-
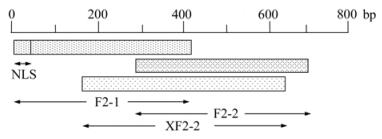
Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV-2) is the most important pathogen of postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS)[1], porcine dermatitis and nephropathy syndrome (PDNS)[16], porcine respiratory disease complex (PRDC)[6] and exudative epidermitis[19]. These diseases are designated as PCV-2-associated disease (PCVAD)[4, 15]. PCV-2 was isolated from pigs with PMWS in Canada[1], and classified in the genus Circovirus , family Circoviridae. The PCV-2 virus particle is non-enveloped, about 17 nm in diameter. The genome of PCV-2 contains a single-stranded, circular DNA of 1767 bp or 1768 bp with 11 putative open reading frames (ORFs). ORF1 and ORF2 are two major ORFs encoding the replication-associated protein (Rep) and capsid protein (Cap) respectively. Rep is associated with the replication of PCV-2[12]; Cap is the unique structural protein and has several specific antigen sites[7, 14]. The dominant epitopes of PCV-2 capsid protein are believed to be within amino acid residues N-65~87 aa, 113~147 aa, 157~183 aa and 193-207 aa. Two polypeptides encoded by 69~83 aa and 117~131 aa are specific to PCV-2 antisera[11]. The capsid protein contains a nuclear localization signal (NLS), which consists of 41 amino acid residues at the N-terminus[9]. The NLS sequence contains several rare codons (30%) and causes difficulties in expressing ORF2 protein in E. coli cells. The fusion expression of the whole ORF2 with glutathione-S-transpherase (GST) or maltose binding protein (MBP) is successful, but only minute amounts are expressed[9, 21]. Fortunately, the whole NLS domain deleted sequence can be expressed in E. coli cells, and a significant amount of recombinant protein can be obtained[21]. Although the NLS deleted protein retains antigenic properties, the NLS may contain some dominant epitopes, and these epitopes may influence the antigenicity of Cap, so it is necessary to perform further studies on NLS[18].
Antigenic properties of truncated PCV-2 ORF2 genes have been detected previously, and poor immunoreactivities were revealed between N-terminal subunits (1-50 aa and 51-100 aa) and anti-PCV-2 antisera, while greater immunoreactivities were observed for the C-terminal subunits (101-150 aa and 151-200 aa)[20]. However, this result is not consistent with the conclusion that dominant epitopes of PCV-2 capsid protein were believed to be within amino acid residues of N-65~87 aa. Truncated protein and polyclonal antibodies were prepared and utilized in diagnosis of PCV-2 infections and monitoring of PCV-2 seroprevalence in fields at home and abroad[20], but the antigenicity of the truncated protein utilized to prepare polyclonal antibodies was not compared with other truncated proteins of Cap.
In our study, we designed 3 pairs of primers to amplify truncated Cap sequences, the sequences were all subcloned into pET-32a (+) expression plasmids respectively, and the recombinant vectors were expressed in Rosetta (DE3) E. coli. We purified and quantified the expressed proteins and then compared the immunoreactivities between the truncated proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera by ELISA. The fusion protein showing best reactivity with antisera was selected and utilized to immunize SPF rabbit to produce polyclonal antibodies. Both prepared fusion protein and polyclonal antibodies were utilized to confirm the PCV-2 infection of field samples by ELISA and propagation of PCV-2 in cells by indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and immuno-peroxidase monolayer assay (IPMA) respectively.
HTML
-
Rosetta (DE3) E. coli was selected as the host bacterium for expression and provided by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Cloning vectors (pMD18-T-Simple) and expression vectors (pET-32a) were provided by TaKaRa Bio Group (Dalian, Liaoning) and Novagen (Madison, Wisconsin) respectively.
-
Bam H I, Hin d Ⅲ, DNA Markers λ-EcoT14 I digest, DL 2 000 and Universal genomic DNA extraction kit were provided by the TaKaRa Bio Group (Dalian, Liaoning). T4 DNA ligase was purchased from the NEB Co. Ltd. (Beijing), HRP-labeled rabbit anti-pig IgG and HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG were purchased from the Solarbio Science, Co. Ltd. (Beijing).
-
Positive and negative anti-PCV-2 sera were prepared and stored in our lab (State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology, Lanzhou).
-
PCV-2 genomic DNA was extracted from PK-15 cells inoculated with PCV-2(TS strain, GenBank Accession No. DQ355153) for 3 days, using a Universal genomic DNA extraction kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, Liaoning) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The truncated PCV-2 ORF2 sequences were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using 3 pairs of primers designed according to the whole genome of PCV-2(TS). Primers for amplification are listed in Table 1. The expected sequences from ORF2 contain 418 bp (F2-1), 418 bp (F2-2) and 493 bp (XF2-2) respectively, and the F2-1 gene contains the 12 bp deleted NLS sequence (Fig. 1). The PCR reaction was carried out in a 50 μL mixture containing 2 mmol/L dNTPs mixture 5 μL, 10×PFU Buffer with MgSO4 5 μL, PFU DNA polymerase (MBI, Fermentas), 100 μmol/L forward primer 1 μL, 100 μmol/L reverse primer 1 μL, template DNA 500 pg, and ddH2O was added to bring the mixture up to 50 μL. Amplicons were detected by electrophoresing through a 1% agarose gel in 1×TAE (40mmol/L Tris-acetate, 2mmol/L EDTA, pH 8.5). Amplified products were 3'-end adenylated with 1 U Taq DNA polymerase in the presence of 200 μmol/L dATP at 72 ℃ for 10 min. The fragments were purified with an Agarose gel DNA Purification Kit and then cloned into pMD18-T Simple vectors by TA cloning strategy to generate recombinant vectors. The recombinant vectors were identified by PCR and double digests. Then the amplified sequences of ORF2 gene were sequenced by the Shanghai Invitrogen Biotechnology Co. Ltd.

Table 1. Primers for amplifying truncated sequences of PCV-2 ORF2 gene
-
The truncated sequences on cloning vectors were double digested by Bam H I and Hin d Ⅲ to reveal sticky ends, gel purified and cloned into pET-32a (+) expression vectors to construct PET-F2-1, PET-F2-2 and PET-XF2-2 recombinant expression vectors. The accuracy of the recombinant expression vectors were also confirmed by PCR and restriction endonuclease digestion.
-
The recombinant expression vectors were all transformed into Rosetta (DE3), and the recombinant bacteria were propagated in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium containing 100 μg/mL ampicillin at 37 ℃ for about 4 h until the OD600 reached 0.6. Then isopropyl β-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was added to a final concentration of 0.5 mmol/L. The culture was incubated for an additional 4 h at 28 ℃. Bacterial culture was collected and centrifuged at 12 000 ×g for 5 min at 4 ℃.
Proteins for SDS-PAGE were mixed with a Laemmli sample buffer in equal volume and heated to 100 ℃ for 5 min. This mixture was separated on a 4 % stacking and 12 % resolving polyacrylamide gel in Tris-glycine buffer (25 mmol/L Tris, 250 mmol/L Glycine, 0.1 % SDS) by electrophoresis, and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. Expressed proteins without stain were then transferred onto a nitrocellulose membrane (NC) at 200 V for 1 h (4 ℃), then blocked with 5 % skimmed milk in Tris-buffered saline with Tween-20 for 0.5 h at 37 ℃. The membrane was incubated with positive and negative anti-PCV-2 sera diluted 1:100 in TBST for 0.5 h at 37 ℃, and then incubated with anti-pig IgG 1:500 diluted for 0.5 h. The reaction was made visible with the system of 3, 3'-diaminobenzidine (DAB)-H2O2-horseradish peroxi-dase (HRP).
