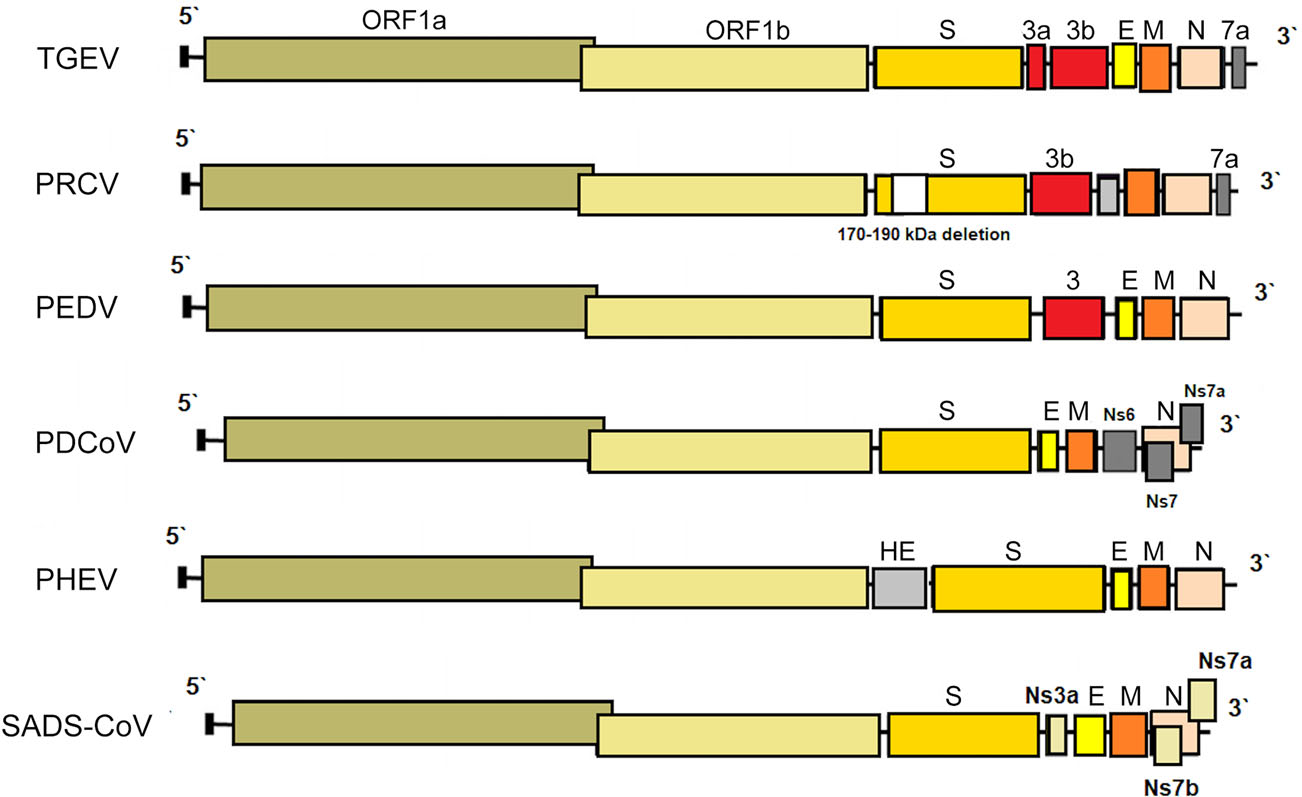
-
Akimkin V, Beer M, Blome S, Hanke D, Höper D, Jenckel M, Pohlmann A (2016) New chimeric porcine coronavirus in swine feces, Germany, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis 22: 1314–1315
doi: 10.3201/eid2207.160179
-
Andries K, Pensaert MB (1980) Immunofluorescence studies on the pathogenesis of hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus infection in pigs after oronasal inoculation. Am J Vet Res 41: 1372–1378
-
Andries K, Pensaert M, Callebaut P (1978) Pathogenicity of hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis (vomiting and wasting disease) virus of pigs, using different routes of inoculation. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B 25: 461–468
-
Annamalai T, Saif LJ, Lu Z, Jung K (2015) Age-dependent variation in innate immune responses to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection in suckling versus weaned pigs. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 168: 193–202
doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.09.006
-
Appel M, Greig AS, Corner AH (1965) Encephalomyelitis of swine caused by a hemagglutinating virus. Ⅳ. Transmission studies. Res Vet Sci 6: 482–489
doi: 10.1016/S0034-5288(18)34728-3
-
Atanasova K, Van Gucht S, Barbé F, Lefebvre DJ, Chiers K, Van Reeth K (2008) Lung cell tropism and inflammatory cytokine-profile of porcine respiratory coronavirus infection. Open Vet Sci J 2: 117–126
doi: 10.2174/1874318808002010117
-
Bevins SN, Lutman M, Pedersen K, Barrett N, Gidlewski T, Deliberto TJ, Franklin AB (2018) Spillover of swine coronaviruses, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 24: 1390–1392
doi: 10.3201/eid2407.172077
-
Bjustrom-Kraft J, Woodard K, Gimenez-Lirola L, Setness B, Ji J, Lasley P, Nelson E, Zhang JQ, Baum D, Gauger P, Main R, Zimmerman J (2018) Serum and mammary secretion antibody responses in porcine epidemic diarrhea-immune gilts following porcine epidemic diarrhea vaccination. J Swine Health Prod 26: 34–40
-
Bohl EH (1989) Transmissible gastroenteritis virus (classical enteric variant). In: Pensaert MB (ed.) Virus infections of vertebrates, vol 2, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 139–153
-
Boley PA, Alhamo MA, Lossie G, Yadav KK, Vasquez-Lee M, Saif LJ, Kenney SP (2020) Porcine deltacoronavirus infection and transmission in poultry, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 26: 255–265
doi: 10.3201/eid2602.190346
-
Boniotti MB, Papetti A, Lavazza A, Alborali G, Sozzi E, Chiapponi C, Faccini S, Bonilauri P, Cordioli P, Marthaler D (2016) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and discovery of a recombinant swine enteric coronavirus, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis 22: 83–87
doi: 10.3201/eid2201.150544
-
Bowman AS, Krogwold RA, Price T, Davis M, Moeller SJ (2015) Investigating the introduction of porcine epidemic Diarrhea virus into an Ohio swine operation. BMC Vet Res 11: 38
doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0348-2
-
Bridgen A, Tobler K, Ackermann M (1993) Identification of coronaviral conserved sequences and application to viral genome amplification. Adv Exp Med Biol 342: 81–82
-
Burlatschenko S, Arsenault C (2015) Elimination of porcine respiratory coronavirus by early weaning and segregation. J Swine Health Prod 23: 208–213
-
Callebaut TP, Pensaert MB, Hooyberghs J (1989) A competitive inhibition ELISA for the differentiation of serum antibodies from pigs infected with transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) or with the TGEV-related porcine respiratory coronavirus. Vet Microbiol 20: 9–19
doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90003-5
-
Callebaut P, Cox E, Pensaert M, Van Deun K (1990) Induction of milk IgA antibodies by porcine respiratory coronavirus infection. Adv Exp Med Biol 276: 421–428
-
Callebaut P, Pensaert M (1995) Expression and immunogenicity of the spike glycoprotein of porcine respiratory coronavirus encoded in the E3 region of adenovirus. Adv Exp Med Biol 380: 65–270
-
Cao L, Ge X, Gao Y, Ren Y, Ren X, Li G (2015) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection induces NF-kappaB activation through the TLR2, TLR3 and TLR9 pathways in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. J Gen Virol 96: 1757–1767
doi: 10.1099/vir.0.000133
-
Carman S, Josephson G, McEwen B, Maxie G, Antochi M, Eernisse K, Nayar G, Halbur P, Erickson G, Nilsson E (2002) Field validation of a commercial blocking ELISA to differentiate antibody to transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) and porcine respiratory coronavirus and to identify TGEV-infected swine herds. J Vet Diagn Invest 14: 97–105
doi: 10.1177/104063870201400202
-
Cartwright SF, Lucas M (1970) Vomiting and wasting disease in piglets. Virological and epidemiological studies. Vet Rec 86: 278–280
doi: 10.1136/vr.86.10.278
-
Chan JF, To KK, Tse H, Jin DY, Yuen KY (2013) Interspecies transmission and emergence of novel viruses: lessons from bats and birds. Trends Microbiol 21: 544–555
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2013.05.005
-
Chattha KS, Roth JA, Saif LJ (2015) Strategies for design and application of enteric viral vaccines. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 3: 375–395
doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-022114-111038
-
Chen Q, Gauger P, Stafne M, Thomas J, Arruda P, Burrough E, Madson D, Brodie J, Magstadt D, Derscheid R, Welch M, Zhang J (2015) Pathogenicity and pathogenesis of a United States porcine deltacoronavirus cell culture isolate in 5-day-old neonatal piglets. Virology 482: 51–59
doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.024
-
Chen F, Knutson TP, Rossow S, Saif LJ, Marthaler DG (2019) Decline of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and its complex evolutionary relationship with porcine respiratory coronavirus in the United States. Sci Rep 9: 3953
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40564-z
-
Chen Y, Liu Q, Guo D (2020) Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J Med Virol 92: 418–423
doi: 10.1002/jmv.25681
-
Cima G (2013) Viral disease affects US pigs: porcine epidemic diarrhea found in at least 11 states. J Am Vet Med Assoc 243: 30–31
-
Crawford K, Lager KM, Kulshreshtha V, Miller LC, Faaberg KS (2016) Status of vaccines for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States and Canada. Virus Res 226: 108–116
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.08.005
-
Dastjerdi A, Carr J, Ellis RJ, Steinbach F, Williamson S (2015) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus among farmed pigs, Ukraine. Emerg Infect Dis 21: 2235–2237
doi: 10.3201/eid2112.150272
-
De Arriba ML, Carvajal A, Pozo J, Rubio P (2002a) Mucosal and systemic isotype-specific antibody responses and protection in conventional pigs exposed to virulent or attenuated porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 85: 85–97
doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(01)00417-2
-
De Arriba ML, Carvajal A, Pozo J, Rubio P (2002b) Rubio Isotype-specific antibody-secreting cells in systemic and mucosal associated lymphoid tissues and antibody responses in serum of conventional pigs inoculated with PEDV. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 84: 1–16
doi: 10.1016/S0165-2427(01)00386-5
-
De Nova PJG, Cortey M, Díaz I, Puente H, Rubio P, Martín M, Carvajal A (2020) A retrospective study of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) reveals the presence of swine enteric coronavirus (SeCoV) since 1993 and the recent introduction of a recombinant PEDV-SeCoV in Spain. Transbound Emerg Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13666
-
Derbyshire JB, Jessett DM, Newman G (1969) An experimental epidemiological study of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis. J Comp Pathol 79: 445–452
doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(69)90064-4
-
Diel DG, Lawson S, Okda F, Singrey A, Clement T, Fernandes MHV, Christopher-Hennings J, Nelson EA (2016) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: an overview of current virological and serological diagnostic methods. Virus Res 226: 60–70
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.05.013
-
Doyle LP, Hutchings LM (1946) A transmissible gastroenteritis in pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 108: 257
-
Duarte M, Laude H (1994) Sequence of the spike protein of the porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus. J Gen Virol 75: 1195–1200
doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-5-1195
-
Enjuanes L, van der Zeijst BAM (1995) Molecular basis of transmissible gastroenteritis virus epidemiology. Coronaviridae 337–376
-
Enjuanes L, Sola I, Almazán F, Ortego J, Izeta A, González JM, Alonso S, Sánchez-Morgado JM, Escors D, Calvo E, Riquelme C, Sánchez CM (2001) Coronavirus derived expression systems. J Biotech 88: 183–204
doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(01)00281-4
-
Fan H, Zhang J, Ye Y, Tong T, Xie K, Liao M (2012) Complete genome sequence of a novel porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in south China. J Virol 86: 10248–10249
doi: 10.1128/JVI.01589-12
-
Fang P, Fang L, Hong Y, Liu X, Dong N, Ma P, Bi J, Wang D, Xiao S (2017) Discovery of a novel accessory protein NS7a encoded by porcine deltacoronavirus. J Gen Virol 98: 173–178
doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000690
-
Fenner F (2017) Chapter 24. Coronaviridae. In: Maclachlan NJ, Dubovi EJ (eds) Fenner's veterinary virology, 5th edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 435–461
-
Fu J, Chen R, Hu J, Qu H, Zhao Y, Cao S, Wen X, Wen Y, Wu R, Zhao Q, Ma X, Huang X (2020) Identification of a novel linear B-cell epitope on the nucleocapsid protein of porcine deltacoronavirus. Int J Mol Sci 21: 648
doi: 10.3390/ijms21020648
-
Garwes DJ, Stewart F, Cartwright SF, Brown I (1988) Differentiation of porcine coronavirus from transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Vet Rec 122: 86–87
doi: 10.1136/vr.122.4.86
-
Gimenez-Lirola LG, Zhang J, Carrillo-Avila JA, Chen Q, Magtoto R, Poonsuk K, Baum DH, Pineyro P, Zimmerman J (2017) Reactivity of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus structural proteins to antibodies against porcine enteric coronaviruses: diagnostic implications. J Clin Microbiol 55: 1426–1436
doi: 10.1128/JCM.02507-16
-
Goede D, Murtaugh MP, Nerem J, Yeske P, Rossow K, Morrison R (2015) Previous infection of sows with a "mild" strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus confers protection against infection with a "severe" strain. Vet Microbiol 176: 161–164
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.12.019
-
Gong L, Li J, Zhou Q, Xu Z, Chen L, Zhang Y, Xue C, Wen Z, Cao Y (2017) A new Bat-HKU2-like coronavirus in swine, China, 2017. Emerg Infect Dis 23: 1607–1609
doi: 10.3201/eid2309.170915
-
Grasland B, Bigault L, Bernard C, Quenault H, Toulouse O, Fablet C, Rose N, Touzain F, Blanchard Y (2015) Complete genome sequence of a porcine epidemic diarrhea s gene indel strain isolated in France in december 2014. Genome Announc 3: e00535-e615
-
Greig AS, Mitchell D, Corner AH, Bannister GL, Meads EB, Julian RJ (1962) A hemagglutinating virus producing encephalomyelitis in baby pigs. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci 26: 49–56
-
Halbur PG, Pallarés FJ, Opriessnig T, Vaughn EM, Paul PS (2003) Pathogenicity of three isolates of porcine respiratory coronavirus in the USA. Vet Rec 152: 358–361
doi: 10.1136/vr.152.12.358
-
Hammerberg C, Schurig GG, Ochs DL (1989) Immunodeficiency in young pigs. Am J Vet Res 50: 868–874
-
Hanke D, Jenckel M, Petrov A, Ritzmann M, Stadler J, Akimkin V, Blome S, Pohlmann A, Schirrmeier H, Beer M, Höper D (2015) Comparison of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses from Germany and the United States, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 21: 493–496
doi: 10.3201/eid2103.141165
-
He WT, Ji X, He W, Dellicour S, Wang S, Li L, Zhang L, Gilbert M, Zhu H, Xing G, Veit M, Huang Z, Han G-Z, Huang Y, Suchard MA, Baele G, Lemey P, Su S (2020) Genomic epidemiology, evolution, and transmission dynamics of porcine deltacoronavirus. Mol Biol Evol 37: 2641–2654
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa117
-
Herrewegh AA, Smeenk I, Horzinek MC, Rottier PJ, de Groot RJ (1998) Feline coronavirus type Ⅱ strains 79–1683 and 79–1146 originate from a double recombination between feline coronavirus type Ⅰ and canine coronavirus. J Virol 72: 4508–4514
doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.4508-4514.1998
-
Hirano N, Ono K (1998) A serological survey of human coronavirus in pigs of the Tohoku District of Japan. Adv Exp Med Biol 440: 491–494
-
Hirano N, Haga S, Fujiwara K (1993) The route of transmission of hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus (HEV) 67N strain in 4-week-old rats. Adv Exp Med Biol 342: 333–338
-
Huang YW, Dickerman AW, Pineyro P, Li L, Fang L, Kiehne R, Opriessnig T, Meng XJ (2013) Origin, evolution, and genotyping of emergent porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains in the United States. mBio 4: e00737–e1713
-
Janetanakit T, Lumyai M, Bunpapong N, Boonyapisitsopa S, Chaiyawong S, Nonthabenjawan N, Kesdaengsakonwut S, Amonsin A (2016) Porcine deltacoronavirus, Thailand, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis 22: 757–759
doi: 10.3201/eid2204.151852
-
Jung K, Saif LJ (2015) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: etiology, epidemiology, pathogenesis and immunoprophylaxis. Vet J 204: 134–143
doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2015.02.017
-
Jung K, Renukaradhya GJ, Alekseev KP, Fang Y, Tang Y, Saif LJ (2009) Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus modifies innate immunity and alters disease outcome in pigs subsequently infected with porcine respiratory coronavirus: implications for respiratory viral co-infections. J Gen Virol 90: 2713–2723
doi: 10.1099/vir.0.014001-0
-
Jung K, Annamalai T, Lu Z, Saif LJ (2015) Comparative pathogenesis of US porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) strain PC21A in conventional 9-day-old nursing piglets vs. 26-day-old weaned pigs. Vet Microbiol 178: 31–40
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.04.022
-
Jung K, Hu H, Saif LJ (2016) Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis. Virus Res 226: 50–59
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.04.009
-
Jung K, Miyazaki A, Saif LJ (2018) Immunohistochemical detection of the vomiting-inducing monoamine neurotransmitter serotonin and enterochromaffin cells in the intestines of conventional or gnotobiotic (Gn) pigs infected with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) and serum cytokine responses of Gn pigs to acute PEDV infection. Res Vet Sci 119: 99–108
doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2018.06.009
-
Killoran KE, Leedom-Larson KR (2016) Porcine respiratory coronavirus. Swine Health Information Center and Center for Food Security and Public Health. http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/pdf/shic-factsheetporcine-respiratory-coronavirus
-
Killoran KE, Leedom-Larson KR (2018) Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus. Swine Health Information Center and Center for Food Security and Public Health. http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/pdf/shic-factsheet-porcine-hemagglutinating-encephalomyelitis-virus
-
Kocherhans R, Bridgen A, Ackermann M, Tobler K (2001) Completion of the porcine epidemic diarrhoea coronavirus (PEDV) genome sequence. Virus Genes 23: 137–144
doi: 10.1023/A:1011831902219
-
Kochhar HS (2014) Canada: porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada: an emerging disease case study. Can Vet J 5: 1048–1049
-
Koonpaew S, Teeravechyan S, Frantz PN, Chailangkarn T, Jongkaewwattana A (2019) PEDV and PDCoV pathogenesis: the interplay between host innate immune responses and porcine enteric coronaviruses. Front Vet Sci 6: 34
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00034
-
Krempl C, Schultze B, Laude H, Herrler G (1997) Point mutations in the S protein connect the sialic acid binding activity with the enteropathogenicity of transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. J Virol 71: 3285–3287
doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.4.3285-3287.1997
-
Krishna VD, Kim Y, Yang M, Vannucci F, Molitor T, Torremorell M, Cheeran MC-J (2020) Immune responses to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in swine and protection against subsequent infection. PLoS ONE 15: e0231723
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231723
-
Lara-Romero R, Gómez-Núñez L, Cerriteño-Sánchez JL, Márquez-Valdelamar L, Mendoza-Elvira S, Ramírez-Mendoza H, Rivera-Benítez J (2018) Molecular characterization of the spike gene of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Mexico, 2013–2016. Virus Genes 54: 215–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-017-1528-x
doi: 10.1007/s11262-017-1528-x
-
Lee S, Lee C (2014) Complete genome characterization of korean porcine deltacoronavirus strain KOR/KNU14-04/2014. Genome Announc 2: e01191–e1214
-
Lee DU, Kwon T, Je SH, Yoo SJ, Seo SW, Sunwoo SY, Lyoo YS (2016) Wild boars harboring porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) may play an important role as a PEDV reservoir. Vet Microbiol 192: 90–94
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.07.003
-
Li G, Chen Q, Harmon KM, Yoon KJ, Schwartz KJ, Hoogland MJ, Gauger PC, Main RG, Zhang J (2014) Full-length genome sequence of porcine deltacoronavirus strain USA/IA/2014/8734. Genome Announc 2: e00278–e314
-
Li W, Hulswit RJG, Kenney SP, Widjaja I, Jung K, Alhamo MA, van Dieren B, van Kuppeveld FJM, Saif LJ, Bosch BJ (2018) Broad receptor engagement of an emerging global coronavirus may potentiate its diverse cross-species transmissibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115: E5135–E5143
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1802879115
-
Li HY, Li BX, Liang QQ, Jin XH, Tang L, Ding QW, Wang ZX, Wei ZY (2020) Porcine deltacoronavirus infection alters bacterial communities in the colon and feces of neonatal piglets. Microbiologyopen 9: e1036
-
Lin CM, Annamalai T, Liu X, Gao X, Lu Z, El-Tholoth M, Hu H, Saif LJ, Wang Q (2015) Experimental infection of a US spike-insertion deletion porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in conventional nursing piglets and cross-protection to the original US PEDV infection. Vet Res 46: 134
doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0278-9
-
Lin CM, Ghimire S, Hou Y, Langel SN, Vlasova AN, Saif LJ, Wang Q (2019) Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of attenuated porcine epidemic diarrhea virus PC22A strain in conventional weaned pigs. BMC Vet Res 15: 26
doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1756-x
-
Liu C, Tang J, Ma Y, Liang X, Yang Y, Peng G, Qi Q, Jiang S, Li J, Du L (2015) Receptor usage and cell entry of porcine epidemic diarrhea coronavirus. J Virol 89: 6121–6125
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00430-15
-
Luo Y, Zhang J, Deng X, Ye Y, Liao M, Fan H (2012) Complete genome sequence of a highly prevalent isolate of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in South China. J Virol 86: 9551
doi: 10.1128/JVI.01455-12
-
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Liang X, Lou F, Oglesbee M, Krakowka S, Li J (2015) Origin, evolution, and virulence of porcine deltacoronaviruses in the United States. MBio 6: e00064
-
Ma Y, Zhang Y, Liang X, Oglesbee M, Krakowka S, Niehaus A, Wang G, Jia A, Song H, Li J (2016) Two-way antigenic cross-reactivity between porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus. Vet Microbiol 186: 90–96
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.004
-
Magtoto R, Poonsuk K, Baum D, Zhang J, Chen Q, Ji J, Piñeyro P, Zimmerman J, Giménez-Lirola LG (2019) Evaluation of the serologic cross-reactivity between transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus and porcine respiratory coronavirus using commercial blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. mSphere 4: e00017–19
-
Mandelik R, Sarvas M, Jackova A, Salamunova S, Novotny J, Vilcek S (2018) First outbreak with chimeric swine enteric coronavirus (SeCoV) on pig farms in Slovakia—lessons to learn. Acta Vet Hung 66: 488–492
doi: 10.1556/004.2018.043
-
Marthaler D, Raymond L, Jiang Y, Collins J, Rossow K, Rovira A (2014) Rapid detection, complete genome sequencing, and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis 20: 1347–1350
-
Mayo KA (2017) Emerging swine enteric coronaviruses: comparison of pathogenicity and antibody response. Graduate Theses and Dissertations 16732
-
Mengeling WL, Cutlip RC (1972) Experimentally induced infection of newborn pigs with hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus strain 67N. Am J Vet Res 33: 953–956
-
Mole B (2013) Deadly pig virus slips through US borders. Nature 499: 388
doi: 10.1038/499388a
-
Moon HW, Kemeny LJ, Lambert G, Stark SL, Booth GD (1975) Age-dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine. Ⅲ. Effects of epithelial cell kinetics on coronavirus production and on atrophy of intestinal villi. Vet Pathol 12: 434–445
doi: 10.1177/0300985875012005-00610
-
Mora-Díaz JC, Piñeyro PE, Houston E, Zimmerman J, Giménez-Lirola LG (2019) Porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus: a review. Front Vet Sci 6: 53
doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00053
-
Mora-Díaz JC, Magtoto R, Houston E, Baum D, Carrillo-Ávila JA, Temeeyasen G, Zimmerman J, Piñeyro P, Giménez-Lirola L (2020) Detecting and monitoring porcine hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus, an underresearched betacoronavirus. mSphere 5: e0019920
-
Narita M, Kawamura H, Haritani M, Kobayashi M (1989a) Demonstration of viral antigen and immunoglobulin (IgG and IgM) in brain tissue of pigs experimentally infected with haemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus. J Comp Pathol 100: 119–128
doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(89)90122-9
-
Narita M, Kawamura H, Tsuboi T, Haritani M, Kobayashi M (1989b) Immunopathological and ultrastructural studies on the tonsil of gnotobiotic pigs infected with strain 67N of haemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus. J Comp Pathol 100: 305–312
doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(89)90108-4
-
Niederwerder MC, Hesse RA (2018) Swine enteric coronavirus disease: a review of 4 years with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada. Transbound Emerg Dis 65: 660–675
doi: 10.1111/tbed.12823
-
Ojkic D, Hazlett M, Fairles J, Marom A, Slavic D, Maxie G, Alexandersen S, Pasick J, Alsop J, Burlatschenko S (2015) The first case of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada. Can Vet J 56: 149–152
-
Ouyang K, Shyu DL, Dhakal S, Hiremath J, Binjawadagi B, Lakshmanappa YS, Guo R, Ransburgh R, Bondra KM, Gauger P, Zhang J, Specht T, Gilbertie A, Minton W, Fang Y, Renukaradhya GJ (2015) Evaluation of humoral immune status in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) infected sows under field conditions. Vet Res 46: 140
doi: 10.1186/s13567-015-0285-x
-
Pan Y, Tian X, Qin P, Wang B, Zhao P, Yang YL, Wang L, Wang D, Song Y, Zhang X, Huang YW (2017) Discovery of a novel swine enteric alphacoronavirus (seacov) in southern China. Vet Microbiol 211: 15–21
doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.09.020
-
Pasick J, Berhane Y, Ojkic D, Maxie G, Embury-Hyatt C, Swekla K, Handel K, Fairles J, Alexandersen S (2014) Investigation into the role of potentially contaminated feed as a source of the first-detected outbreaks of porcine epidemic diarrhea in Canada. Transbound Emerg Dis 61: 397–410
doi: 10.1111/tbed.12269
-
Paul PS, Mengeling WL (1984) Persistence of passively acquired antibodies to hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus in swine. Am J Vet Res 45: 932–934
-
Pejsak Z (2007) Koronawirusowe zapalenie żołądka i jelit świń, in: Ochrona Zdrowia Świń, Państwowe Wyd. Rolnicze, pp, 223–224
-
Peng JY, Punyadarsaniya D, Shin DL, Pavasutthipaisit S, Beineke A, Li G, Wu NH, Herrler G (2020) The cell tropism of porcine respiratory coronavirus for airway epithelial cells is determined by the expression of porcine aminopeptidase N. Viruses 23: 1211
-
Pensaert MB, Callebaut PE (1974) Characteristics of a coronavirus causing vomition and wasting in pigs. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch 44: 35–50
doi: 10.1007/BF01242179
-
Pensaert MB, de Bouck P (1978) A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch Virol 58: 243–247
doi: 10.1007/BF01317606
-
Pensaert MB, de Bouck P, Reynolds DJ (1981) An immunoelectron microscopic and immunofluorescent study on the antigenic relationship between the coronavirus-like agent, CV 777, and several coronaviruses. Arch Virol 68: 45–52
doi: 10.1007/BF01315166
-
Pilchard EI (1965) Experimental transmission of transmissible gastroenteritis virus by starlings. Am J Vet Res 26: 1177–1179
-
Pillatzki A, Gauger P, Madson D, Burrough E, Zhang J, Chen Q, Magstadt D, Arruda P, Stevenson G, Yoon KJ (2015) Experimental inoculation of neonatal piglets with feed naturally contaminated with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). J Swine Health Prod 23: 317–320
-
Putics A, Gorbalenya AE, Ziebuhr J (2006) Identification of protease and ADP-ribose 1''-monophosphatase activities associated with transmissible gastroenteritis virus non-structural protein 3. J Gen Virol 87: 651–656
doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81596-0
-
Qian S, Jia X, Gao Z, Zhang W, Xu Q, Li Z (2020) Isolation and identification of porcine deltacoronavirus and alteration of immunoglobulin transport receptors in the intestinal mucosa of PDCoV-infected piglets. Viruses 12: 79
doi: 10.3390/v12010079
-
Raihana RR, Hayakawa M, Sugiura E, Sugiura H, Hanaki K, Taniguchi T, Honda E (2009) Analysis of the properties of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against the hemagglutinating encephalomyelitis virus and inhibition of HEV infection by specific MAb. J Vet Med Sci 71: 447–452
doi: 10.1292/jvms.71.447
-
Roe CK, Alexander TJA (1958) Disease of nursing pigs previously unreported in Ontario. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci 22: 305–307
-
Saif LJ (1993) Coronavirus immunogens. Vet Microbiol 37: 285–297
doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90030-B
-
Saif LJ, Sestak K (2006) Transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine respiratory coronavirus. In: Straw BE (ed) Diseases of swine, 9th edn. Blackwell Publishing, Ames, pp 489–516
-
Saif LJ, Pensaert MB, Sestak K, Yeo S, Jung K (2012) Coronaviruses. In: Zimmerman JJ, Karriker LA, Ramirez A, Schwartz KJ, Stevenson GW (eds) Diseases of swine, 10th edn. Wiley, Ames, pp 501–524
-
Sestak K, Lanza I, Park SK, Weilnau PA, Saif LJ (1996) Contribution of passive immunity to porcine respiratory coronavirus to protection against transmissible gastroenteritis virus challenge exposure in suckling pigs. Am J Vet Res 57: 664–671
-
Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C, Liu R, He X, Shuai L, Sun Z, Zhao Y, Liang L, Cui P, Wang J, Zhang X, Guan Y, Chen H, Bu Z (2020) Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS–coronavirus 2. BioRxiv: 2020.03.30.015347
-
Song D, Park B (2012) Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus: a comprehensive review of molecular epidemiology, diagnosis, and vaccines. Virus Genes 44: 167–175
doi: 10.1007/s11262-012-0713-1
-
Song D, Moon H, Kang B (2015) Porcine epidemic diarrhea: a review of current epidemiology and available vaccines. Clin Exp Vac Res 4: 166–176
doi: 10.7774/cevr.2015.4.2.166
-
Steinrigl A, Fernández SR, Stoiber F, Pikalo J, Sattler T, Schmoll F (2015) First detection, clinical presentation and phylogenetic characterization of Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in Austria. BMC Vet Res 11: 310
doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0624-1
-
Stevenson GW, Hoang H, Schwartz KJ, Burrough ER, Sun D, Madson D, Cooper VL, Pillatzki A, Gauger P, Schmitt BJ, Koster LG, Killian ML, Yoon KJ (2013) Emergence of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States: clinical signs, lesions, and viral genomic sequences. J Vet Diagn Invest 25: 649–654
doi: 10.1177/1040638713501675
-
Tan L, Li Y, He J, Hu Y, Cai X, Liu W, Liu T, Wang J, Li Z, Yuan X, Zhan Y, Yang L, Deng Z, Wang N, Yang Y, Wang A (2020) Epidemic and genetic characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains circulating in the regions around Hunan, China, during 2017–2018. Arch Virol 165: 877–889
doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04532-7
-
Tang XC, Zhang JX, Zhang SY, Wang P, Fan XH, Li LF, Li G, Dong BQ, Liu W, Cheung CL, Xu KM, Song WJ, Vijaykrishna D, Poon LL, Peiris JS, Smith GJ, Chen H, Guan Y (2006) Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J Virol 80: 7481–7490
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00697-06
-
Teeravechyan S, Frantz PN, Wongthida P, Chailangkarn T, Jaru-Ampornpan P, Koonpaew S, Jongkaewwattana A (2016) Deciphering the biology of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the era of reverse genetics. Virus Res 226: 152–217
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.05.003
-
Theuns S, Conceição-Neto N, Christiaens I, Zeller M, Desmarets LM, Roukaerts ID, Acar DD, Heylen E, Matthijnssens J, Nauwynck HJ (2015) Complete genome sequence of a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from a novel outbreak in Belgium, January 2015. Genome Announc 3: pii: e00506–15
-
USDA (2017) Swine Enteric Coronavirus Disease (SECD) Situation Report. https://www.aphis.usda.gov/animal_health/animal_dis_spec/swine/downloads/secd_sit_rep_11_30_17.pdf. Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service
-
Valkó A, Bálint Á, Bozsa Á, Cságola A (2019) Prevalence of antibodies against transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) in Hungary. Vet Anim Sci 7: 100042
doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2018.11.003
-
Van Deun K, Cox E, Cellebaut P, Pensaert MB (1990) Milk of sows infected with the porcine respiratory coronavirus: induction of IgA antibodies against transmissible gastroenteritis virus and protective capacity against intestinal infection in piglets. In: 11th Congres of the international pig veterinary society at: Lausanne
-
Van Gucht S, Atanasova K, Barbé F, Cox E, Pensaert M, Van Reeth K (2006) Effect of porcine respiratory coronavirus infection on lipopolysaccharide recognition proteins and haptoglobin levels in the lungs. Microbes Infect 8: 1492–1501
doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2006.01.009
-
Van Nieuwstadt AP, Zetstra T, Boonstra J (1989) Infection with porcine respiratory coronavirus does not fully protect pigs against intestinal transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Vet Rec 125: 58–60
doi: 10.1136/vr.125.3.58
-
Vannier P (1990) Disorders induced by the experimental infection of pigs with the porcine respiratory coronavirus (P.R.C.V.). Zentralbl Veterinarmed B 37: 177–180
-
Vlasova AN, Marthaler D, Wang Q, Culhane MR, Rossow K, Rovira A, Collins J, Saif LJ (2014) Distinct characteristics and complex Evolution of PEDV strains, North America, May 2013–February 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 20: 1620–1628
-
Vlasova AN, Saif LJ (2013) Biological aspects of the interspecies transmission of selected coronaviruses. In: Singh SK (ed) Viral infections and global change. Wiley, pp 393–418
-
Wang L, Byrum B, Zhang Y (2014a) Detection and genetic characterization of deltacoronavirus in pigs, Ohio, USA, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 20: 1227–1230
-
Wang L, Byrum B, Zhang Y (2014b) Porcine coronavirus HKU15 detected in 9 US states, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 20: 1594–1595
doi: 10.3201/eid2009.140756
-
Wang L, Byrum B, Zhang Y (2014c) New variant of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, United States, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 20: 917–919
doi: 10.3201/eid2005.140195
-
Wang L, Hu W, Fan C (2020) Structural and biochemical characterization of SADS-CoV papain-like protease 2. Protein Sci 29: 1228–1241
doi: 10.1002/pro.3857
-
Wang Q, Vlasova AN, Kenney SP, Saif LJ (2019) Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr Opin Virol 34: 39–49
doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.12.001
-
Wang YW, Yue H, Fang W, Huang YW (2015) Complete genome sequence of porcine deltacoronavirus strain CH/Sichuan/S27/2012 from Mainland China. Genome Announc 3: e00945–e1015
-
Weingartl HM, Copps J, Drebot MA, Marszal P, Smith G, Gren J, Andonova M, Pasick J, Kitching P, Czub M (2004) Susceptibility of pigs and chickens to SARS coronavirus. Emerg Infect Dis 10: 179–184
doi: 10.3201/eid1002.030677
-
Wesley R (2002) Neutralizing antibody decay and lack of contact transmission after inoculation of 3- and 4-day-old piglets with porcine respiratory coronavirus. J Vet Diagn Invest 14: 525–527
doi: 10.1177/104063870201400617
-
Wesley RD, Woods RD (1996) Induction of protective immunity against transmissible gastroenteritis virus after exposure of neonatal pigs to porcine respiratory coronavirus. Am J Vet Res 57: 157–162
-
Woo PC, Lau SK, Lam CS, Lau CC, Tsang AK, Lau JH, Bai R, Teng JL, Tsang CC, Wang M, Zheng BJ, Chan KH, Yuen KY (2012) Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J Virol 86: 3995–4008
doi: 10.1128/JVI.06540-11
-
Woo PC, Lau SK, Yip CC, Tsoi H, Chan K, Yuen K (2006) Comparative analysis of 22 coronavirus HKU1 genomes reveals a novel genotype and evidence of natural recombination in coronavirus HKU1. J Virol 80: 7136–7145
doi: 10.1128/JVI.00509-06
-
Wood EN (1977) An apparently new syndrome of porcine epidemic diarrhoea. Vet Rec 100: 243–244
doi: 10.1136/vr.100.12.243
-
Xu Z, Zhang Y, Gong L, Huang L, Lin Y, Qin J, Du Y, Zhou Q, Xue C, Cao Y (2019) Isolation and characterization of a highly pathogenic strain of Porcine enteric alphacoronavirus causing watery diarrhoea and high mortality in newborn piglets. Transbound Emerg Dis 66: 119–130
doi: 10.1111/tbed.12992
-
Yang YL, Qin P, Wang B, Liu Y, Xu GH, Peng L, Zhou J, Zhu SJ, Huang YW (2019) Broad cross-species infection of cultured cells by bat HKU2-related swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus and identification of its replication in murine dendritic cells in vivo highlight its potential for diverse interspecies transmission. J Virol 93: e01448–e1519
-
Yount B, Curtis KM, Baric RS (2000) Strategy for systematic assembly of large RNA and DNA genomes: transmissible gastroenteritis virus model. J Virol 74: 10600–10611
doi: 10.1128/JVI.74.22.10600-10611.2000
-
Zhang H, Liang Q, Li B, Cui X, Wei X, DING Q, Wang Y, Hu H, (2019) Prevalence, phylogenetic and evolutionary analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus in Henan province, China. Prev Vet Med 166: 8–15
doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2019.02.017
-
Zhang M, Li W, Zhou P, Liu D, Luo R, Jongkaewwattana A, He Q (2019) Genetic manipulation of porcine deltacoronavirus reveals insights into NS6 and NS7 functions: a novel strategy for vaccine design. Emerg Microbes Infect 9: 20–31
-
Zhang J, Han Y, Shi H, Chen J, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhou L, Liu J, Zhang J, Ji Z, Jing Z, Ma J, Shi D, Feng L (2020) Swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus-induced apoptosis is caspase- and cyclophilin D-dependent. Emerg Microbes Infect 9: 439–456
doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1722758
-
Zhang Y, Han L, Xia L, Yuan Y, Hu H (2020) Assessment of hemagglutination activity of porcine deltacoronavirus. J Vet Sci 21: e12
doi: 10.4142/jvs.2020.21.e12
-
Zhou P, Fan H, Lan T, Yang XL, Shi WF, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Zhang YW, Xie QM, Mani S, Zheng XS, Li B, Li JM, Guo H, Pei GQ, An XP, Chen JW, Zhou L, Mai KJ, Wu ZX, Li D, Anderson DE, Zhang LB, Li SY, Mi ZQ, He TT, Cong F, Guo PJ, Huang R, Luo Y, Liu XL, Chen J, Huang Y, Sun Q, Zhang XLL, Wang YY, Xing SZ, Chen YS Sun Y, Li J, Daszak P, Wang LF, Shi ZL, Tong YG, Ma JY (2018) Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 556: 255–258
doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0010-9
-
Zhou L, Li QN, Su JN, Chen GH, Wu ZX, Luo Y, Wu RT, Sun Y, Lan T, Ma JY (2019a) The re-emerging of SADS-CoV infection in pig herds in Southern China. Transbound Emerg Dis 66: 2180–2183
doi: 10.1111/tbed.13270
-
Zhou L, Sun Y, Lan T, Wu R, Chen J, Wu Z, Xie Q, Zhang X, Ma J (2019b) Retrospective detection and phylogenetic analysis of swine acute diarrhoea syndrome coronavirus in pigs in southern China. Transbound Emerg Dis 66: 687–695
doi: 10.1111/tbed.13008
-
Zhao D, Gao X, Zhou P, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Liu X (2020) Evaluation of the immune response in conventionally weaned pigs infected with porcine deltacoronavirus. Arch Virol 12: 1–6
doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04590-x?utm_campaign=BSLB_AWA_SK01_GL_TrendMD2021&utm_content=null&utm_medium=cpc
-
Zhou Z, Sun Y, Yan X, Tang X, Li Q, Tan Y, Lan T, Ma J (2020) Swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV) antagonizes interferon- production via blocking IPS-1 and RIG-I. Virus Res 278: 197843
doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.197843