HTML
-
Natural killer (NK) cell, a type of lymphocyte, is a key component of innate immunity and plays an important role in the first line of host defense against virus infection by directly destroying virus-infected cells. The "missing self" hypothesis helps NK cells to distinguish target cells from self-ones, enabling the specific killing. NK cells have a wide array of receptors including acti-vating and inhibitory ones (Cooper et al., 2001; Scalzo, 2002; Lodoen and Lanier, 2006). Of the activating receptors, natural cytotoxicity receptors (NKp46, NKp44 and NKp30) and NKG2D are the best characterized and contribute significantly to NK cell activity. During virus infection, the missing self, increased activating signaling and microenvironmental cytokines together empower NK cells to fight against the invading viruses. However, as a counteract measure, many viruses evolve to acquire the capacity of evading NK cell immunity, enabling viral survival and transmission (Scalzo, 2002; Lodoen and Lanier, 2005).
Avian influenza viruses pose significant threat to public health. Currently, H9 and H5 viruses are the most preva-lent subtypes of avian influenza and circulate throughout most areas in China (Su et al., 2015). Of these, H9N2 and H5N1 viruses are of great concern. Due to its wide host range and adaptation in both poultry and mammalian, H9N2 influenza virus plays a crucial role at the animal-human interface. Limited cases of human infection with H9N2 virus have been described in China, but the number of asymptomatic and seropositive patients is indeed much higher than that reported. Around 2.3%-4.6% of poultry workers had antibodies against H9 influenza virus (Sun and Liu, 2015). In addition, H9N2 virus is the gene donor for a couple of other types of influenza viruses infecting humans, such as H5N1, H7N9 and H10N8. H9N2 virus provided six internal genes for H5N1 avian virus (Sun and Liu, 2015).
Avian H5N1 influenza virus was previously known to infect only birds, which however jumped the species barrier from poultry to humans, resulting in fatal human respiratory illness in Hong Kong in 1997(Yuen et al., 1998; Tam, 2002). Subsequently, re-emergence of human cases with H5N1 infection in Asian countries including China was reported (Peiris et al., 2004; Webster and Govorkova, 2006; WHO, 2006). Moreover, probable person-to-person transmission was indicated by a family cluster of H5N1 infection in Thailand in 2004(Ungchusak et al., 2005) and in China in 2008(Nguyen et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2008). According to WHO report, as of 4th Dec 2015, a total of 844 confirmed human cases of H5N1 infection have been identified with a case mortality rate of 53%(449/844) in 15 countries (WHO, 2015). The high mortality and unusual severity of H5N1 have raised worldwide concern that such an influenza virus may evolve to become capable of efficiently transmitting among humans and thus cause a new pandemic (Thomas and Noppenberger, 2007; Gambotto et al., 2008; Van Kerkhove, 2013).
During avian influenza H5N1 infection, viral RNA is detectable up to 3 weeks in the respiratory tract of patients, implying viral evasion of host immune response (de Jong et al., 2006). On the other hand, lymphopenia is frequently reported in H5N1 infection and associated with a poor prognosis. In addition, lymphocyte depletion also occurs in other tissues, such as spleen, lymph nodes and tonsils (Abdel-Ghafar et al., 2008). With flow cytom-etry to analyze specific lymphocyte subsets, it was found that the level of NK cells is significantly lower than the normal during the early phase of H5N1 infection (Zhang et al., 2012). Taken together, these data suggest that avian influenza H5N1 may target NK cells as an immunoevasion strategy.
Indeed, previously, we demonstrated that human influenza H1N1 virus infects NK cells and induces cell apo-ptosis (Mao et al., 2009). In addition, the intact human H1N1 virion and viral hemagglutinin (HA) can directly inhibit NK cell activity (Mao et al., 2010). In this study, we investigated the effects of avian influenza virus infection on primary human NK cell activity. Both H5N1 virus and its precursor H9N2 were included. We found that avian virus could directly infect human NK cells and induce cell apoptosis. In addition, avian influenza virion and HA protein inhibited NK cell cytotoxicity. These data indicate that avian H9N2 and H5N1 influenza viruses evolve to acquire the ability to evade human NK cell immunity, which may contribute to their high pathogenicity.
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were iso-lated from buffy coat obtained from Hong Kong Red Cross by Ficoll-Hypaque (Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) gradient centrifugation. NK cells were magnetically separated from PBMCs with NK cell isolation kit Ⅱ (Miltenyi Biotec, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany) as we described previously (Mao et al., 2009). The purity of isolated CD56+CD3- NK cells was consistently > 97%, as determined by flow cytometry. NK cells were cultured in RPMI 1640(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) media supplemented with 10% autologous serum. The research protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Hong Kong / Hospital Authority Hong Kong West Cluster.
-
Avian influenza virus A/Quail/Hong Kong/G1/97(H9N2) and A/Hong Kong/483/97(H5N1) were used in this study. All laboratory procedures involving these two live viruses were performed in a Biosafety Level-2 and Level-3 facility respectively. The viruses were cultured in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells and viral titers were determined. For live influenza virus infection, purified fresh primary NK cells were incubated with the indicated viral strain at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 2 for 1 h. The cells were washed with excess phosphate-buffered saline to remove un-adsorbed viruses, and then cultured in the cell medium for the indicated period before the subsequent test. Mock-infected cells were treated in parallel except that the virus was not added.
For inactivated viral treatment of NK cells, influenza virus was first inactivated by UV with an energy of 0.2 J. NK cells were then treated with inactivated influenza virus at an MOI of 2 at a similar process like live virus infection, except UV-inactivated virus rather than live one was used. For HA treatment, primary NK cells first were incubated with recombinant A/Hong Kong/483/97(H5N1) HA protein (Protein Sciences, Meriden, CT, USA) with a cell density of 10 million per milliliter. After 2 h, the culture was diluted 10-fold with the final concentration of HA protein as indicated. According to the manufacturer, HA is a full-length glycosylated recombinant protein with biological activity and tertiary structure (Protein Sciences).
-
The following monoclonal antibodies were used in this study: anti-CD3(UCHT1), anti-CD56(NCAM16.2), anti-NKp46(9E2), anti-active caspase 3(C92-605; all from BD Biosciences, San Diego, CA, USA); anti-NKG2D (1D11), anti-CD3ζ(6B10.2)(both from BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA); anti-influenza NP (Chemicon, Temecula, CA, USA). For surface staining, NK cells were collected and stained with the specific antibody. For intracellular staining, cells were fixed with lysing buffer (BD Biosciences), permeabilized with permeabiliztion solution (BD Biosciences) and then labeled with the indicated antibody. To avoid non-specific staining, cells were pre-incubated with FcR blocking reagent (Miltenyi Biotec) prior to specific staining. NK cell apoptosis were determined with the Annexin V-FITC kit according to the manufacturer's instruction (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). All data were acquired on a BD FACSAria (BD Biosciences) with FACS Diva (BD Biosciences) and analyzed using FlowJo software (TreeStar, Ashland, OR, USA).
-
Primary NK cells were first infected with live influenza virus, or treated with inactivated virus or HA protein as described above. Then the cells were collected and determined for their cytotoxicity with LIVE/DEAD Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Kit (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) as described in our previous study (Mao et al., 2009; Li et al., 2013). Briefly, K562 target cells were stained with DiOC18, and then co-cultured with NK cells at the indicated effector/target (E/T) ratio in the presence of PI for 2 h. After incubation, the cytotoxicity was analyzed by flow cytometry and calculated as the percentage of DiO+PI+ cells out of total DiO+ cells. In the case of virus-infected cells as target cells, THP-1 macrophages were first infected with influenza virus prior to co-culture with NK cells.
-
Virus-or mock-infected NK cells were fixed with methanol-acetone (1:1) and then stained with an antibody reagent containing monoclonal antibodies for influenza viral matrix and nucleoprotein antigens (Dako Diag-nostics, Ely, UK) to determine influenza virus infection. Images were obtained with a Zeiss 510-Meta confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
-
Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t test using Prism 5 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Isolation of primary human NK cells
Influenza virus infection and HA treatment of NK cells
Flow cytometry
Cytotoxicity assay
Immunofluorescent staining
Statistical analysis
-
We initially examined whether avian influenza virus could infect human NK cells. As H9N2 influenza virus could be handled in biosafety leve-2 facility, we started the experiment with H9N2 virus first. Freshly isolated primary human NK cells were treated with H9N2 virus at an MOI of 2 for 6 h, and then analyzed by flow cytome-try to check the intracellular expression of influenza viral NP protein. As shown in Figure 1A, around one half of NK cells were successfully infected with avian H9N2 virus. In order to determine the effect of virus infection on NK cell viability, cell apoptosis was further examined. The expression of active caspase 3 was selected as a marker of apoptosis. After 24 h of H9N2 virus infection, the percentage of active caspase 3-positive cells was around four-fold higher in virus-infected NK cells than in mock-infected cells (Figure 1B), which indicated that H9N2 virus infection killed NK cells. By co-staining of viral NP protein and active caspase 3, we showed that about one third of the infected NK cells underwent apoptosis (Figure 1C).
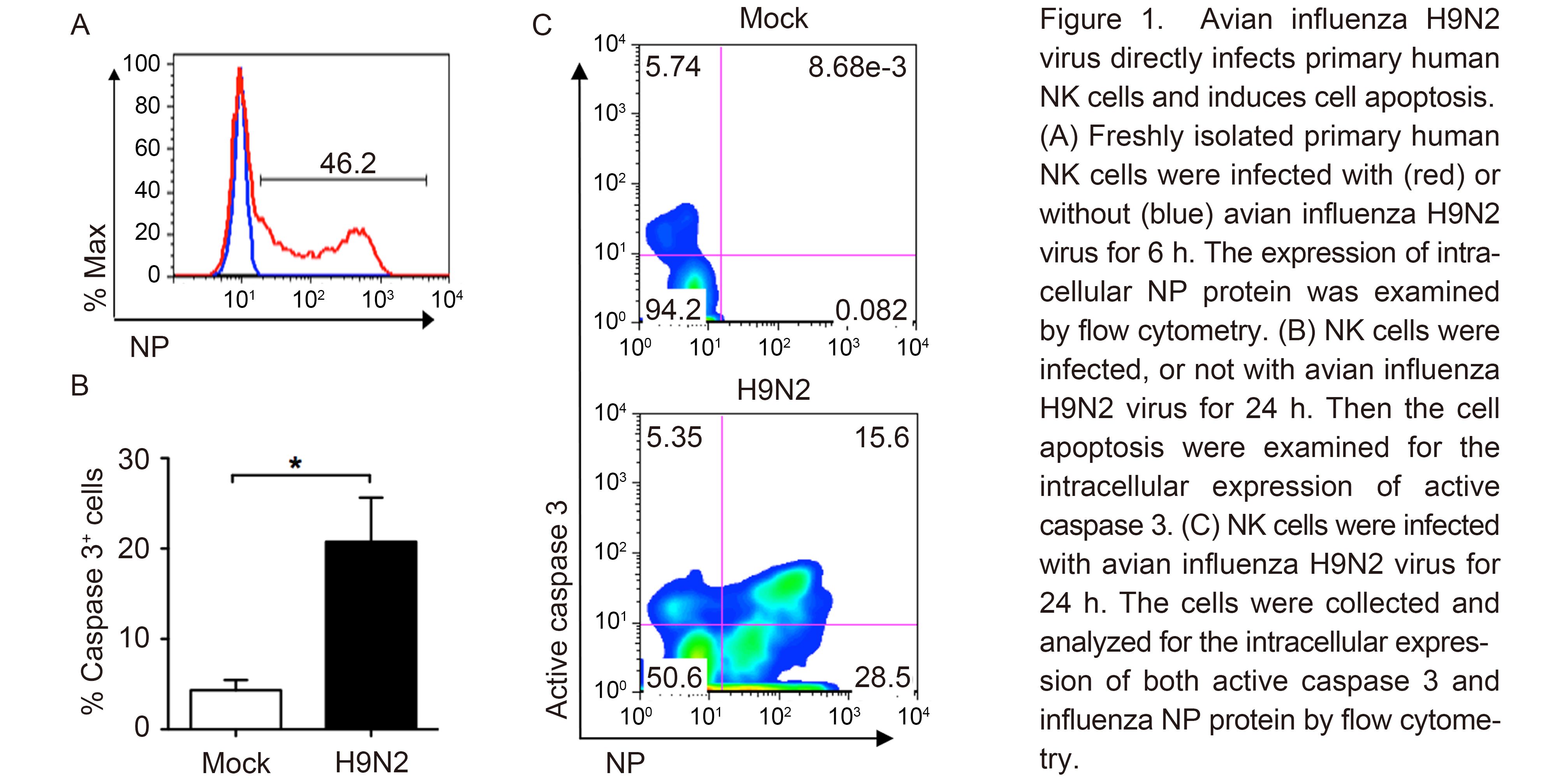
Figure 1. Avian influenza H9N2 virus directly infects primary human NK cells and induces cell apoptosis.(A) Freshly isolated primary human NK cells were infected with (red) or without (blue) avian influenza H9N2 virus for 6 h. The expression of intracellular NP protein was examined by flow cytometry. (B) NK cells were infected, or not with avian influenza H9N2 virus for 24 h. Then the cell apoptosis were examined for the intracellular expression of active caspase 3. (C) NK cells were infected with avian influenza H9N2 virus for 24 h. The cells were collected and analyzed for the intracellular expression of both active caspase 3 and influenza NP protein by flow cytometry.
-
After the demonstration of avian H9N2 virus infection inducing NK cell apoptosis, we continued to check NK cell cytotoxicity. Human NK cells were first infected with H9N2 virus at an MOI of 2 for 24h, and then col-lected and determined for their cytotoxicity against target K562 cells at an effector / target ratio of 20:1. As indicated in Figure 2A, H9N1 virus-infected NK cells showed significantly lower cytotoxicity than mock-infected cells. Considering the decreased NK cell cytotoxicity could be due to the increased cell death by virus infection, we next examined whether H9N2 virion particle itself could modulate NK cell activity. The UV-inacti-vated H9N2 virus was used to treat NK cells for 24 h. As shown in Figure 2B, it did not alter NK cell apoptosis. Then NK cells treated with UV-inactivated H9N2 virus were further determined for their activity. As shown in Figure 2C, the UV-inactivated H9N2 virus also signifi-cantly inhibited the cytotoxicity of NK cells, which indicates that the H9N2 virion particle itself also could suppress NK cell activity.
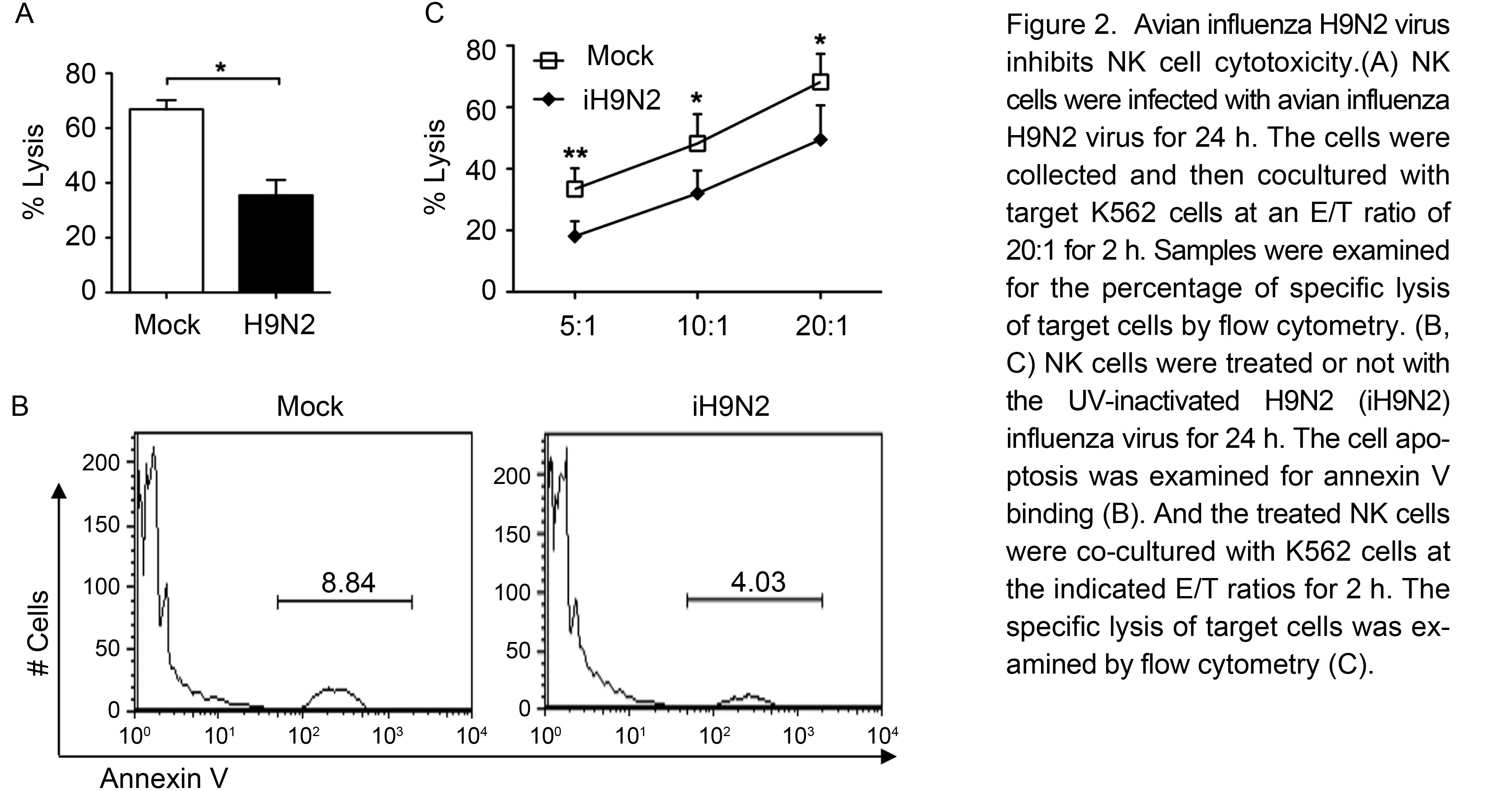
Figure 2. Avian influenza H9N2 virus inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity.(A) NK cells were infected with avian influenza H9N2 virus for 24 h. The cells were collected and then co-cultured with target K562 cells at an E/T ratio of 20:1 for 2 h. Samples were examined for the percentage of specific lysis of target cells by flow cytometry. (B, C) NK cells were treated or not with the UV-inactivated H9N2 (iH9N2) influenza virus for 24 h. The cell apoptosis was examined for annexin V binding (B). And the treated NK cells were co-cultured with K562 cells at the indicated E/T ratios for 2 h. The specific lysis of target cells was examined by flow cytometry (C).
-
To further investigate the mechanisms underlying the inhibition of NK cell activity by H9N2 virions, the expression of NK cell activating receptor was first examined. Among the activating receptors, NKp46 and NKG2D are the major receptors contributing to the NK cell lysis of influenza virus, thus the expressions of these two recep-tors were determined. As shown in Figure 3A and 3B, avian H9N2 virons did not alter the expressions of NKp46 and NKG2D. In previous study, we demonstrated that human influenza H1N1 virions downregulate zeta chain of NK cells to suppress their activity (Mao et al., 2010). Here we also tried to examine the effect of avian influenza H9N2 virions on the expression of zeta chain. NK cells were treated with UV-inactivated H9N2 virus and then examined for zeta chain expression by flow cytom-etry. As shown in Figure 3C, avian H9N2 virions decreased the intracellular expression of zeta chain in NK cells. The expression level of zeta chain in H9N2 virion-treated NK cells was significantly lower than that in mock-treated NK cells (Figure 3D).
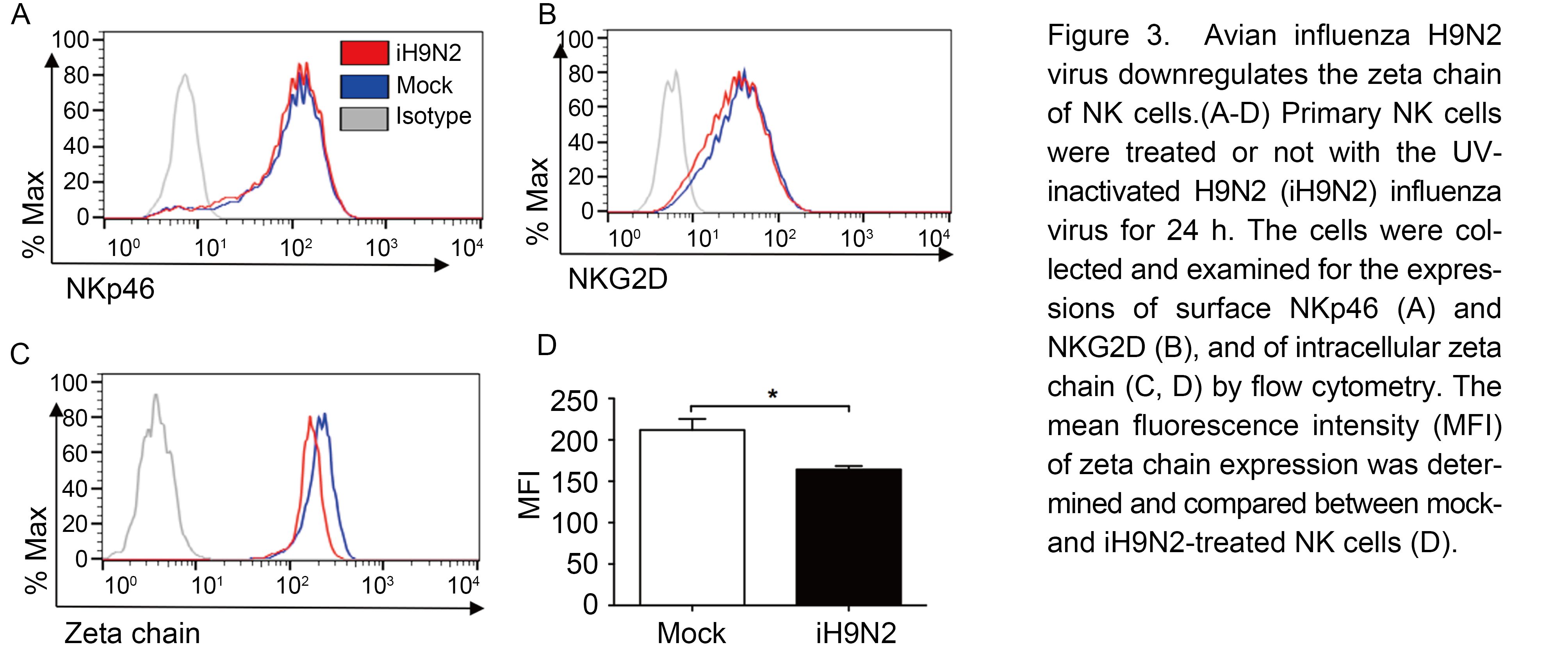
Figure 3. Avian influenza H9N2 virus downregulates the zeta chain of NK cells.(A-D) Primary NK cells were treated or not with the UV-inactivated H9N2 (iH9N2) influenza virus for 24 h. The cells were collected and examined for the expressions of surface NKp46 (A) and NKG2D (B), and of intracellular zeta chain (C, D) by flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of zeta chain expression was determined and compared between mock-and iH9N2-treated NK cells (D).
-
Due to the great importance of H5N1 virus and its potential to cause the next pandemic, we further examined whether this virus could infect NK cells and affect cell activity. NK cells were treated with H5N1 virus in a similar way as H9N2 virus. As shown in Figure 4A, H5N1 viral antigens were present in the infected NK cells post-infection, but not in mock-treated cells, indicating that H5N1 virus could directly infect NK cells. Next we tried to examine whether H5N1 virus could modulate NK cell activity. Due to its high pathogenicity, H5N1 virus must be handled in a biosafety level-3 facility. The samples containing H5N1 virus need to be fixed prior to subsequent analysis, which makes it hard to examine NK cell function. Previously, we demonstrated that H1N1 virus HA protein inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity (Mao et al., 2010). Thus herein we used recombinant H5N1 viral HA protein, instead of live H5N1 virus, to study the effect of H5N1 virus on NK cell activity. Primary human NK cells were treated with H5N1 viral HA protein and then determined for their viability and activity. It was shown that the HA protein did not induce NK cell apoptosis (Figure 4B); however, HA treatment markedly inhibited the cytotoxicity of NK cells against K562 cells (Figure 4C). In addition, we further used influenza virus-in-fected THP-1 macrophages as target cells to check NK cell activity. As shown in Figure 4D, H5N1 viral HA-treated NK cells also showed significantly lower cytotoxicity than mock-in-fected cells against virus-infected target cells. Taken together, avian influenza H5N1 virus directly infected human NK cells and the viral HA protein could inhibit NK cell activity.
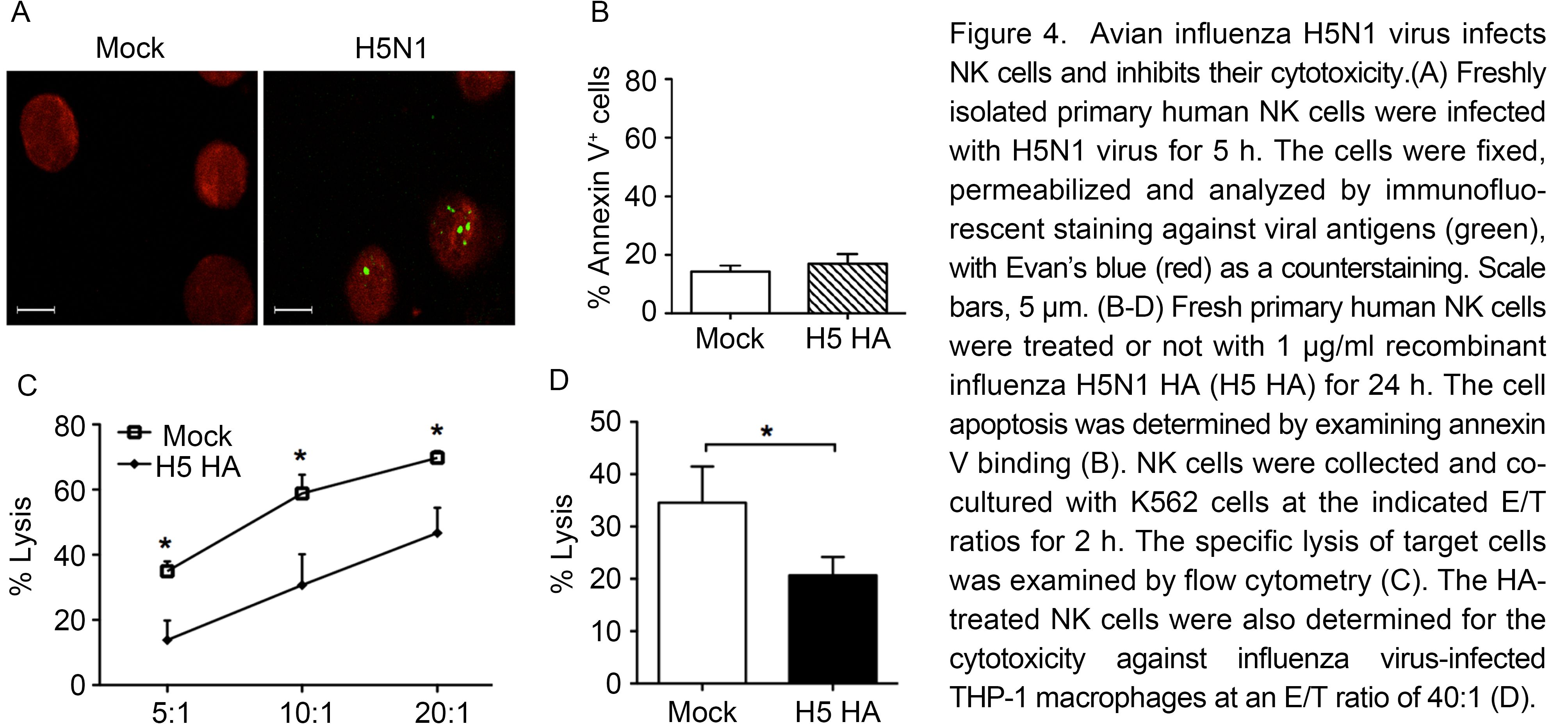
Figure 4. Avian influenza H5N1 virus infects NK cells and inhibits their cytotoxicity.(A) Freshly isolated primary human NK cells were infected with H5N1 virus for 5 h. The cells were fixed, permeabilized and analyzed by immunofluorescent staining against viral antigens (green), with Evan's blue (red) as a counterstaining. Scale bars, 5 μm. (B-D) Fresh primary human NK cells were treated or not with 1 μg/ml recombinant influenza H5N1 HA (H5 HA) for 24 h. The cell apoptosis was determined by examining annexin V binding (B). NK cells were collected and co-cultured with K562 cells at the indicated E/T ratios for 2 h. The specific lysis of target cells was examined by flow cytometry (C). The HA-treated NK cells were also determined for the cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected THP-1 macrophages at an E/T ratio of 40:1 (D).
Avian influenza H9N2 virus directly infects primary human NK cells and induces cell apoptosis
Avian influenza H9N2 virus inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity
Avian influenza H9N2 virus downregulates the zeta chain of NK cells
Avian influenza H5N1 virus infects NK cells and inhibits their cytotoxicity
-
In this study, we demonstrated that avian influenza virus could directly infect primary human NK cells and induce cell apoptosis. In addition, the intact avian influenza virion and HA protein inhibited NK cell activity. Given the important role of NK cells in the first line of host defense against viral infections, our findings suggest a novel strategy used by avian influenza virus to evade NK cell immunity, and provide an important implication for the immunopathogenesis of avian influenza.
Influenza virus infection of target cells is dependent on the sialic acid receptor on cell surface. On binding to the receptor, the virus is internalized into the endosome via receptor-mediated endocytosis. It is well known that human influenza viruses preferentially bind to α2, 6-linked sialic acid (NeuAc α2, 6 Gal), whereas avian vi-ruses mostly recognize α2, 3-linked receptor (NeuAc α2, 3 Gal)(Rogers et al., 1983; Matrosovich et al., 2004). In previous study, we for the first time demonstrated that human influenza H1N1 virus successfully infects human NK cells (Mao et al., 2009). Thereafter an in vivo study also revealed the direct infection of NK cells by influenza H1N1 virus (Guo et al., 2009). Herein we further showed that avian influenza H9N2 and H5N1 viruses also could directly infect human NK cells. These findings are compatible with the fact that human NK cells bear both α2, 6-linked and α2, 3-linked sialic acid recep-tors on the cell surface (Mandelboim et al., 2001; Arnon et al., 2004), which enables the infection of NK cells by human and avian influenza viruses.
NK cells play a critical role in the first line of host defense against viral infections by directly killing infected cells without prior antigen stimulation. However, in response to NK cell immunity, many viruses have developed a variety of strategies to evade their activity, aiming to strive for viral survival and transmission. These NK cell evasion strategies comprise distinct mechanistic categories including regulation of MHC class I molecule, expression of MHC class I homologs, inhibition of activating receptor activity, and direct viral effects on NK cells, which have been reported to be used by various viruses, such as herpesvirus, papillomavirus, retrovirus, poxvirus and flavivirus (Orange et al., 2002; Scalzo, 2002; Lodoen and Lanier, 2005; Jonjic et al., 2008).
Among these evasion strategies, an important one is virus direct targeting of NK cells to modulation cell activity, which includes virus direct infection of NK cells and inhibition of cell function (Orange et al., 2002). For the former, serials of viruses, such as human immunodeficiency virus (Chehimi et al., 1991), Epstein-Barr virus (Isobe et al., 2004) and ectromelia virus (Parker et al., 2008), have been reported to infect NK cells and induce cell apoptosis. In addition to direct infection, viral components also regulate NK cell function, which has been described for hepatitis C virus (Crotta et al., 2002), human immunodeficiency virus (Zocchi et al., 1998; Peruzzi et al., 2000) and cytomegalovirus (Arnon et al., 2005).
Indeed, influenza virus and NK cells are also in a constant battle. NK cells participate in the control of influenza virus infection. Virus-infected accessory cells including epithelial cells, dendritic cells and macrophages induce the activation of NK cells, which in turn kill vi-rus-infected cells (Mandelboim et al., 2001; Spies and Groh, 2006; Draghi et al., 2007). However, in response to NK cell killing, influenza virus has developed a couple of evasion strategies, including indirect and direct ones, in order to establish a successful acute infection. For the former one, Influenza infection induces increased binding of NK inhibitory receptors (Achdout et al., 2008), and prevents the recognition of HA by NK cell receptors (Bar-On et al., 2014), leading to impaired NK cell killing. In addition, recent influenza virus isolates acquire two new glycosylation sites in HA protein, which renders the infected cells less susceptible to NK cell killing (Owen et al., 2007).
Besides the indirect evasion strategy, influenza virus also can directly target NK cells to modulate cell function. Previously, we have demonstrated that human influenza H1N1 virus infects human NK cells and induces cell apoptosis (Mao et al., 2009). In addition, the intact H1N1 virion and HA protein could directly inhibit NK cell cytotoxicity (Mao et al., 2010). Herein, we further showed that avian influenza viruses also could directly infect human NK cells and induce cell apoptosis, which is compatible with the clinical findings that NK cells are significantly decreased during the early phase of avian influenza virus infection (Zhang et al., 2012). Like human H1N1 virus, the virion particle and HA protein of avian influenza viruses were also demonstrated to be capable of inhibiting NK cell function in this study. Taken together, these data suggest that direct targeting NK cells may be a common strategy used by both human and avian influenza viruses to evade NK cell immunity.
In summary, herein we demonstrated a novel immunoevasion strategy of avian influenza virus. The virus di-rectly targets NK cells by inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting cell activity. The main function of viral NK cell evasion is to allow the virus sufficient time to expand and subsequent spread before the onset of the specific immune response, which is particularly beneficial for the acute virus infection like influenza virus (Fernandez-Sesma et al., 2006; Jonjic et al., 2008; Katze et al., 2008). Thus, the novel evasion strategy described here has obvious advantages for avian influenza virus, enabling it to replicate to a high level necessary for successful transmission to new hosts and cause clinical illness before the initiation of adaptive immune responses. In addition, avian influenza is a public health threat that causes serious illness and death in humans. Our findings also provide an important clue for the immunopathogenesis of avian influenza.
-
This work was supported in part by Theme-based Research Scheme (Project No. T11-705/14N), the General Research Fund (HKU 780113M, 17121214 and 17115015), Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong SAR, and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee (JCYJ20140411175241066), China.
-
The authors declare that they have no competing interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
-
HM, JSMP, YLL and WT designed the study. HM, YL and SFS performed the study. HM and WT analyzed the data and wrote the paper.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: