV TAg helicase mutants show somewhat reduced ability to activate Chk1(Li et al., 2013). BKPyV mediated DDR activation seems to be viral DNA synthesis dependent as neither Tag expression alone nor infection with a replication deficient virus was sufficient to activate DDR in primary renal proximal tubule epithelial cells(Verhalen et al., 2015). Supporting these findings, SV40 TAg helicase mutants and replication deficient viral origin mutants were shown to have severely lowered ATM and ATR activation(Sowd et al., 2013). All things taken together, it seems that the induction of DDR is a complex event dependent upon multiple interactions between the viral proteins and cellular factors as well as PyV replication itself, and it may also be cell type dependent(See Table 1 for a summary).

Table 1. Comparison of polyomabirus-induced cell cycle arrest, genomil instability and DDR activation induced by TAg expression alone.
-
There is growing evidence that many DNA viruses replicate in specific intracellular sites termed replication factories that are dedicated to viral replication and assembly(Novoa et al., 2005; Wileman, 2007; Erickson et al., 2012). These centers contain the viral genome, viral proteins, and certain host factors that contribute to a successful viral replication(Erickson et al., 2012) and can be easily visualized in certain PyV infections as punctate foci through TAg immunofluorescence staining. While not observed or investigated in all species of PyVs, these foci have been seen during infection with SV40, JCPyV and MCPyV(Shi et al., 2005; Zhao et al., 2008; Boichuk et al., 2010; Orba et al., 2010; Erickson et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013; Sowd et al., 2013; Tsang et al., 2014).
In SV40, replication foci often contain phosphorylated H2AX(γH2AX), which is associated with DSBs. More detailed analyses have shown recruitment of several DDR components into these foci including: components of the MRN complex, FANCD2, RPA32, TopBP1, ATM, DNA polymerase α, ATR, ATRIP, Chk1, and Chk2(Shi et al., 2005; Zhao et al., 2008; Boichuk et al., 2010; Sowd et al., 2013). JCPyV and MCPyV demonstrate a similar phenotype with clear accumulation of many proteins associated with DDR in nuclear foci(Orba et al., 2010; Erickson et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013; Tsang et al., 2014). In a comprehensive investigation of MCPyV replication foci, it was observed that TAg and the viral origin of replication mediate accumulation of DDR factors at sites of active DNA synthesis based on BrdU staining (Li et al., 2013). Moreover, it was shown that these DDR foci coincide with viral DNA visualized by fluorescence in situ hybridization(FISH). It was then convincingly shown that formation of these foci is dependent upon active viral replication comparing TAg helicase mutants to wild type virus. Whereas activation of the host DDR is partially mediated by TAg, as discussed above, formation of DDR foci appears to be dependent upon the interaction of several viral factors all leading to active viral DNA synthesis(Li et al., 2013).
Interestingly, it was reported that ATM inhibition is sufficient to prevent the formation of discrete nuclear foci of both TAg and γH2AX during SV40 infection (Zhao et al., 2008) and that both ATR and ATM siRNA knockdowns reduce the abundance of replication foci during MCPyV infection(Tsang et al., 2014). In SV40 at least one functional consequence associated with loss of replication foci is diminished degradation of the MRN complex(Zhao et al., 2008). Degradation of the MRN complex, and its component proteins, may allow TAg to reinitiate DNA synthesis, which is normally inhibited by cellular licensing mechanisms. Inactivation of this complex is, in fact, associated with higher incidence of polyploidy in host cells infected with SV40(Wu et al., 2004). An intriguing sub-function of these replication foci may be that they are required to target the MRN complex to the CUL7 ubiquitin ligase; however, the implications of these findings are complicated by the observation that other PyVs do not degrade MRN but induce polyploidy (Jiang et al., 2012). Ultimately the activation, coordination, and accumulation of DDR factors to sites of viral replication may be a result of cooperation between viral replication with DDRs and serve as a key component in the orchestration of many events required for the productive infection of PyVs.
-
The roles that ATM and ATR play regarding expression of viral proteins are mixed across Polyomaviridae. Multiple studies indicate that ATM knockdown has no effect on total SV40, MCPyV, or mPyV TAg levels(Shi et al., 2005; Zhao et al., 2008; Boichuk et al., 2010; Tsang et al., 2014). Conversely, it was observed that for JCPyV caffeine treatment(targeting both ATR and ATM) and ATR siRNA knockdown severely attenuate levels of TAg, VP1 and agnoprotein(Orba et al., 2010). ATM knockdown during BKPyV infection had no effect on TAg expression, and ATR knockdown decreased TAg expression by about 50%. Knockdown of either protein does not affect BKPyV VP1 protein levels(Jiang et al., 2012).
As with viral proteins, the extent to which ATM and ATR affect PyV genome replication is varied by species, but all reports indicate that abrogation of ATM or ATR affect viral DNA synthesis to some level. In the earliest investigations, Southern blot analysis revealed that mPyV DNA replication is lowered by caffeine by as much as 50%(Dahl et al., 2005). Similarly, caffeine was also found to diminish JCPyV genome replication by approximately 50%(Orba et al., 2010). Similar to caffeine treatment in mPyV and JCPyV, siRNA double knockdown of ATR and ATM decreases BKPyV genome replication to ~50%, but individual knockdowns have minimal effect (Jiang et al., 2012). MCPyV DNA replication is dramatically inhibited by either chemical inhibition or siRNA knockdown of ATM and ATR ultimately resulting in a 70% and 50% decrease in viral replication, respectively (Tsang et al., 2014). Additionally, it has been repeatedly shown that ATM is essential for SV40 DNA replication with knockdown of ATM resulting in as much as a 90% decrease in viral DNA(Shi et al., 2005; Boichuk et al., 2010) and treatment with caffeine throughout infection dramatically lowers viral DNA(Sowd et al., 2013). Conversely, ATR appears to have a debatable role in SV40 DNA replication with ATR siRNA knockdown having no effect on genome copy number in one study (Boichuk et al., 2010), but later chemical treatment with an ATR inhibitor VE-821 was found to result in a 90% loss of detectable viral DNA(Sowd et al., 2013).
Strikingly, despite mixed effects on viral protein level and DNA replication, inhibition of ATM or ATR results in attenuated formation of infectious PyV progeny. Caffeine treatment yields as much as two log fewer mPyV and JCPyV infectious progeny(Dahl et al., 2005; Orba et al., 2010). For BKPyV, siRNA knockdown of ATM or ATR individually decreased infectious progeny by ~50%, while double knockdown of ATM and ATR results in ~90% loss of infectious progeny(Jiang et al., 2012). The events leading to this more dramatic and ubiquitous phenotype compared to the viral DNA levels may be explained by insightful work from the Fanning lab, in which they provided evidence that ATM and ATR are involved in the resolution of viral replication intermediates. By two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, it was revealed that ATM inhibition accumulates unidirectional viral replication intermediates and increased recombination signatures while ATR inhibition led to fork stalling and breakage of converging replication forks(Sowd et al., 2013). A follow-up report indicates that ATM activity promotes homology-directed repair while preventing the activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase(DNA-PK) and its associated NHEJ at viral replication centers. ATM drives selective recruitment of factors associated with homology directed repair(CtIP, BRCA2, RAD52, BLM, RMI1/2, Topoisomerase Ⅲα) to TAg foci—whereas DNA-PK and NHEJ factors(KU70/80) are excluded(Sowd et al., 2014). These findings may explain how SV40 utilizes the ATM kinase for replication of its genome(Sowd et al., 2014).
Additionally the ATM kinase has been shown to serve as a TAg kinase. ATM is responsible for phosphorylation of SV40 TAg at Ser120, which is required for optimal viral DNA synthesis(Shi et al., 2005). However, in vitro phosphorylation of TAg at Ser120 decreases its DNA binding affinity(Cegielska et al., 1994). An interesting hypothesis is that ATM-dependent phosphorylation of TAg may liberate TAg from the viral minichromosome during DNA synthesis. A recent report indicates that activated ATM phosphorylates MCPyV TAg at Ser816. Mutagenesis of this residue corresponds to increased cellular proliferation and decreased apoptosis(Li et al., 2014). The authors postulate that the pro-apoptotic nature of this phenomenon may be linked to spread of virions or an intrinsic cellular defense to viral infection.
-
Utilizing host nuclear factors to facilitate their own reproduction is typical of many DNA viruses. Relying on host DNA replication machinery eases the burden of encoding these proteins on limited viral genomes. To take advantage of these host factors, many DNA viruses have evolved regulatory elements that induce cell cycle progression into S phase to optimize access to the host replication machinery(reviewed in(Chaurushiya and Weitzman, 2009)). Canonically, PyVs induce their host cell into S-phase through TAg interactions with pRb. As discussed above, TAg binds pRb and frees E2F allowing for entry into S-phase(Dyson et al., 1990). Moreover, the polyomavirus small T Antigen(tAg) has been shown to drive S-phase entry, and subsequent DNA synthesis in a number of cell lines in a protein phosphatase 2A dependent manner(Mullane et al., 1998; Andrabi et al., 2011). Additionally, PyVs functionally inactivate p53 while simultaneously stabilizing it in order to avoid apoptosis (Pipas and Levine, 2001).
In addition to their ability to induce entry into S-phase, many PyVs appear to block progression into mitosis at the G2→M checkpoint(Orba et al., 2010; Rohaly et al., 2010; Demetriou et al., 2012; Jiang et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013; Tsang et al., 2014). The exact events leading to G2 arrest are undefined. ATR dependent phosphorylation of Chk1 is a major contributor to G2 arrest(Liu et al., 2000). Studies indicate that SV40 TAg can act upon Chk1(possibly through ATR) by showing that UCN-01, a Chk1 inhibitor, induces mitosis during SV40 infection (Okubo et al., 2003). These findings were corroborated by the observation that, during infection of SV40, ATR is responsible for activating p53 isoform Δp53 leading to stabilization of the intra-S checkpoint. Interference with this pathway through addition of dominant negative forms of ATR and Δp53, or short hairpin knockdown of p21 resulted in loss of polyploidy and an increase in cells accumulating in the G1 phase(Rohaly et al., 2010). It was found that JCPyV also induces G2 arrest through ATR as well as ATM and that this effect is mediated, in part, by localization of TAg to cellular DNA(Orba et al., 2010). In contrast, neither chemical inhibition nor siRNA knockdown of ATM or ATR had any significant effect on the cell cycle profile of the MCPyV-infected cells(Tsang et al., 2014).
PyVs exploit the host DDR to mediate their own replication. The functional consequences of viral interference, or deregulation, of DDR to its host cell are somewhat mysterious. It is becoming increasingly clear that PyVs in general induce cellular damage and confer genomic instability to their host. This can most obviously be demonstrated by induction of polyploidy characteristic of infection with many PyVs(Orba et al., 2010; Rohaly et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013). It is possible that the accumulation of this genomic DNA is linked with an inhibition of mitosis conjoined with licensing of multiple rounds of replication.
Intriguingly, it appears that despite active DDR, PyV infection might interfere with repair of host genotoxic stress. Expression of both MCPyV and SV40 TAgs induce genomic damage detectable by comet assay(Boichuk et al., 2010; Li et al., 2013). Moreover, it appears that infection with JCPyV induces mutation in the host genome most likely caused by disruption of homologous recombination(Trojanek et al., 2006). It is possible that this is a byproduct of sequestering DDR proteins to viral replication centers, which could physically prevent recognition of host DNA damage. Supporting this, SV40 infected murine mesothelial cells showed enhanced susceptibility to asbestos-induced DSBs(Pietruska and Kane, 2007). MPyV infection sensitizes host cells to DNA damaging agents—possibly through TAg binding to RPA(Banerjee et al., 2013). This indicates that recognition of host DNA damage may occur, but its repair is attenuated. Taken together, PyVs may impede the repair of host genotoxic stress that accumulates during infection.
The above stated model is contrasted, however, by the observation that BKPyV infection of primary renal proximal tubule epithelial cells in the absence of ATM and ATR DDRs leads to the formation of fragmented nuclei in a proportion of infected cells(Jiang et al., 2012). Closer examination of BKPyV infected cells by metaphase-spread analysis shows a dramatic shattered chromosome phenotype in a large proportion of infected cells when ATM or ATR is knocked down. These shattered chromosomes are not observed in BKPyV-infected, DDR genome is concurrent with damage. Alternatively, it is possible that repair is in fact inhibited on the host chromosome and accumulated host DNA damage is observed only during mitotic stress(which would normally be avoided by ATR and ATM-mediated cell cycle arrest). A detailed and comprehensive report on genomic instability induced by SV40 TAg found that formation of characteristic indicators of genomic instability including micronuclei, anaphase bridges, and aberrant kinetochore-microtubule attachments accompanies mitotic stress, which is dependent upon TAg interaction with the Bub1 kinase (Hu et al., 2013). Interestingly, the mPyV TAg was also shown to induce arrest at the mitotic checkpoint and inhibit chromosomal alignment at the metaphase plate and induced cell death in a mitosis dependent manner consistent with mitotic catastrophe(Pores Fernando et al., 2014). These findings further highlight the importance of G2→M arrest for preventing the appearance of host genomic damage during PyV infection.
-
PyVs are masters of cellular subterfuge and disruption. Studying PyV interaction with its host has greatly improved our understanding of basic biological processes and host-pathogen relationships. Through interaction with DDR proteins and careful manipulation of the functionality of these responses, PyVs induce a cellular environment conducive to their own replication while keeping their host on the edge of catastrophe. Activation and sequestration of the ATM and ATR DDR components permit effective PyV replication through direct and indirect interactions between these DDR proteins and viral factors while simultaneously locking the host into a favorable condition for viral replication despite accumulation of damage. Beyond ATM and ATR DDRs it is becoming apparent that other DDR factors may also succumb to the manipulation by PyVs. For example, homology-direct repair has recent been shown to be used preferentially over NHEJ during SV40 infection to repair the replicating viral genome(Sowd et al., 2014).
In future studies of PyV and DDR it would be interesting to underst and the molecular details of how DDR components regulate viral replication. Additionally the link between DDR activation and oncogenesis may be an important area of discussion as more evidence is compiled relating the various PyVs with human tumors. Further studies investigating the interactions of PyVs with their host with a focus on the mechanisms underlying PyV hijacking DDR and the origin of host genomic damage will provide insight into viral replication and pathogenesis.
-
We thank members of the Jiang lab for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the UAB Department of Microbiology start-up fund, a UAB faculty development grant, a UAB Cancer Center Pilot Program Project grant, and a YSB UAB Cancer Center New Faculty Development Award to M Jiang.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: