-
Dear Editor,
Myristoylation is a naturally occurring post-translational modification for targeting cytoplasmic proteins to intracellular membranes. Unlike enveloped animal viruses, which enter host cells by membrane fusion, nonenveloped animal viruses must disrupt the cell membrane to initiate infection. Some animal viruses and several nonenveloped viruses such as reovirus and poliovirus were shown to contain myristoylated structural proteins (Ivanovic et al. 2008).
Aquareovirus spp., belonging to the Reoviridae family, infect several aquatic animals, including fish, shellfish, and mollusks. Generally, aquareoviruses show low pathogenicity in aquatic cultures and are identified during routine examination. Grass carp reovirus (GCRV), which causes severe hemorrhagic disease in grass carp fingerlings and yearlings, is considered as one of the most important pathogens (Rangel et al. 1999). Similar to other reoviruses, GCRV consists of an 11-segment dsRNA genome core surrounded by a double-layered icosahedral particle, with an overall diameter of approximately 75–80 nm. The 11-segment dsRNA genome encodes seven structural (VP1–VP7) and five nonstructural (NS16, NS26, NS31, NS38, and NS80) proteins (Chen et al. 2016). Phylogenic analysis indicated that aquareoviruses have a close evolutionary relationship with orthoreoviruses (Attoui et al. 2002; Fang et al. 2000). Three-dimensional image reconstruction and cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) revealed that protein structure and particle organization in GCRV and striped bass reovirus are considerably similar to that in Orthoreovirus spp. (Cheng et al. 2008, 2010; Fang et al. 2005; Shaw et al. 1996). The GCRV outer capsid proteins VP5 and VP7 are homologs of the mammalian reovirus (MRV) proteins μ1 and σ3, respectively. Furthermore, the autocleavage of outer capsid protein VP5 at its N-terminus is proposed to be required for viral entry into host cells during infection (Li and Fang 2013; Yan et al. 2015).
Similar to most animal viruses, nonenveloped reovirus enter the host cells by a series of stepwise capsid rearrangements or disassembly and structural changes to traverse the host membrane via the formation of metastable intermediate infectious subviral particles (ISVPs). The MRV outer capsid consists of 200 μ1/σ3 heterohexamers, and membrane penetration is mediated by the outer capsid protein μ1. Previous studies suggest that protease digestion of the 76-kDa μ1 protein generates μ1δ (63 kDa) and a C-terminal small fragment ϕ(13 kDa). The autocleavage of μ1δ further leads to the formation of the N-terminal μ1N fragment and the C-terminal δ fragment. Reovirus μ1 was identified as a multifunctional protein that plays important roles in regulating cell death induction and controlling entry-related conformational changes for the critical balance of virus disassembly (Snyder and Danthi 2017). Moreover, myristoylated μ1 is recognized as the primary and sufficient determinant of pore formation required for membrane penetration (Ivanovic et al. 2008). The N-myristoylated peptide (μ1N) interacts with the target-cell membrane, and the released μ1N is sufficient for membrane pore formation in vitro (Agosto et al. 2006). Particles with a mutant form of μ1N42A, which is unable to release μ1N, were shown to lack the ability to associate with cell membranes (Ivanovic et al. 2008).
Cryo-EM structure of aquareovirus at 3.3 Å resolution revealed that the myristoylated group covalently linked to the N-terminus and embedded in the hydrophobic pockets of the protein VP5 (Zhang et al. 2010), indicating that release of the myristoyl group from autocleavaged VP5 is essential for cell entry during membrane penetration. Further, recoated GCRV particles carrying an Asn-to-Ala substitution at residue 42 of VP5 were not infectious in vitro, indicating that VP5 autocleavage is required for efficient infection (Yan et al. 2015). However, the permeability of N-terminal myristoylated VP5N (myrVP5N) peptides in live cells has not yet been directly visualized and characterized. Therefore, in this study, we investigated the role of myr-VP5N in cell entry and infection to understand the molecular mechanism underlying aquareovirus infection initiation.
To visualize whether VP5N myristoyl group is necessary for cell entry, the GCRV VP5N peptide consisting of amino acids 2–42 with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) - labeled C-terminus and myristoylated N-terminus (myrGNASSIVQTINVTGDGNVFKPSAETSSTAVPSLSLSPG MLN-FITC, myr-VP5N) was synthesized by ChinaPeptide Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China); the same peptide without myristoylation (VP5N) was also prepared. The synthetic peptide was dissolved in DMSO and supplemented with Eagle's minimum essential medium (MEM). To determine the effective peptide concentration and avoid potential toxic effects, we initially assayed a range of concentrations of synthesized peptides in Ctenopharyngodon idellus kidney (CIK) cells (data not shown). Then, we tested the penetration effect of different concentrations of the synthesized peptides (including the myr-VP5N and VP5N) on CIK cells. As shown in Fig. 1A-1, many myr-VP5N peptides diffused into the cell membrane after treatment with increasing concentrations of myr-VP5N peptide for 120 min, whereas no diffusion was observed with 20 μmol/L VP5N peptide. Meanwhile, quantification and statistical analysis showed that more than 95% cells exhibited efficient penetration (Fig. 1A-2), indicating that myr-VP5N fragment could permeate the cell membrane. To further optimize the incubation condition, myr-VP5N peptides (20 μmol/L) were incubated with CIK cells at different time points. The cell membrane permeability of myristoylated peptides enhanced as incubation time increased, but no obvious difference was observed in the permeation efficiency of myr-VP5N peptides after incubation for 60 and 120 min (Fig. 1B-1, Fig. 1B-2), indicating that 60 min incubation is sufficient for the cell membrane permeation of myristoylated peptides.
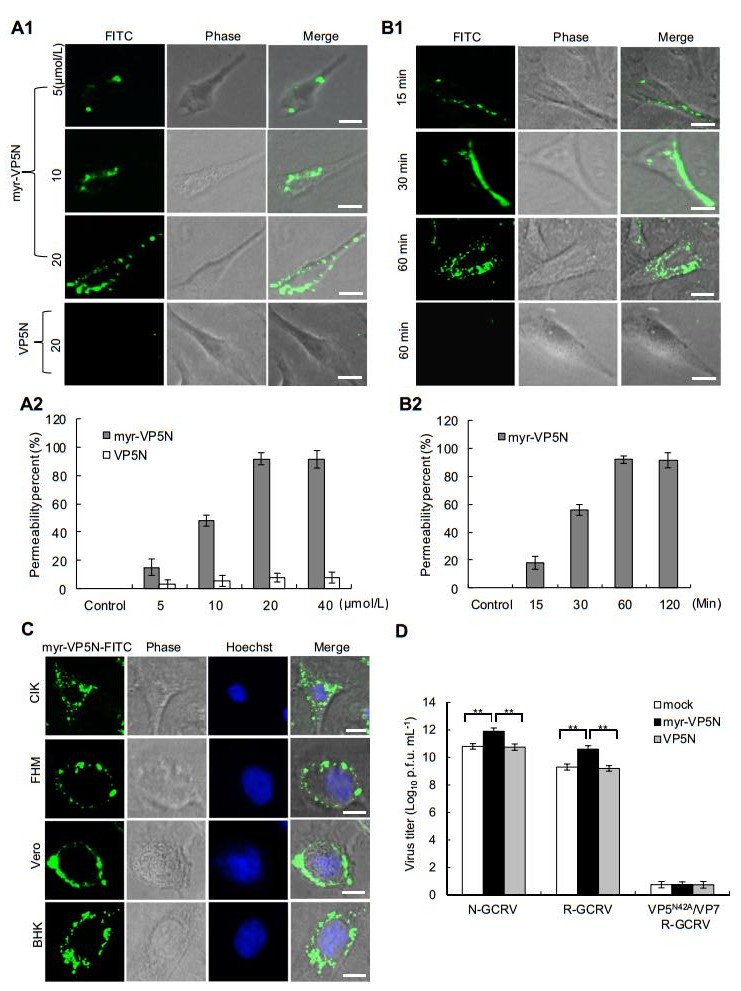
Figure 1. Characterization of N-terminal myristoylated VP5 (VP5N) peptide of GCRV during entry into host cells. A1, B1 Direct visualization of the permeation of myr-VP5N peptides (green fluorescent dots) in CIK cells by fluorescence microscopy. The VP5N peptide modified with myristoylated N-terminus consisting of amino acids 2–42 was labeled with FITC in the C-terminus. Cells were incubated with different concentrations of myr-VP5N or VP5N for 120 min (A1), or 20 μmol/L myr-VP5N or VP5N at different time points (B1) at 28 ℃, and then observed under a fluorescence microscope. A2, B2 Penetration efficiency quantified by calculating the percentage of cells showing the fluorescence permeability. Graphs represent means and standard deviations of normalized data points for triplicate samples from each of the three independent experiments. C Images of myr-VP5N peptides in GCRV-susceptible and -non-susceptible cells. Cells were incubated with 20 μmol/L myr-VP5N peptides for 60 min at 28 ℃. D Promotion of viral infectivity detected using plaque assays. Cells were pretreated with culturing medium (mock), myr-VP5N and VP5N, and infected with three different particles (N-GCRV, VP5/VP7 R-GCRV, or VP5N42A/VP7 R-GCRV) respectively. X axis refers to above three indicated particles in infected cells with different pretreatment: mock, myr-VP5N and VP5N. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test. Double asterisks indicates P < 0.01. Error bars denote standard deviations. Scale bar: 10 μm
Next, we studied the penetration specificity of myrVP5N peptides in different cell lines. Here, the susceptible fish cell lines CIK and FHM, and the non-susceptible mammalian cells including BHK and Vero from CCTCC (China center for type culture collection) were used. MyrVP5N peptides were efficiently distributed into the cell membrane of CIK and FHM cells as well as the Vero and BHK cells, indicating lack of cell specificity of penetration of myristoylated peptides (Fig. 1C). Furthermore, our results showed that of the presence of bound myr-VP5N on/around cytoplasmic membranes in different cells after incubation for more than 120 min (data not shown). These results indicate that myr-VP5N peptides possess excellent cell line-independent cell membrane permeability.
We next investigated the ability of the hydrophobic short peptides in promoting virus infectivity. To test the role of myr-VP5N peptide in viral infection, recoated particles (VP5/ VP7 R-GCRV and VP5N42A/VP7 R-GCRV) were prepared with either in vitro-expressed wild-type VP5/VP7 or a mutant form of VP5N42A/VP7, which does not undergo VP5N cleavage (Yan et al. 2015); the cultivated native GCRV (NGCRV) and recoated particles were further purified and used in infectivity assays. CIK cells were incubated either with myr-VP5N or VP5N peptides (20 μmol/L) for 60 min and then infected with various particles (N-GCRV, VP5/VP7 R-GCRV, or VP5N42A/VP7 R-GCRV), which were previously incubated at 30 ℃ for 90 min for the generation of ISVPs. Infected cells, pre-incubated with culturing medium (MEM) under the same condition were used as mock group. As shown in Fig. 1D, the virus titer increased by more than 1 log10 PFU in native GCRV infected cells pretreated with synthetic myr-VP5N, compared to that in MEM and VP5N pretreated cells. Likewise, a similar enhanced virus titer was detected in cells infected by wild type R-GCRV with pretreatment of myr-VP5N peptide, suggesting that myristoyl groups in the N-terminus of protein VP5 are important for promoting activity of viruses. Additionally, such activity enhancement was not observed in cells infected by recoated mutant VP5N42A/VP7 particles (VP5N42A/VP7 R-GCRV) with pretreatment of myr-VP5N peptide, indicating that the myr-VP5N did not promote viral activity in the absence of VP5 autocleavage. Collectively, our results reveal that autocleavage of the myristoylated N-terminal fragment of VP5 is essential for cell entry and effective initiation of viral infection.
The mechanisms underlying host cell membrane penetration by nonenveloped animal viruses are relatively less understood, compared to the membrane fusion mechanisms used by enveloped viruses. As nonenveloped viruses lack a lipid membrane, they utilize different mechanisms to cross the host cell membrane and initiate effective infection. For example, poliovirus can trigger structural changes in the capsid by binding to host cell receptors and release myristoylated peptide VP4 during cell entry (Tuthill et al. 2006). Similarly, reovirus undergoes a programmed stepwise disassembly leading to membrane penetration; in addition to structural changes in μ1, the autocleavage and release of myristoylated protein μ1 is critical for the formation of sizeselective pores in red blood cell membranes (Ivanovic et al. 2008). In this study, we found that myr-VP5N of GCRV is required for membrane permeation and infection promotion.
Using fluorescently labeled VP5N for direct visualization of the permeation, we found that myr-VP5N quickly permeates live cell membranes. Moreover, using cells susceptible and non-susceptible to GCRV infection, we showed that the cell membrane permeation of myristoylated peptide was not cell specific. Further infectivity assays suggested that cleavage of myristoylated VP5N was critical for promoting activity, while the noncleaving mutant VP5N42A/ VP7 particles were shown to be defective in infectivity despite synthetic myr-VP5N being able to associate with the cells, indicating that the myristoylated VP5N peptide was required for cell entry but not sufficient for initiating productive infection of reovirus. In fact, recent studies revealed that residues 340–343 of μ1 play cooperated role with μ1N to maintain the proper balance between capsid stability and conformational flexibility during reovirus entry and infection (Snyder and Danthi 2017). Taking together, our results demonstrated that myr-VP5N promotes viral infectivity and that VP5N autocleavage is essential for such enhanced viral activity. A similar role has been proposed for the MRV that pore-forming short peptide μ1N released from particles was sufficient for promoting activity (Agosto et al. 2008).
In conclusion, our studies demonstrate that myr-VP5N not only causes cell membrane permeation but also promotes virion activity for more effective infection. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the direct visualization of myr-VP5N permeation through host cell membranes and the increased virus particle activity due to myrVP5N. Our results provide strong foundation for further studies aimed at understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of aquareovirus penetration protein VP5 in host cell membrane interaction during cell entry.
HTML
-
This work is supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31672693, 31372565, 31172434).
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: