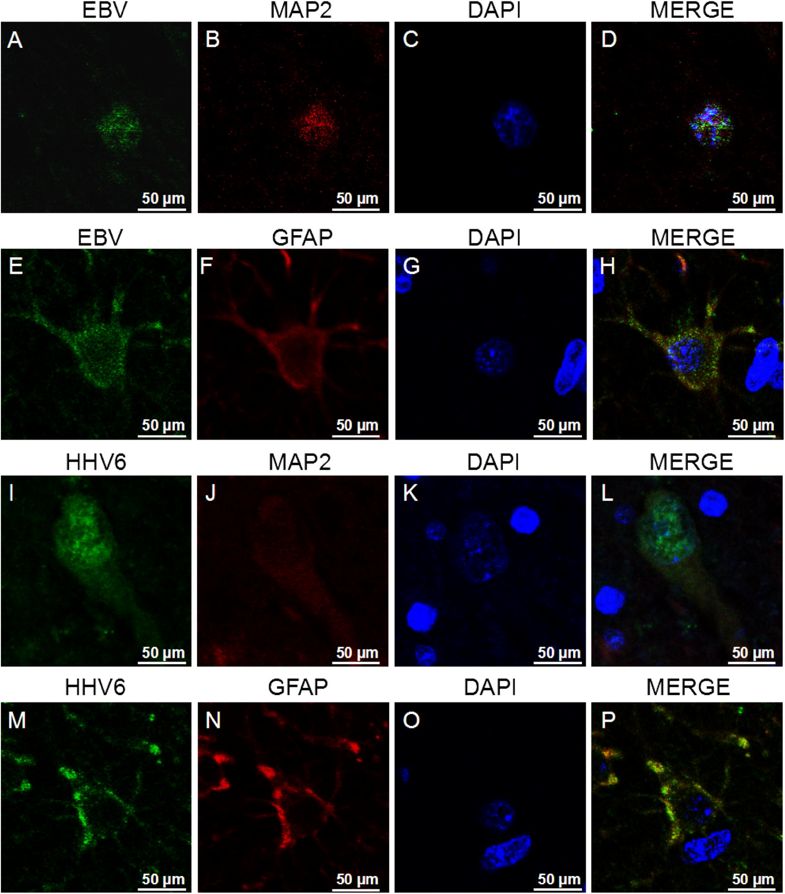
-
Ascenção BB, Gonçalves AC, Luís N, Sá J, Brito AP, Poças JM (2016) Epstein-Barr virus hemorrhagic meningoencephalitis: case report and review of the literature. J Neurovirol 22:695-698
doi: 10.1007/s13365-016-0430-y
-
Atkins MR, Terrell W, Hulette CM (1995) Rasmussen's syndrome: a study of potential viral etiology. Clin Neuropathol 14:7-12
-
Bien CG, Bauer J, Deckwerth TL, Wiendl H, Deckert M, Wiestler OD, Schramm J, Elger CE, Lassmann H (2002) Destruction of neurons by cytotoxic T cells: a new pathogenic mechanism in Rasmussen's encephalitis. Ann Neurol 51:311-318
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1531-8249
-
Bien CG, Tiemeier H, Sassen R, Kuczaty S, Urbach H, von Lehe M, Becker AJ, Bast T, Herkenrath P, Karenfort M, Kruse B, Kurlemann G, Rona S, Schubert-Bast S, Vieker S, Vlaho S, Wilken B, Elger CE (2013) Rasmussen encephalitis: incidence and course under randomized therapy with tacrolimus or intravenous immunoglobulins. Epilepsia 54:543-550
doi: 10.1111/epi.2013.54.issue-3
-
Chen S, Chen S, Guan Y, Zhang Y, Qi X, An J, Wang Y, Luan G (2016) Elevated expression of human papillomavirus antigen in brain tissue of patients with Rasmussen's encephalitis. Epilepsy Res 126:119-125
doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.07.008
-
Jay V, Becker LE, Otsubo H, Cortez M, Hwang P, Hoffman HJ, Zielenska M (1995) Chronic encephalitis and epilepsy (Rasmussen's encephalitis): detection of cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus 1 by the polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization. Neurology 45:108-117
doi: 10.1212/WNL.45.1.108
-
Kano K, Katayama T, Takeguchi S, Asanome A, Takahashi K, Saito T, Sawada J, Saito M, Anei R, Kamada K, Miyokawa N, Nishihara H, Hasebe N (2017) Biopsy-proven case of EpsteinBarr virus (EBV)-associated vasculitis of the central nervous system. Neuropathology 37:259-264
doi: 10.1111/neup.2017.37.issue-3
-
Kawamura Y, Nakayama A, Kato T, Miura H, Ishihara N, Ihira M, Takahashi Y, Matsuda K, Yoshikawa T (2015) Pathogenic role of human herpesvirus 6B infection in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J Infect Dis 212:1014-1021
doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiv160
-
Luan G, Gao Q, Zhai F, Chen Y, Li T (2016) Upregulation of HMGB1, toll-like receptor and RAGE in human Rasmussen's encephalitis. Epilepsy Res 123:36-49
doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.03.005
-
Merkler D, Horvath E, Bruck W, Zinkernagel RM, Del la Torre JC, Pinschewer DD (2006) Viral deja vu elicits organ-specific immune disease independent of reactivity to self. J Clin Invest 116:1254-1263
doi: 10.1172/JCI27372
-
Ning S (2011) Innate immune modulation in EBV infection. Herpesviridae 2:1
doi: 10.1186/2042-4280-2-1
-
Pardo CA, Vining EP, Guo L, Skolasky RL, Carson BS, Freeman JM (2004) The pathology of Rasmussen syndrome: stages of cortical involvement and neuropathological studies in 45 hemispherectomies. Epilepsia 45:516-526
doi: 10.1111/epi.2004.45.issue-5
-
Power C, Poland SD, Blume WT, Girvin JP, Rice GP (1990) Cytomegalovirus and Rasmussen's encephalitis. Lancet 336:1282-1284
doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92965-K
-
Rasmussen T, Olszewski J, Lloydsmith D (1958) Focal seizures due to chronic localized encephalitis. Neurology 8:435-445
doi: 10.1212/WNL.8.6.435
-
Readhead B, Haure-Mirande JV, Funk CC, Richards MA, Shannon P, Haroutunian V, Sano M, Liang WS, Beckmann ND, Price ND, Reiman EM, Schadt EE, Ehrlich ME, Gandy S, Dudley JT (2018) Multiscale analysis of independent alzheimer's cohorts finds disruption of molecular, genetic, and clinical networks by human herpesvirus. Neuron 99:64.e7-82.e7
-
Salahuddin SZ, Snyder KA, Godwin A, Grewal R, Prichard JG, Kelley AS, Revie D (2007) The simultaneous presence and expression of human hepatitis C virus (HCV), human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6), and human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) in a single human T-cell. Virol J 4:106
doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-4-106
-
Varadkar S, Bien CG, Kruse CA, Jensen FE, Bauer J, Pardo CA, Vincent A, Mathern GW, Cross JH (2014) Rasmussen's encephalitis: clinical features, pathobiology, and treatment advances. Lancet Neurol 13:195-205
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70260-6
-
Walter GF, Renella RR (1989) Epstein-Barr virus in brain and Rasmussen's encephalitis. Lancet 1:279-280
-
Wang X, Wang Y, Liu D, Wang P, Fan D, Guan Y, Li T, Luan G, An J (2017) Elevated expression of EBV and TLRs in the brain is associated with Rasmussen's encephalitis. Virol Sin 32:423-430
doi: 10.1007/s12250-017-4058-8
-
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Chen S, Chen S, Guan Y, Liu C, Li T, Luan G, An J (2017) Expression of human cytomegalovirus components in the brain tissues of patients with Rasmussen's encephalitis. Virol Sin 32:115-121
doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3917-z