The bacterial pellets were resuspended with 1:10 volume of phosphate lysis buffer (20 mmol/L Sodium Phosphate, 500 mmol/L Sodium Chloride, 0.2% Trition-X-100, 1 mg/mL Lysozyme, and 10 mg/mL DNase 1, pH 7.8) and then lysed by 50 cycles of sonication at 5 s each with 5 s intervals sonicated on ice. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 12 000×g for 30 min at 4 ℃. The sediment was resuspended with 1:10 volume of binding buffer (8 M urea, 20 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 500 mmol/L NaCl, 20 mmol/L imidazole, pH 8.0 and 1 mmol/L β-mercaptoethanol). After centrifugation at 12 000×g for 30 min at 4 ℃, the supernatant was collected and purified by Ni2+-immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) (His GraviTrap, GE Healthcare Bioscience, USA). Purification effect was detected by SDS-PAGE. Concentration of purified protein was determined by the Bradford method using bovine serum albumin as a reference[3].
-
Recombinant proteins in different amounts (10-0.001 μg) and PBS (pH 7.4) as blank control were coated in 0.05 mol/L carbonate-bicarbonate buffer and incubated overnight at 4 ℃. The unoccupied sites of the wells were then blocked with 0.1 % bovine serum albumin in PBS (pH7.4) with Tween-20 for 90 min at 37 ℃. The plates were rinsed three times with PBS-Tween. The positive and negative anti-PCV-2 sera samples were 1:200 diluted in PBS-Tween. Diluted serum sample (100 μL) was added to each well and incubated for 30 min at 37 ℃. The plates were then washed three times with PBS-Tween. 100 μL of HRP-labeled rabbit anti-pig IgG immunoglobulins 1:1 000 diluted (dilution depending on antiserum quality) in PBS-Tween were added and incubated for 30 min at 37 ℃ after which the plates were washed three times with PBS-Tween. Tetramethyl benzidine (TMB, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was added and incubated for 15 min at 37 ℃. Color development was stopped by the addition of 50 μL/well of 2 mol/L H2SO4. The optical densities (OD) were read at 450 nm with a microplate reader and analyzed by statistical analysis.
-
Specificity detections between recombinant fusion protein with best immunoreactivity and positive sera against PCV-2, Porcine circovirus type 1 (PCV-1), Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), Pseudorabies virus (PRV), Porcine parvovirus (PPV), Classical swine fever virus (CSFV) and Foot and mouth disease virus (FMDV) were performed. The selected protein was coated at different amounts, and sera samples were 1:200 diluted in PBS-Tween. 100 μL of HRP-labeled rabbit anti-pig IgG immunoglobulins 1:1 000 diluted in PBS-Tween were added. Color development was stopped by the addition of 50 μL/well of 2 mol/L H2SO4. The OD values were read at 450 nm and analyzed by statistical analysis.
-
SPF rabbit was immunized intramuscularly with the purified recombinant protein. The first inoculation was carried out with 100 μg protein emulsified in Freund's complete adjuvant, and the second inoculation was in 2 weeks with 150 μg antigen emulsified in Freund's incomplete adjuvant. The immunization was boosted in 4 weeks with 150 μg antigen emulsified in Freund's incomplete adjuvant too. Blood was collected at 28 d and 35 d to detect the antibody against recombinant protein. When antibody titer reached 1:10 000-50 000, the rabbit was subsequently euthanized, blood was collected and sera samples were isolated by centrifugation at 4 ℃.
-
264 sera samples were collected from Taian, Jinan, Jining, Heze, Linyi, Liaocheng and Weifang districts of Shandong province. The Mandibular lymph node of each pig was also collected for PCV-2 detection by PCR. The sequence of the forward primer for PCV-2 detection was 5'-GCAGTTTGTAGTCTCAGCC-3' and the sequence of the reverse primer was 5'-ACAGTC AGAACGCCCTCC-3'. The fusion protein with best immunoreactivity was coated as antigen to detect sera samples in the field by indirect ELISA. The detailed procedure of indirect ELISA had been described before. Sera samples in field, positive and negative anti-PCV-2 sera were 1:200 diluted in PBS-Tween. HRP-labeled rabbit anti-pig IgG immunoglobulins were 1:1 000 diluted in PBS-Tween.
Polyclonal antibody against recombinant fusion protein was applied in immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and immunoperoxidase monolayer assay (IPMA) to detect PCV-2 cultured in PK-15 cells. PCV-2 TS strain was isolated and stored in our laboratory, and virus titer was 104.8 TCID50/0.1 mL as determined in the inoculum. PCV-1 free PK-15 cells were grown in modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum. Each cell culture flask made of glass was dried and fixed with ice-cold acetone, then stained with 1:500 diluted rabbit sera for 30 min at 37 ℃. Cells were stained with 1:2 000 diluted fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG for 30 min at 37℃, and examined with a fluorescence microscope. Cells stained with diluted rabbit sera were also stained with 1:500 diluted HRP-conjugated recombinant protein A (Biosynthesis Biotechnology, Beijing) at 37℃, then AEC (Boster Biological Technology, Wuhan) was added and incubated for 15 min in room temperature, and stopped by distilled water.
Bacterial strain and vectors
Enzymes and reagents
Experimental anti-PCV-2 sera
Amplification and identification of truncated PCV-2 ORF2 genes
Construction and identification of recombinant expression vectors
Expression, detection and purification of truncated Cap proteins
Comparison of immunoreactivity between recombinant proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera
Detection of nonspecific reactions between recombinant protein and control sera
Preparatio n of polyclonal antibodies against recombinant protein
Potential application of recombinant protein and polyclonal antibodies
-
Genomic DNA was extracted from PK-15 cells inoculated with PCV-2 and three DNA fragments containing 418 bp (F2-1), 418 bp (F2-2) and 493 bp (XF2-2) respectively were amplified (Fig. 2). All of the fragments were cloned into pMD18-T-Simple vectors by TA cloning. The recombinant cloning vectors were identified by PCR and double digest. F2-1, F2-2 and XF2-2 were digested by Bam H I and Hin d Ⅲ in the cloning vectors and then cloned into pET-32a (+) vector. Recombinant expression vectors were also confirmed by PCR and double digest (Fig. 3).
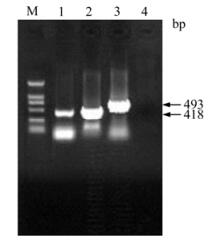
Figure 2. Amplifications of truncated PCV-2 ORF2 genes by PCR. Lanes 1-3, Amplification of F2-1, F2-2 and XF2-2 by PCR, respectively; Lane 4, Negative control; M, DNA Marker DL 2000.
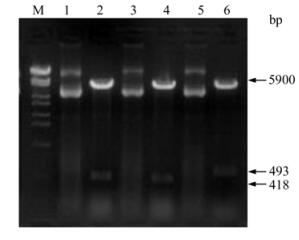
Figure 3. Identification of recombinant expressing vectors by Bam H I and Hin d Ⅲ digestion. Lanes 1, 3 and 5, Recombinant expression vectors of PET-F2-1, PET-F2-2 and PET-XF2-2; Lanes 2, 4 and 6, Identification of PET-F2-1, PET-F2-2 and PET-XF2-2 by enzyme digestion, respectively; M, DNA Marker λ-Eco T14Ⅰdigest.
-
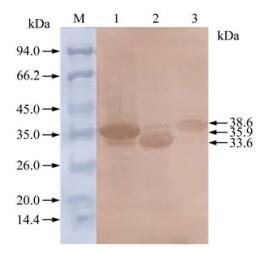
The recombinant bacteria were induced by IPTG and three proteins with histidine-tag were successfully expressed in Rosetta (DE3). Results following the SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the recombinant proteins of anticipated sizes were expressed and proteins of His-F2-1, His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2 were about 35.9 kDa, 33.6 kDa and 38.6 kDa respectively (Fig. 4). The expression level of His-F2-1, His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2 were calculated to be 30 mg/ L, 25 mg/L and 20 mg/ L respectively. In western blotting analysis, all of the recombinant proteins showed positive reaction with anti-PCV-2 antisera (Fig. 5). The majority of the resulting proteins were deposited as insoluble inclusion bodies. Fusion proteins were successfully purified with Ni2+-IMAC system (Fig. 4-6), and the concentrations of the eluted proteins were confirmed as 0.4 μg/μL, 0.4 μg/μL and 0.6μg/μL respectively by the Bradford method. The final concentration of each purified protein was adjusted to 2 μg/μL by condensation with PEG 8000.
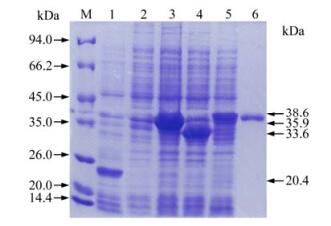
Figure 4. SDS-PAGE analysis of expressed proteins in E.coli. Lane 1, Bacterial protein of PET-32a after induction; Lane 2, Bacterial protein without induction; Lane 3, Bacterial protein of PET-F2-1 after induction; Lane 4, Bacterial protein of PET-F2-2 after induction; Lane 5, Bacterial protein of PET-XF2-2 after induction; Lane 6, Expressed protein by PET-XF2-2 in E.coli after purification; M, Protein Molecular Weight Marker.
-
Immunoreactivity between expressed fusion proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera were detected by ELISA. OD values of PCV-2 negative sera were averaged to define a positive threshold. The OD450 values of collected negative sera ranged from 0.18 to 0.42 and showed a normal distribution. The positive/ negative cut-off value was set at mean + 3 SD. The positive threshold determined from M=0.37 and SD=0.10, was set at 0.67. OD450 values of His-F2-1, His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2 were detected and analyzed by SPSS13.0 (using the One-Way ANOVA test) to find the variability of OD450 values between recombinant proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera at the same amount (Table 2). Variability of OD450 values between His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2 was not significant, but average OD450 values of His-XF2-2 were larger than His-F2-2. Immunoreactivity of His-XF2-2 was the greatest in different amounts as described and the His-XF2-2 recombinant protein was selected for further studies.

Table 2. Variability of OD450 values between recombinant proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera (X±SD).
-
His-XF2-2 showed greater reactivity with anti-PCV-2 antisera than the other two recombinant proteins. Nonspecific reactions between His-XF2-2 and positive sera against PCV-1, PRRSV, PRV, PPV, CSFV and FMDV were detected, and OD values were analyzed by SPSS13.0 (One-Way ANOVA). Differences were not significant among control sera. No positive reaction was detected between His-XF2-2 and control sera. The minimum amount of His-XF2-2 for extremely significant difference among the reactions was 1.0 μg/well (Table 3).

Table 3. Variability of OD450 values between His-XF2-2 and control sera (X±SD)
-
In the serological investigation of PCV-2 by ELISA, His-XF2-2 was coated at 1.0 μg/well, positive and negative anti-PCV-2 sera samples were diluted in 1:200 in PBS-Tween, positive sera against PCV-1, PRRSV, PRV, PPV, CSFV and FMDV were simultaneously detected as negative control. The OD450 values of negative sera ranged from 0.24 to 0.48, the average OD450 value was 0.38 and SD was 0.072. The positive/negative cut-off value was set at mean + 3 SD. The positive threshold determined as 0.60. The seropositivity rate of sera samples ranged from 19.4 % to 32.3 % among different districts, and average seropositivity rate was 27.7 % (Table 4).

Table 4. Positivity rate of PCV-2 infection detected by PCR and ELISA with His-XF2-2
PCV-2 infection was also detected by PCR assay. Whole genomes of mandibular lymph nodes which had the same origins with sera samples were extracted as templates to amplify PCV-2 sequences. 76 samples were confirmed as positive in PCV-2 DNA detection, and average positive rate was 28.8 % (Table 4). The consistency between ELISA and PCR assay was as high as 96.2 %, and the constructed ELISA method was considered to be valid.
-
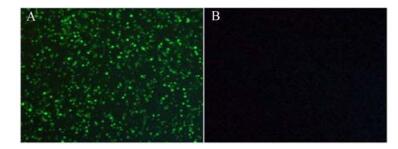
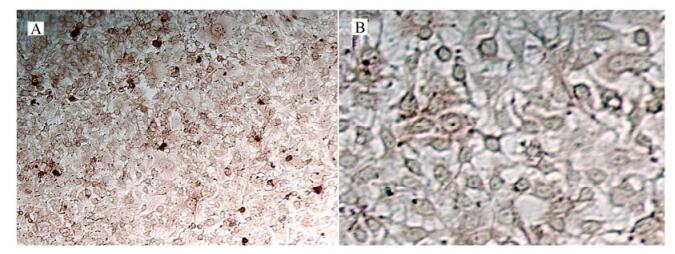
IFA and IPMA were performed to check the immunoreactivity between prepared polyclonal antibodies and viral proteins. IFA was performed after inoculation of PCV-2 in PK-15 cells. Fluorescence could not be detected in PK-15 cells (Fig. 6B), but specific fluorescence in PK-15 cells inoculated with PCV-2 could be detected three days after the inoculation (Fig. 6A). In IPMA, positive signals could be found in PK-15 cells two days after inoculation with PCV-2 stained by AEC (Fig. 7A), while no signal was found in PK-15 cells (Fig. 7B).
Amplification and identification of truncated ORF2 sequences
Expression, detection and purification of recombinant protein
Comparison of immuno reactivity
Detection of nonspecific reactions between His-XF2-2 and control sera
Application of His-XF2-2 for serological investiga-tion of PCV-2
Application of polyclonal antibodies against His-XF2-2 in IFA and IPMA
-
PCV-2 can cause a series of syndromes in swine herds and is now widely spread in all major pig producing countries of the world. PCV-2 can lead to immunosuppression once it is in a swine body, and usually co-infects with other pathogens. It is very important to construct efficient methods for diagnosis of PCV-2 infection. In our study, we attempted to find a truncated capsid protein which can cause effective immunoreactivity with anti-PCV-2 antisera and weaker nonspecific reaction with antisera against other pathogens such as porcine circovirus type 1 (PCV-1), which is another genotype of porcine circovirus. We designed three pairs of specific primers according to the distribution of epitopes in the capsid protein to amplify truncated sequences of ORF2, and with the intention of reducing the nonspecific reaction between expressed proteins and anti-PCV-2 antisera.
The capsid protein of PCV-2 has been expressed in several eukaryotic expression systems[2, 8, 13], but all of them represent expensive strategies for expression, and the recombinant proteins are difficult to purify. Proteins expressed in E.coli can generated in large amounts and are easy to purify[9, 17, 20], so it is a good choice for the detection of antibody against PCV-2. However, PCV-2 ORF2 is difficult to express in E. coli because of the existence of arginine and rare codons in the N-terminal region. The N-terminal part of ORF2 is mainly composed of the 41 amino acid NLS [9] and the deletion of the NLS region could lead to high-level expression of ORF2 in E. coli. The whole ORF2 gene has also been expressed in codon optimized E. coli cells (BL21-Codon-Plus (DE3)-RIPL cells), which contain extra copies of the argU, ileY, leuW, and proL tRNA genes, but the level of expression is low. In our study, three truncated sequences from ORF2 named F2-1, F2-2 and XF2-2 were cloned and expressed as histidine tagged fusion proteins in Rosetta (DE3). The sequence of F2-1 covers the main functional gene for nuclear localization, F2-2 and XF2-2 are NLS deleted. The three truncated sequences were successfully expressed as fusion proteins in Rosetta (DE3) E. coli cells which contain extra copies of the AUA, AGG, AGA, CUA, CCC and GGA in tRNA genes and allow the expression of heterologous proteins. The expression of His-F2-1 is at a high level, and the NLS sequence is successfully expressed at high levels with a 12 bp deletion in the N-terminal region. His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2 are expressed at normal levels, and most of the expressed proteins are insoluble inclusion bodies even expressed at lower temperatures. Inclusion bodies of recombinant proteins were denatured and purified by chromatography on nickel chelating agarose columns, and then renatured to restore their natural conformation or biological functions.
The immunoreactivities between anti-PCV-2 antisera and the three truncated proteins are confirmed by western blotting. Positive reactions could be detected, and truncated genes of capsid protein were correctly expressed in prokaryotic expression host. The truncated proteins expressed in E. coli are immunogenically similar to the PCV-2 structural protein.
The antigenic properties of truncated PCV-2 ORF2 genes have been detected before, and poor immu-noreactivities were revealed between N-terminal subunits (1-50 aa and 51-100 aa) and positive swine sera of PCV-2, while greater immunoreactivities were observed for the C-terminal subunits (101-150 aa and 151-200 aa). After purification and quantification, immunoreactivities of the three fusion proteins were compared by ELISA. The assay revealed similar results, and greatest reaction was detected between His-XF2-2 (55-218 aa) and anti-PCV-2 antisera, while weakest reaction was found between His-F2-1 (5-143 aa) and anti-PCV-2 antisera. In our study, we demonstrate the potential application of the expressed fusion capsid protein and polyclonal antibodies against it. The PCV-2 capsid protein has been used as a diagnostic antigen for serologic detection of PCV-2 infection, but nucleotide variation of ORF2 can cause reduced effectiveness in different geographic areas. Therefore, it is better to select a truncated protein which contains a region of ORF2 which is more highly conserved for use as a diagnostic antigen.
The significance of the variability of OD values between the recombinant protein and the anti-PCV-2 antisera was determined by statistical analysis, the variability between His-F2-1 and His-XF2-2 was significant at the quantity of 1 μg, 0.1 μg and 0.01 μg, while the variability was not significant between His-F2-2 and His-XF2-2. Because of the better immunoreactivity between His-XF2-2 recombinant protein and anti-PCV-2 antisera, His-XF2-2 was selected as immunogen to prepare polyclonal antibodies, and applied as coating protein in investigation of antibody against PCV-2 in field samples. Nonspecific reactions were also detected between His-XF2-2 and positive antisera against PCV-1, PRRSV, PRV, PPV, CSFV and FMDV, and no positive reaction was found. No positive reaction was detected between His-XF2-2 and antisera against PCV-1 either, this might be caused by the deletion of the homologous capsid protein between PCV-2 and PCV-1, and the addition of tag protein of pET-32a (+).
Sera samples from certain districts of Shandong province were collected to detect PCV-2 infection with His-XF2-2 in ELISA. The seropositivity rate of PCV-2 infection ranged from 19.4 % to 32.3 %, and the average seropositivity rate was 27.7 % (73/264). In the absence of a standard testing method for PCV-2 antibodies, the PCV-2 infection data were identified by PCR assay for substitution, and the positive rate of PCV-2 infection was similar with the result obtained by ELISA. Thus, the constructed ELISA method was considered to be valid. The survey performed with the two methods indicated that PCV-2 is widely spread among swine herds of certain districts in Shandong province, the seropositivity rate of PCV-2 was present in high levels, and greater attention should be given to the potential risks.
PCV-2 can propagate in PK-15 cells, and a diagnostic method for detecting antibodies against PCV-2 based on cell cultures infected with PCV-2 was constructed[2]. However, PCV-2 infection can also be detected by cell culture. IFA and IPMA were performed with prepared polyclonal antibodies and specific fluorescence was detected with 40 % of total cells exhibiting positive signals. Positive signals were also detected in IPMA, but the percentage was less than IFA. The distinction might be caused by the different sensitivity of the two methods. The assay results all showed that PCV-2 infection could be detected in PK-15 cells with prepared polyclonal antibodies against His-XF2-2.
A virtual vaccine for PCV-2 prevention has not been developed until now, but PCV-2 has become widespread all over the world. PCV-2-associated disease has caused great loss in pig industry, and it is necessary to construct efficient methods for detection of PCV-2 infection on a large scale. Accurate and timely detection of PCV-2 infection will benefit the integrated control of PCVAD. Our results will help efforts to achieve this goal.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: