HTML
-
Vaccination is the most cost-effective strategy for the prevention and control of infectious diseases (Jang and Seong 2013; Reid et al. 2019). With the development of animal husbandry and the prosperity of the pet market, the number of vaccines administered to animals is significantly increasing (Baron et al. 2018). Noninactivated vaccines, including recombinant viral vector vaccines, attenuated live vaccines, and genetically engineered vaccines (protein subunit vaccines and nucleic acid vaccines), account for a large market share (Melief et al. 2015; Meri et al. 2008).
The activity of the noninactivated vaccines depends on their immunogenicity and delivery strategies, as well as on the stability of the vaccines during storage and transportation (Peetermans 1996; Walters et al. 2014). Several factors, including ambient temperature, pH, freezing effect and dehydration, might result in lipid damage, protein damage, and nucleic acid degradation (Abdul-Fattah et al. 2007; Chen et al. 2010); ultimately, these factors may affect the stability of the vaccines (Kasper and Friess 2011). Therefore, most of the noninactivated vaccines are directly stored at temperatures under 4 ℃ or distributed through cold chain transportation after lyophilization, which significantly increases the cost and greatly restricts the accessibility and feasibility of the vaccines, especially in underdeveloped areas (Briggs and Ilett 1993; Hansen et al. 2015). Determining how to keep the vaccines stable at ambient temperature, reduce the loss of vaccine activity and control the economic cost of vaccine production and distribution are major challenges for the vaccine industry (Madan et al. 2018).
Freeze-drying protectants are complex reagents that prevent active component denaturation in vaccines during freeze-drying processes (Hansen et al. 2015). Under the condition of cold chain logistics, the relatively effective and common formula of cryoprotectants includes monosaccharide, polyalcohol, amino acids, salts and cryoprotectant derivatives (Basu and Domb 2018; Borde et al. 2011; Ohtake et al. 2011) such as sucrose, phosphate, glutamic acid and albumin (SPGA); lactose, gelatin, sorbitol and HEPES buffer (LGS); potassium phosphate buffer, hydrolysate gelatin and sorbitol (BUGS); and lactose hydrolysate and sucrose (LS) (Chen et al. 2012; Prabhu et al. 2014; Zheng et al. 2019). However, the thermostability and protection of these freeze-drying protectants are unsatisfactory (Siow et al. 2016). In particular, viral vaccines in cryoprotection medium are not stable at temperatures above 8 ℃ (Hansen et al. 2015; Orr et al. 2014). The loss of activity increases as the temperature rises. Furthermore, viral vaccines require cold chain logistics (processing, storage and distribution) (Orr et al. 2014). It is necessary to further improve their thermal stability and protective effect, especially in ambient temperatures.
Polyethylene glycol (PEG), dextran (DEX), and bovine serum albumin (BSA) are often individually used for the freeze-drying protection of clinical drugs, lactic acid bacteria, and microbes (Mody et al. 2014). PEG can reduce the damage to the virus through dehydration. DEX, a type of oligosaccharide, can protect viral activity from damage (Kraan et al. 2014). BSA, a kind of enzyme stabilizer, can prevent enzyme decomposition and denaturation. In addition, l-glutamic acid, with both acidic and basic amino acid ions, can buffer the pH changes in the freeze-drying process and can protect the vaccine activity. Use of l-glutamate has not been reported as a freeze-drying protective agent. The materials described here might be components of novel cryoprotectants.
In this study, we selected recombinant viral vector vaccines as representative noninactivated vaccines, including enveloped poxvirus recombinant vaccine and nonenveloped adenovirus recombinant vaccine, to explore the effect of the newly constructed vaccine protectant on the stability and immunogenicity of noninactivated vaccines under cold and ambient temperatures (4 ℃ and 25 ℃). We hope to provide proof of the new freeze-drying formula to protect the activity of the noninactivated vaccines for animal vaccinations.
-
DNA vaccines expressing OVA and ENV were constructed by cloning the target genes into pSV-1.0 vector and all DNA vaccines used in this study were prepared by using the Endo-free Plasmid Giga Kit (Qiagen, Cat#12391). Recombinant Tiantan vaccinia encoding OVA (rTTV-OVA) was constructed in our previous work (Qiu et al. 2014). The virus was propagated in Vero cells (ATCC CCL-81, passage 135e160). The cells were cultivated in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Corning) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, BI) with 1% penicillin/streptomycin solution (P/S, ScienCell), and DMEM with 2% FBS (BI) was used for maintenance. Adenovirus type 5 encoding ENV (Ad5-ENV) was constructed and amplified by Shanghai Seven Sea Pharmtech Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
-
The mice used in this study were 8–10 week-old female C57BL/6 mice, which were purchased from the B&K Universal Group Limited (Shanghai, China) and maintained under specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions at the animal facilities of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (Shanghai, China). For each experimental group, there were at least six mice analyzed at each collection time point. For vaccination experiments, mice were intramuscular (i.m) inoculated with either 100 ng DNA vaccine (pSV1.0-OVA or pSV1.0-ENV) or empty vector pSV1.0 as control. The viral vaccine including 107 PFUs of rTTV-OVA or 108 TCID50 of Ad5-ENV in a volume of 100 μL was also inoculated intranasally. The mice were immunized twice with DNA vaccine followed by the viral vaccine at 2-week intervals. After vaccination, mice were monitored daily for clinical symptoms and survival. For immunoassay, immunized mice were sacrificed on day 14 after the last immunization for collection of peripheral blood and spleen tissues from which mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and single-splenocytes were obtained and analyzed, respectively. The animal experiments were performed in accordance with Home Office guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Shanghai Public Health Center.
-
We used deionized water as the solvent and prepared five freeze-drying protectants consisting of PEG, DEX, BSA and L-Glu. The detailed formulas, including the weight/volume ratio of each ingredient, are indicated in Table 1. The final concentration of the protectant was 1 mg/mL. Then, the constructed protectant was mixed with the different viral vaccines in 1 mL, and the protectant-to-vaccine volume ratio was 49:1. The viruses were then stored at − 80 ℃ overnight and were lyophilized at − 50 ℃ and 0.05 mbar for 24 h. Batches of freeze-dried vaccines were stored for 7, 14 and 28 days at 4 ℃ and 25 ℃, respectively.
Ingredients Formulation 1 Formulation 2 Formulation 3 Formulation 4 Formulation 5 (FR1, w/v) (FR2, w/v) (FR3, w/v) (FR4, w/v) (FR5, w/v) PEG 50 50 50 50 50 DEX 9 5 10 – 1 BSA – 4 9 – – L-Glu – – – 9 8 PEG: polyethylene glycol; DEX: dextran; BSA: bovine serum albumin; L-Glu: l-glutamic acid.
"–" means not included.Table 1. Compositions of the freeze-drying formulations.
-
After storage at the indicated temperature and time as mentioned above, the samples containing the rTTV-OVA and Ad5-ENV vaccines were separately rehydrated and serial diluted by tenfold in DMEM with 10% FBS.
Vero cells were cocultured with different concentrations of rTTV-OVA in duplicate in 24-well plates (500 μL/well) within maintenance medium at 37 ℃ for 48 h. Thereafter, a titrating mixture consisting of 2 × DMEM and low-melting-point agarose (1:1) with X-gal (200 μg/mL) was added to the culture (300 μL/well). After the mixture in the plate solidified at 4 ℃, the plate was continuously incubated at 37 ℃ for 4 h. The titer of the vaccine was determined by counting the blue viral plaques per well.
On the other hand, Ad5-ENV was titrated with different cell culture models. Different concentrations of Ad5-ENV were cocultured with 293A cells in ten replicates within 96-well plates (100 μL/well) at 37 ℃ for 10 days. The titer of Ad5-ENV was determined by observing the cell cytopathic effect (CPE) per well according to the formula: T = 101+d(S − 0.5)/0.1 mL (d: Log10 dilution, S: the number of wells that have CPE in ten replicates).
-
The vTTV-OVA- or Ad5-ENV-induced immune responses of mice were investigated using IFN-γ ELISPOT assays (BD Bioscience, Cat# 551083). A 96-well ELISPOT plate was coated with an anti-mouse IFN-γ monoclonal antibody (1:250 diluted with coating buffer, 100 μL/well) at 4 ℃ overnight. Then, the mouse splenocytes collected above (2 × 105) and the peptides (OVA peptide : OVA (257–264) and OVA (323–339); ENV peptide pool: ENV(B strain, RL 42)) (10 μg/mL) were added into each well (50 μL/well) (OVA peptide were synthesized by Shanghai Science Peptide Biological Technology Co. Ltd and ENV peptide pool were synthesized by GL Biochem (Shanghai) Ltd). The response induced by OVA was detected using peptide OVA (257–264) and OVA (323–339), and the response induced by ENV was detected using the ENV peptide pool (B strain, RL 42). The plate was incubated at 37 ℃ for 20 h in a fully humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 and was subjected to the detection of IFN-γ release using an automated ELISPOT plate reader (ChampSpot III Elispot Reader, Saizhi, Beijing, China). Each spot represented an IFN-γ-producing splenocyte, and more than 50 spots/106 cells were determined to be positive.
-
Freshly isolated splenocytes or lymphocytes were plated into round-bottom 96-well plates (2 × 106 cells per well) and stimulated with 5 μg/mL OVA peptide: OVA(257–264) and OVA(323–339) and ENV peptide pool: ENV(B strain, RL 42). 1 h later, brefeldin A (Cell Signaling Technology Cat#9972S) and monesin (Sigma Cat#1445481) were added to each well at final concentrations of 1 μg/mL and 1 μmol/L. Then 7 h later, the stimulation were stopped by washing the plates with R10 medium and 4 cell surface markers (CD3, CD8, CD44, and CD62L) were stained on ice with uorescein labeled antibodies, including PerCP-Cy5.5-labeled anti-mouse CD3 (Clone: 17A2, Biolegend Cat# 100218), Pacic Blue labeled anti-mouse CD8 (Clone: 53-6.7, Biolegend Cat# 100725), FITC-labeled anti-mouse CD44 (Clone: IM7, eBioscience Cat# 11-0441-81), and APC-eFluor780-labeled anti-mouse CD62L (Clone: MEL-14, eBioscience Cat# 47-0621-80). Next, the cells were fixed and permeablized, and intracellular IFN-γ was stained with PE-conjugated anti-mouse IFN-γ (Clone: XMG1.2, Biolegend Cat# 505808). Stained samples were measured using BD FACS Aria I. Data analysis was done by using FlowJo X software (Tree Star, Inc).
-
ELISA was used to assess the serum antibody titers against OVA and ENV. Each well of a 96-well EIA/RIA plate was coated with 100 μL of OVA protein (1 μg/mL) or ENV protein (1 μg/mL) at 4 ℃ overnight and was blocked with 200 μL 10% FBS. The immunized mice sera were diluted twofold, and 100 μL/well was added to the plate. The goat anti-mouse IgG (1:2000) was used to detect the antibody against OVA or ENV in mouse serum. Mouse serum antibody titers were assessed with the microplate reader (absorbance at 450–570 nm) and calculated by the correction number larger than 2 × (negative mean + SD).
-
All data were expressed as the mean ± SD of each group, and the difference comparison between two groups was conducted by unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-tests. The difference was considered statistically significant when P values were < 0.05 (***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05).
Vaccine Strains and Cell Lines
Animal Study
Formulations of the Freeze-Drying Protectant and Lyophilization
Titration of Viral Vaccines
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Spot (ELISPOT) Assay
Intracellular Cytokine Staining (ICS)
Antibody Titration
Statistical Analysis
-
To test the protection of the formulations from freeze-drying damage, the titration of vaccine rTTV-OVA or Ad5-ENV was performed after storage at the indicated temperature and time as mentioned above.
The titer of poxvirus vaccine rTTV-OVA post lyophilization in formulation #3 (FR3) was the highest compared to those in PBS (P = 0.0058) and other formulations (Fig. 1A). Then, we explored the protection of freeze-drying formulations under cold chain conditions. After storage at 4 ℃ for 7 to 28 days, the titers of rTTV-OVA in FR2 (4.37 × 107 PFUs/mL) and FR3 (4.35 × 107 PFUs/mL) were higher than those in other formulations 28 days post storage (P < 0.001) (Fig. 1B). Therefore, FR2 and FR3 were used as the optimal formulations for rTTV-OVA stored at 4 ℃ in the next study.
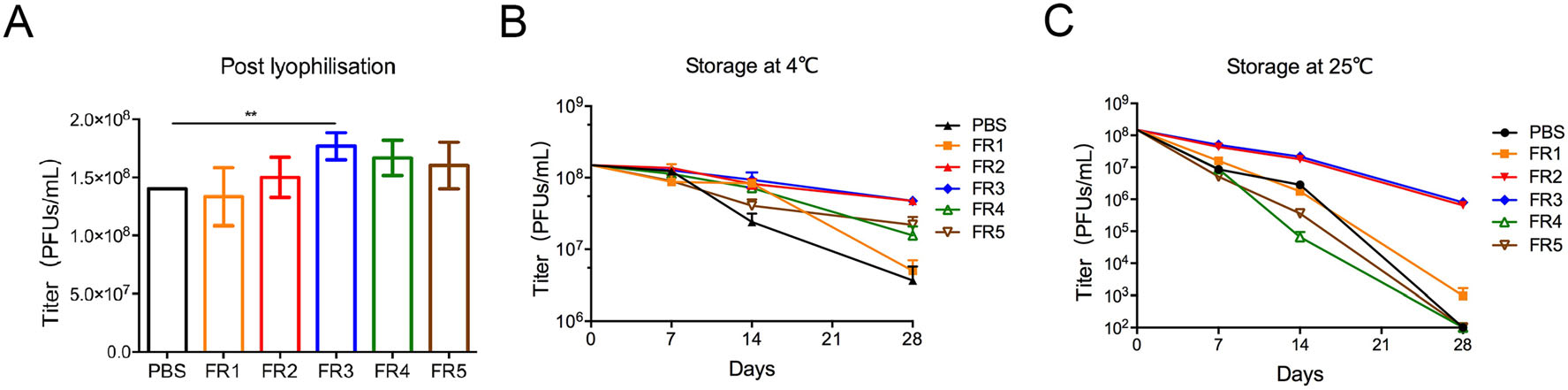
Figure 1. Freeze-drying formulations #2 and #3 effectively protected the activity of poxvirus vaccine. The infectivity of recombinant poxvirus vaccines (rTTV-OVA) protected by six formulations were detected post lyophilization and in different storage conditions. The titer is detected by counting the blue viral plaques per well. A Titers of poxvirus in six formulations post lyophilization. The titer of FR3 was slightly higher than that of the other formulations (**P < 0.01). B–C The protected rTTV-OVAs were stored at 4 ℃ (B) or 25 ℃ (C) for 7/14/28 days post lyophilization. The titers of vaccines in FR2 and FR3 are higher than that in any other formulation.
After 28 days of storage at 25 ℃, the titers of rTTV-OVA in FR2 and FR3 were still above 1 × 106 PFUs/mL, while the titers of other groups were almost unable to be detected (Fig. 1C). Therefore, the freeze-drying formulations #2 and #3 maintained the infectivity of rTTV-OVA when stored at 4 ℃ and at the ambient temperature.
However, FR2 and FR3 did not protect the adenovirus vaccine Ad5-ENV post lyophilization (data not shown). In contrast, the titers of Ad5-ENV maintained in FR4 (4.28 × 108 TCID50/mL, P < 0.001) and FR5 (3.93 × 108 TCID50/mL, P < 0.001) were effectively protected (Fig. 2A). Ad5-ENV was treated similarly to rTTV-OVA. After storage at 4 ℃ for up to 28 days, the titer of Ad5-ENV was reduced slightly (0.3 to 0.5 log of TCID50/mL) when it was stored in FR4, FR5 and FR1, but those stored in PBS were reduced significantly (3 log of TCID50/mL) (Fig. 2B). After stored at 25 ℃ for 28 days, the titer of Ad5-ENV in FR4 and FR5 decreased 0.6 to 1 log of TCID50/mL (5.73 × 107 TCID50/mL and 1 × 107 TCID50/mL, respectively), while those in other groups were almost unable to be detected (Fig. 2C). The freeze-drying formulations #4 and #5 maintained the infectivity of Ad5-ENV at storage temperatures of 4 ℃ and the ambient temperature.
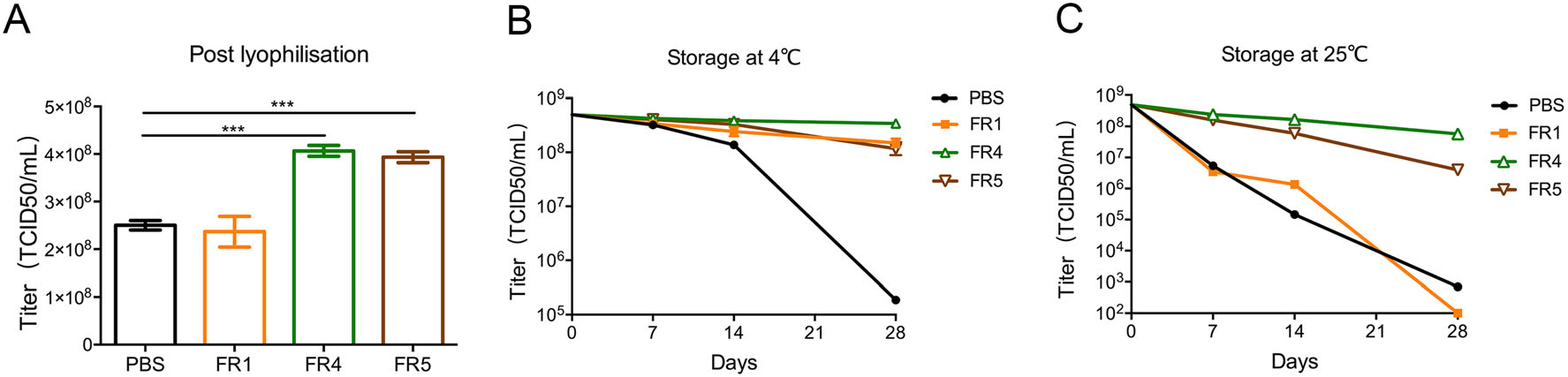
Figure 2. Freeze-drying formulations #4 and #5 effectively protected adenovirus vaccine activity. The infectivity of recombinant adenovirus vaccines (Ad5-ENV) protected by different formulations was detected post lyophilization. The titer is detected by 293A cells. A Image showing titers of adenovirus in four formulations post lyophilization. The titers of vaccines in FR4 and FR5 were higher than those in PBS (***P < 0.001). B–C The protection of Ad5-ENV stored at 4 ℃ (B) or 25 ℃ (C) for 7/14/28 days post lyophilization. The titers of vaccines in FR4 and FR5 are higher than that in FR1.
-
According to the previous screening results, FR2 and FR3 were used to protect rTTV-OVA, and FR4 and FR5 were used to protect Ad5-ENV in the following immunogenicity study.
-
To determine whether the newly prepared freeze-drying formulations FR2 and FR3 could protect the immunogenicity of the recombinant poxvirus vaccine rTTV-OVA, we immunized C57BL/6 mice with a prime/boost strategy (Fig. 3A). Briefly, four groups of mice were immunized three times with 14 days interval. The empty DNA vector pSV1.0 was used for all three inoculations in the mock group. In the other three experimental groups, the first two inoculations of priming antigens were all DNA vaccines (pSV1.0-OVA), but the boosting antigens of the 3rd inoculation was different and consisted of rTTV-OVA without lyophilization or with lyophilization in FR2 or FR3, respectively.
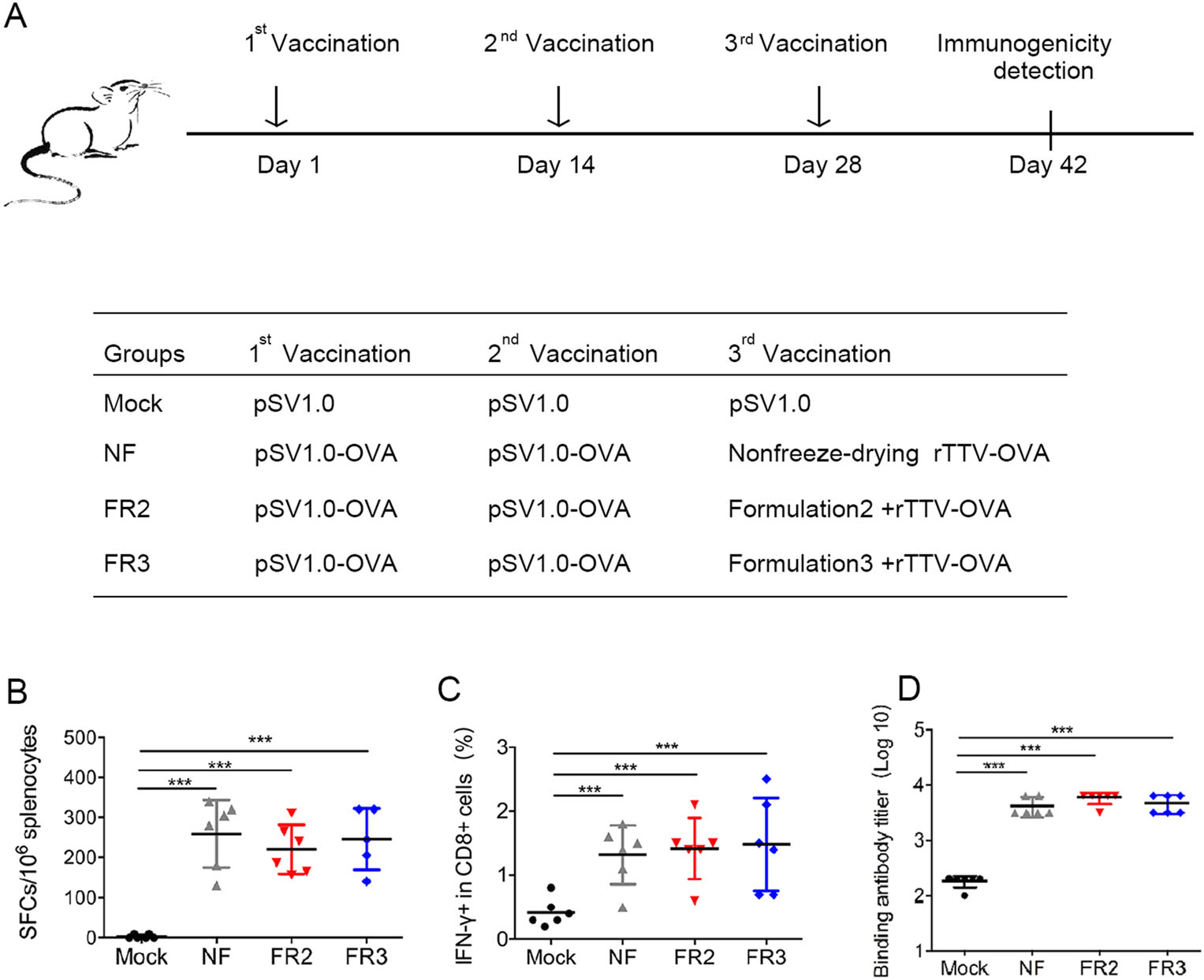
Figure 3. Freeze-drying formulations #2 and #3 protect the immunogenicity of poxvirus vaccine from being damaged due to lyophilization. A Vaccination schedule in C57BL/6 mice. Three different groups were designed using the same two inoculations of the DNA vaccine and different treatments of recombinant poxvirus vaccine. Each DNA vaccine (pSV1.0-OVA 100 ng per mouse) and poxvirus vaccine (rTTV-OVA 107 PFUs per mouse) were administered into mice via intramuscular injection at 2-week intervals. Two weeks after the last vaccination, we detected immunogenicity of viral vaccines. B–C The protection of antigen-specific T cell responses was detected by ELISPOT (B) and intracellular cytokine staining (C). Mouse splenocytes were stimulated by peptide OVA(257–264) and OVA(323–339). D The protection of specific binding antibodies was measured by ELISA at the same time. Data are the mean of each cohort (N = 6), and error bars indicate SD (***P < 0.001).
Two weeks after the last vaccination with rTTV-OVA, the mice were euthanized, and the splenocytes were collected for immune response detection.
First, the IFN-γ response was detected using ELISPOT, and there was no significant difference in the number of spot-forming cells (SFCs)/106 splenocytes in the lyophilized group FR2 (202.20 ± 48.08) or group FR3 (246.00 ± 77.25) compared to the nonfreeze-drying group (NF) (246.00 ± 77.25) (Fig. 3B). The same phenomenon was also observed when the IFN-γ response in CD8+ T cells was detected using intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) (Fig. 3C). Moreover, the humoral immune response was investigated using antibody titration. The titer of the binding antibody in non-freeze-drying group (NF) was 3.605 ± 0.142, which was comparable to those in groups FR2 (3.755 ± 0.112) and FR3 (3.66 ± 0.150) (Fig. 3D).
These results suggested that FR2 and FR3 could effectively protect the immunogenicity of the poxvirus vaccine during lyophilization, and the protected vaccine could activate cellular and humoral immunity comparable to those induced by the fresh vaccine.
-
The protective effect of the freeze-drying formulations FR4 and FR5 on the immunogenicity of the recombinant adenovirus vaccine Ad5-ENV was investigated using C57BL/6 mice with a prime/boost strategy (Fig. 4A) similar to that used for the recombinant poxvirus vaccine rTTV-OVA, except the boosting antigens were Ad5-ENV without lyophilization or Ad5-ENV with lyophilization in FR4 or FR5, respectively.
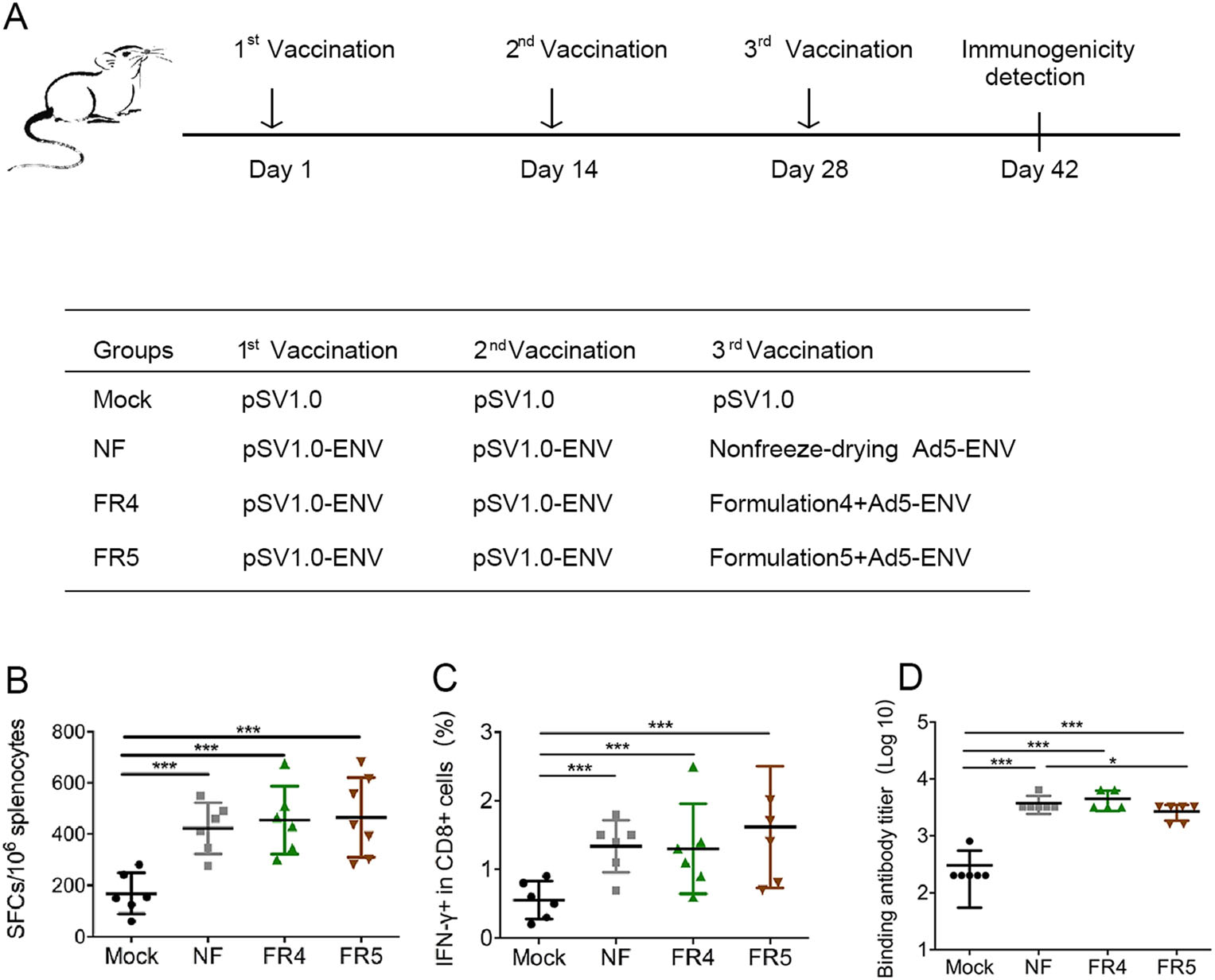
Figure 4. Freeze-drying formulations #4 and #5 protect the immunogenicity of adenovirus vaccine from being damaged due to lyophilization. A Vaccination schedule in C57BL/6 mice. Three different groups were designed using the same two inoculations of the DNA vaccine and different treatments of recombinant adenovirus vaccine. Each DNA vaccine (pSV1.0-ENV 100 ng per mouse) and adenovirus vaccine (Ad5-ENV 108 TCID50 per mouse) were administered into mice via intramuscular injection at 2-week intervals. Two weeks after the last vaccination, we detected the immunogenicity of the viral vaccines. B–C The protection of antigen-specific T cell responses was detected by ELISPOT (B) and intracellular cytokine staining (C). Mouse splenocytes were stimulated by the ENV peptide pool. D The protection of specific binding antibodies was measured by ELISA at the same time. Data are the mean of each cohort (N = 6), and error bars indicate SD (***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05).
The immune responses were also detected using ELISPOT and ICS. There was no significant difference in SFCs/106 splenocytes observed between the Ad5-ENV lyophilized groups FR4 (463.82 ± 102.01) and FR5 (452.92 ± 246.67) and the Ad5-ENV nonlyophilized group NF (425.00 ± 218.79) (Fig. 4B). The same phenomenon was also observed in the IFN-γ response in CD8+ T cells detected using ICS (Fig. 4C).
In addition, the humoral immune response induced by ENV was investigated using antibody titration. The titer of the binding antibody induced by Ad5-ENV in group NF and group FR4 was similar (3.555 ± 0.112 vs 3.625 ± 0.147), while the titer in group FR5 (3.405 ± 0.141) was comparable, although slightly decreased (Fig. 4D).
These data implied that FR4 and FR5 could protect the immunogenicity of the recombinant adenovirus vaccine during lyophilization, and the protected vaccine could activate comparable cellular and humoral immunity to those induced by the fresh vaccine.
Efficacy of Different Formulations for Two Kind of Vaccines Under Different Conditions
Immunogenicity and Efficacy of the Viral Vaccines in Different Formulations
Immunogenicity and Efficacy of rTTV-OVA Under the Protection of FR2 and FR3
Immunogenicity and Efficacy of Ad5-ENV Under the Protection of FR4 and FR5
-
Previous investigations on vaccine storage conditions were focused on improving the effect of cold chain processing and transportation that consumes more resources (Shin et al. 2018). We designed novel formulations, which could preserve the activity and stability of viral vaccines such as poxvirus vaccine and adenovirus vaccine, during storage at an ambient temperature. Particularly, with the protection of FR4, the titer of the adenovirus vaccine stored at 25 ℃ for 28 days only decreased 0.6 log. Compared with Ad5 protected in only PEG, we used FR4 (PEG+L-Glu) to lengthen the storage time by 4 times while the titer value declined by 0.6 log. Improving the protection of vaccine at 25 ℃ could break the financial and technological barriers to widespread vaccine distribution.
Four ingredients were added to the freeze-drying protectant and were PEG, DEX, BSA and L-Glu. PEG can reduce the damage of the virus through a dehydration effect. DEX, a type of oligosaccharide, can protect viral activity from damage. BSA, a kind of enzyme stabilizer, can prevent enzyme decomposition and denaturation. The materials described here might be components of novel cryoprotectants. l-glutamate has not been reported as a freeze-drying protective agent. However, Glu has both acidic and basic amino acid ions, can buffer the pH changes in the freeze-drying process and can protect the activity of the vaccines. Different kinds of viral vaccines had their own optimized formulation. The poxvirus vaccine has an entire envelope structure, but the adenovirus vaccine has non-envelope structure. An ingredient shared by FR4 and FR5, but not present in other formulations, is L-Glu. Therefore, we speculate that the protective effect of FR4/FR5 on non-enveloped virus might be conferred at least in part by L-Glu through its activity as a protein antioxidant (Babu and Bawari 1997). In addition to the replication-competent adenovirus vectored vaccine such as Ad5 used in this study, the replication-incompetent adenovirus vectors are also commonly used in vaccine development to avoid strong and lasting immune response caused by replication-competent vector (Lapuente et al. 2018). Given that the replication-incompetent adenovirus vectors were generally constructed by deletion of genes involved in viral replication and proliferation such as E1, E3 without changing structure-related genes, whether the vaccine efficacies of these vectors can also be improved by the freeze-drying protectant will be of interest for future studies to assess.
Many studies on vaccine lyophilization focus on vaccine morphology characteristics or use thermography to prove the combination of vaccines and ingredients (Shokri et al. 2019; Yusuf et al. 2019). The number of solutions was determined for prolonged storage at 4 ℃. Jae U. Jung found a stable and safe formula that can protect the antigenicity of the Sabin inactivated poliovirus vaccine for 4 weeks at an ambient temperature (Shin et al. 2018). J. Drew found a system that can keep the adenovirus titer at 105 (PFU/mL) at ambient temperature (Stewart et al. 2014). Many studies have only explored the protection of viral vaccine infectivity while ignoring the protection of vaccine immunogenicity, which is another important part of vaccine stability. The formulations in our work successfully increased two aspects of vaccine stability and maintained them at a high level (keeping the adenovirus titer above 108 TCID50/mL); these formulations not only maintained vaccine activity but also protected the vaccine antigenicity from being damaged.
Currently, the storage and transportation of antibodies, proteins and nucleic acids remains a large challenge. It also remains undetermined if our freeze-drying formulas can protect other vaccines, such as poliovirus, rubella virus, and influenza vaccines or parts of vaccine-like liposomes, proteins, and antigens. However, a formulation to protect all aspects of viral vaccine activity remains to be developed.
-
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program (2016YFC1303402), the National 13th Five-Year Grand Program on Key Infectious Disease Control (2018ZX10301403, 2017ZX10202102-006), and the Intramural Funding from Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center.
-
WY, JX and XZ designed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. WY contributed reagents for the formulations. YC, QL and YZ detected the titers of the poxvirus and adenovirus vaccines. YC and TC performed the animal vaccination and challenge experiments. YC analyzed the antibody responses and specific CD8+ T cell responses. WY, JX and XZ supervised all experiments and finalized the manuscript.
Author Contributions
-
The authors declare no competing interests.
-
Animal care and experiments were conducted with a protocol that was strictly reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (Permit Number: 2013-E013). All experiments were performed at least two times with similar results, and one representative result is shown.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: