-
Tea, Camellia sinensis, is cultivated mainly at tropical and sub-tropical latitudes. Relative to the main tea-producing countries such as China and India, Japan is located at a more northerly latitude. Although it is the eighth largest tea-producing country in the world (10), most of Japan's harvested tea is not exported but consumed domestically as green tea (Fig. 1). As tea is cultivated intensively in Japan, its production has been heavily dependent on chemical fertilizers and pesticides: the annual rate of nitrogen application is 500-600 kg/ha in Shizuoka prefecture, for example, and conventional chemical pesticides are applied more than 10 times per year (18). However, several tea pests have now developed pesticide resistance due to such intensive use of chemical agents. Moreover, since green tea contains vitamins and functional compounds like cathechins (21), consumers prefer this type not only for its flavor but also for its health benefits, and liberal use of chemical pesticides is ill-suited to the demands of consumers. Given this background, new pest control strategies are needed for controlling tea pests.
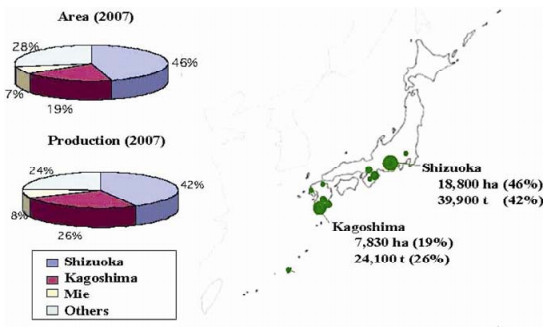
Figure 1. Tea-producing prefectures in Japan. Solid circles on the map represent relative production from individual prefectures. The two highest-producing prefectures, Shizuoka and Kagoshima, account for almost 70% of Japan's annual tea production.
Tea is a perennial evergreen plant which seldom needs to be re-planted for several decades. The structure of cultivated tea trees is unique: the plucking surface has a dense covering of leaves, but the interior has very little foliage, providing both a habitat for various pests and a refuge for natural enemies (Fig 2A). Kawai (13) described the ecological characte-ristics of tea fields in Japan and identified the major insect pests as Kanzawa spider mite (Tetranychus kanzawai), tea leaf roller (Caloptilia theivora), oriental tea tortrix (Homona magnanima), smaller tea tortrix (Adoxophyes honmai), mulberry scale (Pseudau-lacaspis pentagona), black citrus aphid (Toxoptera aurantii), yellow tea thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis), tea green leafhopper (Empoasca onukii), mugwort looper (Ascotis selenaria), and chafer (Heptophylla picea).

Figure 2. Tea tree under conventional chemical control in Kyoto (A). Closer look of plucking surface of tea tree showing dense tea leaves and interior with little foliage. Tea field treated with Adoxophyes honmai entomopoxvirus in Saitama (B). Numerous spider webs are shown on the plucking surface of the tea trees.
In response to the problems mentioned above, alter-natives to chemical pesticides have been developed to control tea pests. Kodomari (16) mentioned that the prominent biological control agents in Japanese tea fields were a pesticide-resistant predatory mite (Ambly-seius womersleyi) against the Kanzawa spider mite, as well as granuloviruses (Baculoviridae) and sex phero-mones against H. magnanima and A. honmai (Lepi-doptera, Tortricidae). In tea fields, where various pests still need to be controlled primarily by chemical pesticides, biological control agents that are sensitive to chemical pesticides should not be used. Baculovi-ruses, sex pheromones and resistant natural enemies are all suitable agents for use in field situations that require chemical control, such as tea. Furthermore, as well as an abundance of insect pests, tea has various indigenous natural enemies which play a role in suppressing pest populations (13). Biological control agents such as granuloviruses should therefore be applied in a way that does not disturb these natural enemies.
HTML
-
Control of A. honmai and H. magnanima has depended on chemical treatments such as sprayed chemical pesticides. However, since both of these species have acquired resistance to chemical pesticides including IGRs (insect growth regulators) and carbamate in-secticides (17, 31, 34, 38, 40), and since consumers are increasingly concerned about food safety, trials of new management strategies aimed at reducing chemical pesticide usage have attracted attention (15, 18). The first field trials for an Adoxophyes GV were started in apple orchards. A. orana, which is closely related to A. honmai, is an apple pest, and the efficacy of a GV against this species was demonstrated experimentally in apple orchards in the 1970s (33). A GV isolated from the same species has also been studied in Europe, and is registered as a viral control agent for A. orana (11). Extensive studies for GVs against tea pests were subsequently carried out at the MAFF Fruit Research Institute and at the Shizuoka Prefectural Experimental Station to provide detailed evaluations of mass production, field application, interactions with other natural enemies, and safety issues (27). Experiments to determine the field efficacy of GVs were started by the Kagoshima prefectural government, with national government funding, in 1985 (18, 27). From 1993, Kagoshima prefecture first focused on "production of clean tea, " a program which addressed the issues of both chemical pesticides and ash from the nearby Mt. Sakurajima volcano, and then promoted an integrated pest management (IPM) program involving appli-cation of GVs. Five facilities for mass-producing GVs were built in Kagoshima, with state subsidy, in 1990-1992. In these facilities, a GV of A. orana (AdorGV) was propagated in A. honmai larvae and a GV of H. magnanima (HomaGV) was propagated in H. mag-nanima larvae, because the two GVs are not cross-infectious. After propagation, both GVs were mixed in a single bottle at different doses. AdorGV was prepared for 2, 000 infected moribund larvae (IML)/ha, and HomaGV for 1, 000 IML/ha, and 2, 000 l/ha were sprayed in the fields. Healthy and GV-infected insects were reared in separate rooms (27).
GVs were usually sprayed once at the first occur-rence of A. hommai and H. Magnanima larvae in April or May, after the first tea harvest. The timing of GV application was determined from data forecasting insect occurrence, which were collected by pest control stations in the prefecture in each region and announced to the farmers. A. hommai and H. mag-nanima are multivoltine, so that insect larvae occur 4-5 times per year, but the efficacy of the sprayed virus was normally sustained throughout the year after a single GV application in the spring. The area sprayed with GVs was 5, 850 ha in Kagoshima prefecture in 1995, equivalent to 80 % of all the tea fields in the prefecture.
Several factors contributed to the success of GV application in Kagoshima. First, effective viral agents were available and an efficient application program was established. Second, machine sprayers were well distributed throughout the prefecture. This is a riding type sprayer, which makes application easier and quicker. Most lepidopteran insect larvae become less susceptible to baculoviruses as they grow, a pheno-menon that is known as developmental resistance (14, 39). If the GV application is spread over a long period, therefore, the control efficacy will be diminished. Efficient, machine-based application was critical to the successful extension of GV-spraying this area, because it enabled 0.1 ha of tea plants to be sprayed in as little as 10 min (personal communication by Mr. Yasunari Kouzaki, Kagoshima Prefecture Tea Experi-mental Station). A third factor was that stable cooperatives for tea planters were operating in Kagoshima. These organizations provided effective oversight and coordination of GV production and spraying throughout the area.
The Agricultural Chemicals Regulation Law was revised in 2002, to counter the import and use of non-registered chemical pesticides in Japan. This revision encompassed all pest control agents, including biological control agents as well as chemical pesticides, and meant that the GVs could no longer be locally propagated and now required registration. The GVs of H. magnanima and A. honmai were registered in 2003 and produced by Arysta LifeScience Cor-poration.
In recent years, sales of sex pheromone of A. honmai and H. magnanima have increased, and these compounds were used on 3 000 ha in Kagoshima prefecture in 2006, but the use of GVs has declined. There are several reasons for this decreasing appli-cation of GVs in tea fields in Japan, one of which is the changing pattern of occurrence of other pests. Mulberry scale, for example, has been increasing recently. Chemical treatment is required to control mulberry scale at the same time of GVs-spraying, but it also kills H. magnanima and A. honmai. Fur-thermore, GVs have been applied in Kagoshima for more than 10 years, and the populations of H. magnanima and A. honmai have been reduced (26). Sex pheromones become a more efficient control stra-tegy at reduced insect population densities, whereas baculoviruses are more effective at higher levels of infestation. Pheromone-resistant A. honmai have been observed, however, and the current product has a modified chemical structure and has overcome this resistance (35). The availability of both GVs and sex pheromones should permit effective field control of lepidopteran tea pests over a wide and fluctuating range of insect population densities.
-
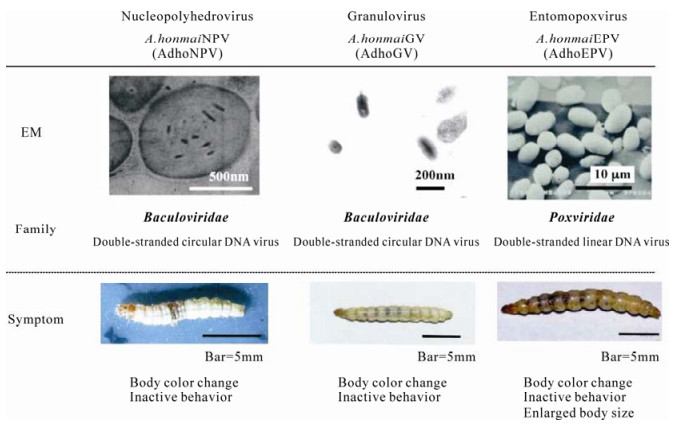
Consumers' concerns about viral control in tea cultivation mostly reflect anxiety about the human health risks posed by GVs. The word "virus" itself may create a negative impression if baculoviruses are confused with other human pathogenic viruses. However, baculoviruses are only found in arthropod hosts, and infectivity in humans and other mammals has never been reported (5). GVs have a particularly narrow host range and only replicate in lepidopteran insects. As mentioned above, for example, AdorGV is infectious to A. honmai but not H. magnanima larvae, and vice versa for HomaGV, even though both host species are in the same family.
The development of resistance in insects to viral control agents is much less common than resistance to chemical pesticides and BT products (biopesticides based on the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis). Recently, however, a Cydia pomonella strain was found to have developed resistance against a GV of the codling moth C. pomonella GV (CpGV) in Europe, which was the first field report of acquired resistance in a wild insect pest species against baculoviruses (2). Various pest species of insect have been shown to acquire decreased susceptibility to baculoviruses in laboratory selection experiments, in which insect populations were administered an ~80% lethality dose of virus and the surviving individuals were then passaged repeatedly (1, 6). In the insect propagation facilities in Kagoshima prefecture, the laboratory strain of A. honmai eventually became less susceptible to AdorGV (28). These observations show that it is possible for insects to develop resistance against baculoviruses, and it is thus essential to monitor pest populations, by conducting physiological, biological and genetic studies, for their susceptibility to insect viruses. Such information will provide insights for resistance management, which needs to take account of how acquired resistance against baculoviruses can develop and of how resistance traits can be inherited in the field. One measure to overcome resistance is to identify new virus isolates which can kill the resistant insects. To counter the resistance of C. pomonella against CpGV, other closely related virus isolates were found to be excellent alternatives (4, 8). As well as AdorGV, A. honmai is a host for a nucleopoly-hedrovirus (AdhoNPV) and an entomopoxvirus (AdhoEPV) (12, 37), and AdhoEPV is also infectious to H. magnanima larvae in Japan. These agents could be used for resistance management of A. honmai and H. maginanima.
As noted above, H. magnanima and A. honmai occur in 4 to 5 discrete generations per year, and the larval periods of successive generations do not overlap. However, a single application of GV, during the first generation, sustains the pesticidal effect through the whole year, and this happens because larvae infected by the first spraying transmit GVs successfully to the next generation. This trait is appreciated by farmers, whose labor is reduced. Successful transmission of these particular GVs in the field is attributed to their slow-killing characteristics: infected larvae produce large numbers of occlusion bodies (OBs), and survive and carry active viruses in their bodies until young and susceptible next-generation larvae appear (as a result of reproduction among the survivors). The slow-killing properties of these GVs are considered as advantageous characteristics, not only for virus transmission in the field but also for virus production. Inoculation of insects with GVs is carried out by dipping egg masses into a suspension of viral OBs. The neonate larvae consume the GV-contaminated egg surface when they hatch, and as noted above are most susceptible to infection during the youngest stages. GV-infected larvae die during the final larval instars, when the production of OBs is maximal (24), and the cadavers remain intact and can be collected by hand. Tea leaves are harvested in the spring before the pest insects appear, and the price of tea from the first plucking is considerably more expensive than that from the second and third pluckings in summer. Thus, the economic injury levels for damage by H. mag-nanima and A. honmai are relatively high, and the pests are not necessarily better controlled by faster-killing agents.
In the Kagoshima program, AdorGV and HomaGV were propagated in living larvae because viruses need living host individuals or cultured cells for their replication. All procedures including propagation of healthy insects, inoculation with viruses, collection of insect cadavers, and formulation were done by hand, and therefore required high personnel costs. Reducing the production costs of virus insecticides is a chal-lenging task. Studies have been carried out for industrial-scale production of the other baculoviruses in cell lines and using serum-free medium (42). However, few have conquered the obstacle of high production costs for cell systems, and all viral control agents currently on the market are produced in vivo (5).
-
A. honmai and H. magnanima have various natural enemies in tea fields (22, 36). However, a common outcome of conventional pest control using large volu-mes of chemical pesticide is a tea field environment in which there are fewer pests, but also fewer natural enemies. The author has tried to collect hymenopteran parasitoids by sweeping with insect nets in conven-tionally controlled tea fields in Shizuoka, but often caught nothing. Less chemical treated tea fields com-monly have numerous spider webs, which are also sparse in fields that have been treated with conven-tional chemical pesticides (Fig 2B). Natural enemies including parasitoid wasps are more susceptible to chemical pesticides than the hosts/pests (41). Since baculoviruses do not infect the natural enemies of their hosts, virus application should have no direct impact on natural enemies when a biological control program is started. Indeed, GV application in Kagoshima was highly effective because A. honmai and H. magnanima larvae were killed not only directly by the GVs but also by several species of hymenop-teran parasitoids (15). Thus, resident natural enemy populations should be evaluated in the field, and biological control agents should be used in a way that is compatible with their beneficial effects.
-
To manage pests with natural enemies, it is important to quantify the population of, or the extent of parasitism by, resident natural enemies in the field. A. honmai and H. magnanima are known to have various parasitic natural enemies including, as the dominant parasitoids, Campoplex homonae (Ichneumonidae), Ascogaster reticulata (Braconidae), and Apanteles adoxophyesi (Braconidae) (Fig. 3). Studies performed in Tsukuba showed that A. reticulata and EPVs are the dominant natural enemies for A. honmai (23). A. honmai larvae in the second and third generations are attacked by the parasitoids in summer, but those in the over-wintering generation are relatively highly infected with EPVs. Moreover, those generations with high virus prevalence show lower parasitism, which suggests that the viruses and parasitoids interact in some way (23).

Figure 3. Resident hymenopteran parasitoids of Adoxophyes honmai larvaein Japan. A: Ascogaster reticulata (Braconidae). B: Apanteles adoxophyesi (Braconidae). C: Meteorus ictericus (Braconidae). D: Campoplex homonae (Ichneumonidae) (D). Bar=5mm
When GVs are sprayed in fields that have high rates of parasitism, both virus and parasitoid larvae can share the same host at the same time. For larvae of koinobiont endoparasitoids, development may be affected by simultaneous virus infection of the host. In a series of laboratory experiments, we used different viruses to inoculate A. honmai larvae that were parastized by A. reticulata (an egg-larval parasitoid and one of the most important parasitic natural enemies of A. honmai). As well as AdorGV, other viruses that have been isolated from A. honmai are AdhoEPV and AdhoNPV, and all of them have different pathological characteristics (Fig. 4). We found that survival of A. reticulata is affected by virus infection of the host (25). Generally, the outcome of competition between viruses and parasitoids was determined by their respective growth rates, except for a special case in which a toxic protein encoded by the virus killed the endoparasitoid (29). Some endoparasitoids regulate the endocrinology of their host, whereas others are themselves constrained by the host's development (9, 20). Baculoviruses and EPVs also regulate host endocrinology and may prevent pupation or molting (24, 30, 32). These additional impacts of host regulation may also affect the outcome of the virus-parasitoid interaction. A. honmai larvae parasitized by A. reticulata and infected with EPV, for example, showed premature molting to the fifth instar and died before A. reticulata could complete its development in the host. On the other hand, A. reticulata were able to emerge from GV-infected A. honmai, although they invariably died after emergence (25). In the majority of virus-parasitoid interactions, parasitoid survival rate decreases when the virus infects earlier stages of the host (7), and most viral control agents target the younger, more susceptible stages of pest larvae. A comprehensive picture of the complex interactions between viruses and parasitoids will have to await meticulous field experiments that compare untreated control and conventional pesticide-treated fields.
-
An agricultural ecosystem involves various organisms, including natural enemies. The impact of virus application on such non-target organisms needs to be studied in more detail, and the results communicated to farmers so that they can more fully understand the direct and indirect effects of biological pest control.
As the use of insect natural enemies increases, chemical pesticides having less impact on natural enemies will be sought. Many farmers are already aware, from their own experience, of the value of resident natural enemies. The roles played by these organisms are beginning to be evaluated scientifically and environmental manipulations are developed to enhance their activities (3, 19). Careful assessment and exploration of the effects (whether detrimental or beneficial) on resident natural enemies of biological control agents such as viral pesticides will be necessary for successful environmental adaptive biological and/or ecological control programs.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: