HTML
-
The innate immune system is the first line of host defense against viral infection(Akira et al. 2006). As the most common pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), viral nucleic acids derived from viral genome or its replication intermediates are recognized by a series of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) (Cao 2016; Roers et al. 2016). It has been demonstrated that the Toll-like receptors (TLRs) detect the extracellular viral RNAs in immune cells while the Retinoic acid-inducible gene (RIG)-I-like receptors (RLRs) function as the cytosolic viral RNAs sensors in most type of cells (Alexopoulou et al. 2001; Yoneyama et al. 2004). Recognition of viral RNAs initiates activation of transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB which lead to induction of type I interferons (IFNs). Type I IFNs then activate JAK-STAT signaling to induce the expression of a wide range of downstream antiviral genes and innate antiviral responses (Honda et al. 2006; Randall and Goodbourn 2008).
The RLRs family comprises of three members, RIG-I, MDA5 and LGP2. RIG-I and MDA5 both contain two N-terminal caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARDs), a central DexD/H-box RNA helicase domain and a C-terminal regulatory domain (CTD). After sensing viral RNA, the helicase domain undergoes conformational changes and exposes the CARDs that are responsible for signaling to the downstream adaptor protein. LGP2 lacks CARDs and functions as a regulator of RLR-signaling (Andrejeva et al. 2004; Kowalinski et al. 2011; Meylan et al. 2005). It has been shown that RIG-I preferentially binds to short dsRNA (up to 1 kb) and 5'-triphosphate dsRNA while MDA-5 preferentially recognizes long dsRNA (more than 2 kb). After binding to viral RNAs, RIG-I and MDA5 are recruited to the mitochondrial membrane-located adaptor protein VISA (also known as MAVS, CARDIF and IPS-1) through their CARDs. VISA forms large prion-like polymers that recruit various downstream molecules and further activate the classical IKK complexes and the kinases TBK1/IKKε, which in turn activate transcription factors NF-κB and IRF3 respectively, leading to the introduction of type I IFNs (Seth et al. 2005; Xu et al. 2005). The association of VISA with RIG-I and MDA5 is an important regulatory target in RLR-signaling. Several proteins have been demonstrated to regulate such events. For example, ECSIT bridges RIG-I and MDA5 to VISA by acting as an essential scaffolding protein and thereby enhances type I IFN induction (Lei et al. 2015). ZCCHC3 potentiates the association of VISA with RIG-I and MDA5 by mediating K63-linked polyubiquitination of RIG-I and MDA5 through TRIM25 (Lian et al. 2018).
Signal recognition particle 54 (SRP54) is a universally conserved component of the ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex that targets nascent signal sequence-carrying peptides to the translocon at the surface of the ER (Egea et al. 2005; Kurita et al. 1996; Luirink and Dobberstein 1994). SRP54 has three functionally distinct domains: a N-terminal domain (N domain) and a central GTPase domain (G domain) that are involved in the GTP-dependent interaction with SRP receptor on the ER membrane, and a C-terminal M domain which associates with RNP 7SL RNA and the signal peptide of the nascent polypeptide (Focia et al. 2004; Freymann et al. 1997; Janda et al. 2010; Samuelsson, 1992; Zopf et al. 1990). Recently, it has been demonstrated autoantibodies against SRP (most cases are SRP54) and HMGCR are important biomarkers of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (Watanabe et al. 2016). It also has been reported that the loss-of-function mutations of SRP54 are associated with Shwachman-Diamond-like syndrome and impaired SRP54 function leads to enhanced ER stress, autophagy, and apoptosis of neutrophils and their precursors (Bellanné-Chantelot et al. 2018; Carapito et al. 2017).
In this study, we report that SRP54 is a negative regulator of RLRs-mediated signaling pathway. We found that knockdown of SRP54 markedly potentiated RNA virusinduced induction of type I IFNs and cellular antiviral responses. Mechanistically, SRP54 interacted with RIG-I and MDA5 and impaired their associations with VISA in an RNA binding and GTPase activity-independent manner. Our findings reveal a novel function of SRP54 in cellular antiviral innate immune response.
-
HEK-293T (Transformed Human Embryonic Kidney 293 cell line, ATCC) cells, HFF (Human Foreskin Fibroblast cell line, ATCC) cells and A549 (Human Lung Adenocarcinoma cell line, ATCC) cells were maintained in DMEM High Glucose (HyClone) supplemented with 10% FBS (Biological Industries) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 37 ℃ with 5% CO2. The Sendai virus (SeV) and vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) were provided by Prof. Cong-Yi Zheng from Wuhan University. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were infected with SeV or VSV [multiplicity of infection (MOI) is 0.1 if it was not indicated]. One hour after infection, cells were washed with PBS and then medium was added.
-
Poly(I:C) (Invitrogen); IFN-γ (R&D System); dual-specific luciferase assay kit (Promega); Mouse monoclonal antibodies against Flag, β-actin (Sigma), HA (Biolegend), phospho-IjBα, Myc (Cell Signaling Technology), TBK1, phospho-TBK1 (Abcam), IRF3 (Proteintech); rabbit monoclonal antibodies against phospho-IRF3 (Cell Signaling Technology); rabbit polyclonal antibodies against SRP54 (ABclonal). The rabbit polyclonal antibodies against VSV were previously described (Zhong et al. 2008).
-
HEK-293T cells (~1 × 105) were seeded in 48-well plates using the calcium phosphate precipitation method for transfection. For normalizing the transfection efficiency, 0.01 μg pRL-TK Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid was added to each transfection. To ensure that each transfection receives the same amount of total DNA, the indicated plasmids were transfected with empty vector as control. Luciferase assays were performed using a dual-specific luciferase assay kit (Promega) (Yang et al. 2016).
-
Total RNA was isolated from cells using Trizol reagent (TaKaRa) according to the manufacturer's instructions. cDNA was synthesized from purified total RNA using reverse transcriptase (Vazyme). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (BioRad) to measure mRNA expression levels of tested genes. GAPDH was used as a reference gene, human gene specific primer sequences were as follows: GAPDH: 5'-GAGTCAACGGATTTGGTCGT-3' (forward), 5'-GACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCAG-3' (reverse); IFNB1: 5'-TTGTTGAGAACCTCCTGGCT-3' (forward), 5'-TGACTATGGTCCAGGCACAG-3' (reverse); RANTES: 5'-GGCAGCCCTCGCTGTCATCC-3' (forward), 5'-GCAGCAGGGTGTGGTGTCCG-3' (reverse); ISG56: 5'-TCATCAGGTCAAGGATAGTC-3' (forward), 5'-CCACACTGTATTTGGTGTCTAGG-3' (reverse); CXCL-10: 5'-GGTGAGAAGAGATGTCTGAATCC-3' (forward), 5'-GTCCATCCTTGGAAGCACTGCA-3' (reverse); TNFA: 5'-GCCGCATCGCCGTCTCCTAC-3' (forward), 5'-CCTCAGCCCCCTCTGGGGTC-3' (reverse); and SRP54: 5'-AGCCAGTCACAGATGGCAA-3' (forward), 5'-CAGCACCCTGTTGAAACTGC-3' (reverse).
-
Double-strand oligonucleotides corresponding to the target sequences were cloned into the pSuper.Retro RNAi plasmid (Oligoengine). The target sequences for the human SRP54 constructs were as follows: #1, 5'-CTGAAGGAGTAGAGAAATT-3', #2, 5'-CCTCAGTAATAGTGACAAA-3' and #3, 5'-TGGCAAGGCTAAAGAAATT-3'. A pSuper. Retro RNAi plasmid targeting GFP was used as control for all shRNAi experiments. The siRNA sequences targeting human SRP54 were as follows: 1#, 5'- GCAGGACTTCAGTCAATGA-3' and 2#, 5'-GATGGGAGGTATCAAAGGA-3'.
-
The HEK-293T cells (~1 × 107) were transfected with indicated plasmids. 24 h after transfection, cells were harvested and lysed in 1 mL of NP40 lysis buffer (20 mmol/L Tris–HCl, pH 7.4, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 1 mmol/L EDTA, 1% Nonidet P-40, 10 μg/mL aprotinin, 10 μg/ml leupeptin and 1 mmol/L phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride). For each immunoprecipitation, 0.8 mL of cell lysate was incubated with 0.5 μg of the indicated antibody or control IgG and 25 μL of 50% slurry of Gamma Bind G Plus-Sepharose (Amersham Biosciences) at 4 ℃ for 2 h. The Sepharose beads were then washed three times with 1 mL of lysis buffer containing 500 mmol/L NaCl. The precipitates were then subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis.
Cell Culture and Viral Infection
Reagents and Antibodies
Luciferase Reporter Assays
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
RNA Interference
Co-immunoprecipitation
-
IFN-β promoter, ISRE and NF-κB luciferase reporter plasmids, mammalian expression plasmids for HA- or Flag-tagged RIG-I, MDA5, VISA, TBK1, IRF3, were previously described (Hu et al. 2017; Zhong et al. 2008). Mammalian expression plasmids for Flag- or Myc-tagged SRP54 and its mutants were constructed by standard molecular biology techniques.
-
The HEK-293T (~5×105) cells were cotransfected with SRP54-GFP and RIG-I-Cherry, MDA5-Cherry, or VISACherry. 24 h after transfection, cells were fixed with 4% PFA for 10 min and permeabilized with PBS containing 0.3% Triton X-100 for 15 min on ice. Then DAPI dye (Invitrogen) was added at a concentration of 1:2000 in PBS to localize the nucleus. Images were collected using a Nikon confocal microscope under a 60 × oil objective and analyzed by NIS-Elements F 3.20.02 software (Nikon) (Carty et al. 2019).
-
All data were analyzed by GraphPad Prism 8 using Student's t test. Asterisks indicated the statistical significance: ns, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Fluorescent Confocal Microscopy
Statistical Analysis
-
Viral infection-induced production of IFN is delicately regulated to ensure proper immune response. To determine whether SRP54 is involved in virus-triggered signaling, we constructed a mammalian expression plasmid of SRP54. As shown in Fig. 1A, in reporter assays, overexpression of SRP54 significantly inhibited SeV-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter, ISRE and NF-κB in a dose-dependent manner. Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) analysis showed that overexpression of SRP54 dramatically inhibited SeV-induced transcription of antiviral genes such as IFNB1, ISG56, CXCL10 and TNFA (Fig. 1B). SRP54 also impaired SeV-induced phosphorylation of TBK1, IRF3 and IjBα, which are hallmarks of activation of the RLR-mediated signaling pathway (Fig. 1C). However, overexpression of SRP54 had little effects on IFN-γ-triggered activation of the IRF1 promoter (Fig. 1D). Taken together, these data suggest that SPR54 is a negative regulator of RLR-induced signaling pathway.

Figure 1. Overexpression of SRP54 inhibits RLRs-mediated signaling. A HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were co-transfected with indicated luciferase reporters (0.05 μg each) together with empty vectors or increased amounts (0/0.05/0.1/0.2 μg) of SRP54 expression plasmids. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before luciferase assays were performed. Cell lysate was collected for Western blot analysis. B HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with an empty vector or SRP54 expression plasmid (1 μg). Twenty hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 10 h before quantitative RT-PCR was performed. C HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with empty vector or SRP54 expression plasmids (1 μg). After 24 h, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for the indicated times. Cell lysates were then analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. D Similar luciferase reporter assays as in (A) were performed except the IRF-1 promoter reporters were transfected and cells were treated with IFN-γ (0.1 μg/mL) for 12 h before luciferase reporter assays were performed. Cell lysate was collected for Western blot analysis. β-actin was used as internal control for Western blot assay. GAPDH was used as internal control for quantitative RT-PCR. Graphs show mean ± SD. n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
-
We next investigated the effects of endogenous SRP54 on RLR-mediated signaling. We constructed three SRP54-shRNA plasmids targeting different sequences of human SRP54 mRNA and examined their knockdown efficiency by Western blot. As shown in Fig. 2A, all three SRP54-shRNA plasmids significantly inhibited the expression of SRP54. In reporter assays, knockdown of SRP54 markedly potentiated SeV-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter, ISRE and NF-κB (Fig. 2B). qPCR results indicated that knockdown of SRP54 potentiated SeV-triggered transcription of IFNB1, ISG56, CXCL10 and TNFA in HEK-293T cells (Fig. 2C). To further confirm the function of endogenous SRP54 in other cell types, we generated two SRP54 siRNAs with different targeting sequences from SRP54-shRNAs and examined effects on SeV-triggered signaling in A549 cells. In accordance with the data in HEK-293T cells, knockdown of SRP54 significantly potentiated SeV-induced transcription of IFNB1, ISG56, CXCL10 and TNFA in A549 cells (Fig. 2D) as well as phosphorylation of TBK1, IRF3 and IjBα (Fig. 2E). It has been reported that RIG-I and MDA5 bind to cytoplasmic poly(I:C), a synthetic analog of dsRNA, with different length preference. Reporter assays showed that knockdown of SRP54 potentiated activation of the IFN-β promoter induced by both high and low molecular weight poly(I:C) (Fig. 2F), indicating that SRP54 affects both RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated signaling. In similar experiments, knockdown of SRP54 had little effects on DNA virus HSV-1-induced transcription of IFNB1, ISG56, and IL-6 in HFF cells and IFN-γ-triggered activation of the IRF1 promoter (Fig. 2G, 2H). These data suggest that endogenous SRP54 negatively regulates RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated signaling.

Figure 2. Knockdown of SRP54 potentiates RLRs-mediated signaling. A Knockdown efficiency of SRP54-shRNA on expression of SRP54. In the upper panels, HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were co-transfected with SRP54-Flag (0.2 μg), HA-actin (0.05 μg) and the indicated SRP54-shRNA plasmids (0.8 μg) or GFP-shRNA as control. Thirtysix hours after transfection, immunoblot was performed with antiFlag or anti-HA antibodies. In the lower panels, HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with the indicated RNAi plasmids (1 μg) for 46 h before immunoblot analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. B The HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were transfected with the indicated RNAi plasmids (0.25 μg). After 36 h, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before reporter assays were performed. C HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with the GFP-shRNA as control or indicated SRP54-shRNA plasmids (1 μg). Thirty-six hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before RT-PCR experiments were performed. D Similar experiments as (C) were performed in A549 cells using siRNA. E HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with control or SRP54-shRNA plasmids (1 μg). After 36 h, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for the indicated times. Cell lysates were then analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. F HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were transfected with the control or SRP54-shRNA plasmids (0.25 μg). After 36 h, cells were left untreated, transfected with low molecular weight poly(I:C) (1 μg/mL), or transfected with high molecular weight poly(I:C) (1 μg/mL). 12 h later, luciferase assays were performed for the IFN-β reporter. G Similar experiments as (C) were performed in HFF cells using siRNA. Thirty-six hours after siRNA transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with HSV-1 for 9 h before RTPCR experiments were performed. H Similar luciferase reporter assays as in (B) were performed except the IRF-1 promoter reporters were transfected and cells were treated with IFN-γ (0.1 μg/mL) for 12 h before luciferase reporter assays were performed. β-actin was used as internal control for Western blot assay. GAPDH was used as internal control for quantitative RT-PCR. Graphs show mean ± SD. n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
-
Since SRP54 functions as a negative regulator of RLR-mediated signaling, we next determined whether SRP54 participated in the regulation of cellular antiviral response. HEK-293T cells were infected with GFP-tagged VSV. Immunofluorescence microscopy and Western blot showed that viral replication was elevated in cells overexpressing SRP54 but impaired in SRP54-knockdown cells (Fig. 3A, 3B). These results indicate that SRP54 functions as a negative regulator of cellular antiviral response.
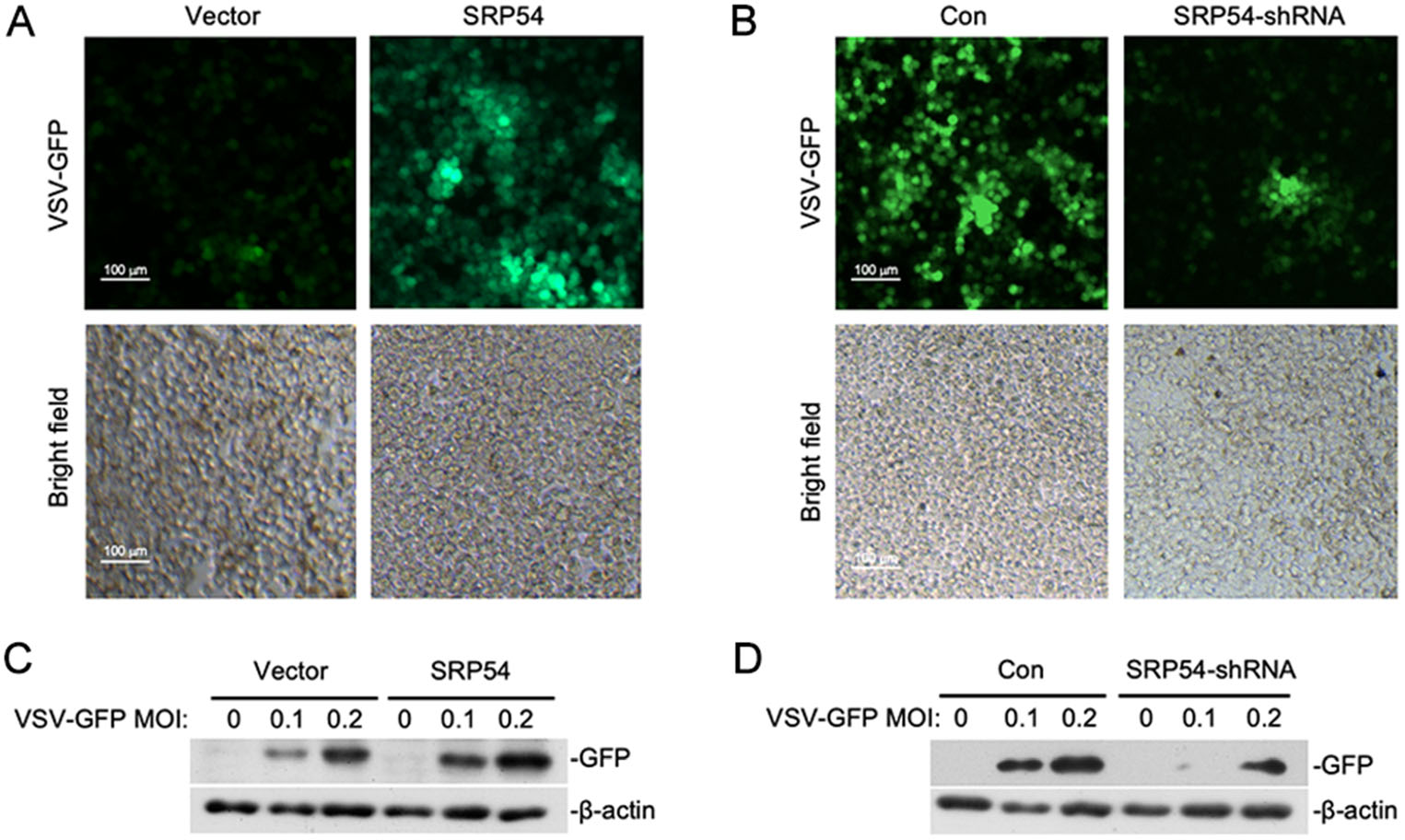
Figure 3. SRP54 inhibits cellular antiviral responses. A HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with the empty vector or SRP54 expression plasmids (0.25 μg). Twelve hours after transfection, cells were infected with VSV-GFP (MOI = 0.1) for 1 h before cells were imaged by fluorescence microscopy. B Similar experiments as in (A) were performed except the control plasmids GFP-shRNA or SRP54-shRNA plasmids (1 μg) were transfected for 36 h. C HEK-293T cells (5 × 105) were transfected with the empty vector or SRP54 expression plasmids (1 μg). Twelve hours after transfection, cells were infected with indicated mounts of VSV-GFP for 10 h. Cell lysates were then analyzed by immunoblotting with the anti-GFP antibody. D Similar experiments as in (C) were performed except the control plasmids GFP-shRNA or SRP54-shRNA plasmids (1 μg) were transfected for 36 h. b-actin was used as internal control for Western blot assay.
-
To elucidate the regulatory mechanism of SRP54 in RLR-mediated signaling, we examined the effects of SRP54 on activation of the IFN-β promoter mediated by different components of the RLR signaling pathway. In reporter assays, SRP54 inhibited activation of the IFN-β promoter induced by RIG-I and MDA5 but not downstream components VISA, TBK1 and IRF3 (Fig. 4A). Transient transfection and coimmunoprecipitation experiments showed that SRP54 specifically interacted with RIG-I and MDA5 but not VISA, TBK1 and IRF3 (Fig. 4B). Confocal microscopy also indicated that SRP54 colocalized well with RIG-I and MDA5 (Fig. 4C). Endogenous coimmunoprecipitation experiments indicated that SRP54 was associated with RIG-I and MDA5 in SeV-dependent manner (Fig. 4D). Consistent with previous experiments, transient transfection and co-immunoprecipitation experiments showed that SRP54 interacted with ER protein SRα but not STING (Fig. 4E). These results suggest that SRP54 negatively regulates virus-triggered signaling at the level of RIG-I and MDA5.
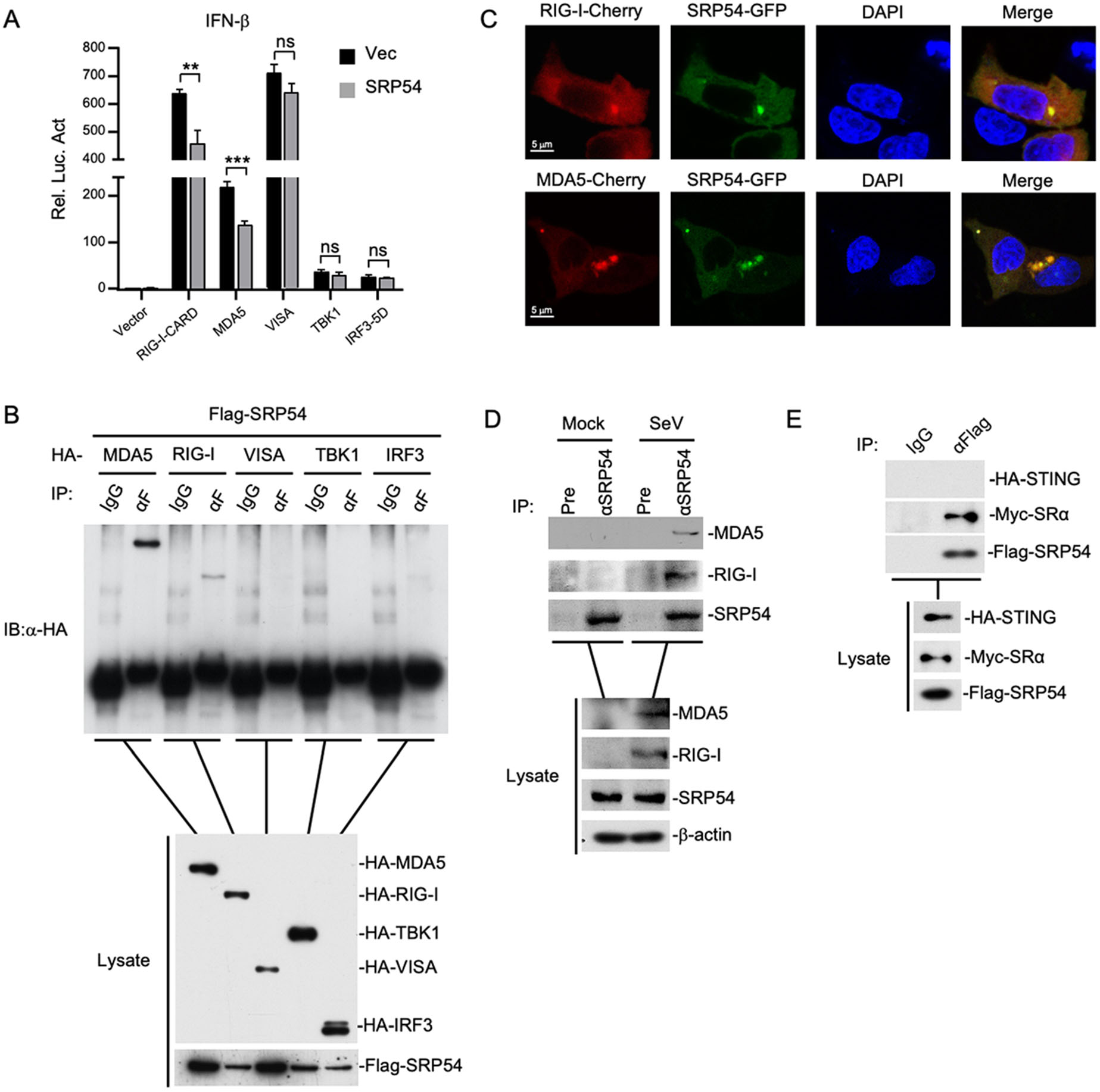
Figure 4. SRP54 targets RIG-I and MDA5. A HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were co-transfected with vector or SRP54 expression plasmids (0.25 μg), IFN-β reporter (0.05 μg) and the indicated plasmids (0.05 μg each) for 24 h before luciferase assays were performed. B HEK-293T cells (1 × 107) were co-transfected with Flag-SRP54 and HA-tagged MDA5, RIG-I-CARD, VISA, TBK1 and IRF3-5D. Co-immunoprcipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. C HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were co-transfected with GFP-tagged SRP54 and Cherry-tagged RIG-I or MDA5. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min and confocal microscopy experiments were performed. D HEK-293T cells (6 × 107) were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 26 h. After virus infection, cells were lysed by NP40 lysis buffer, and the co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies. E Similar experiments as in (B) were performed in HEK-293T cells with the indicated plasmids and antibodies. β-actin was used as internal control for Western blot assay. Graphs show mean ± SD. n = 3. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
-
Since SRP54 has been reported to bind 7SL RNA, we wondered whether SRP54 affects dsRNA binding RIG-I and MDA5. Poly(I:C) pull-down assays showed that SRP54 did not bind to poly(I:C), nor did it affect the binding of RIG-I and MDA5 to poly(I:C) (Fig. 5A, 5B). We next investigated whether SRP54 disrupts the interaction of RIG-I and MDA5 with the adaptor protein VISA. The competitive coimmunoprecipitation experiments indicated that SRP54 disrupted the RIG-I-VISA and MDA5-VISA interactions dose-dependently (Fig. 5C, 5D). These data suggest that SRP54 inhibits virus-induced signaling by disrupting the interactions of RIG-I or MDA5 with VISA.
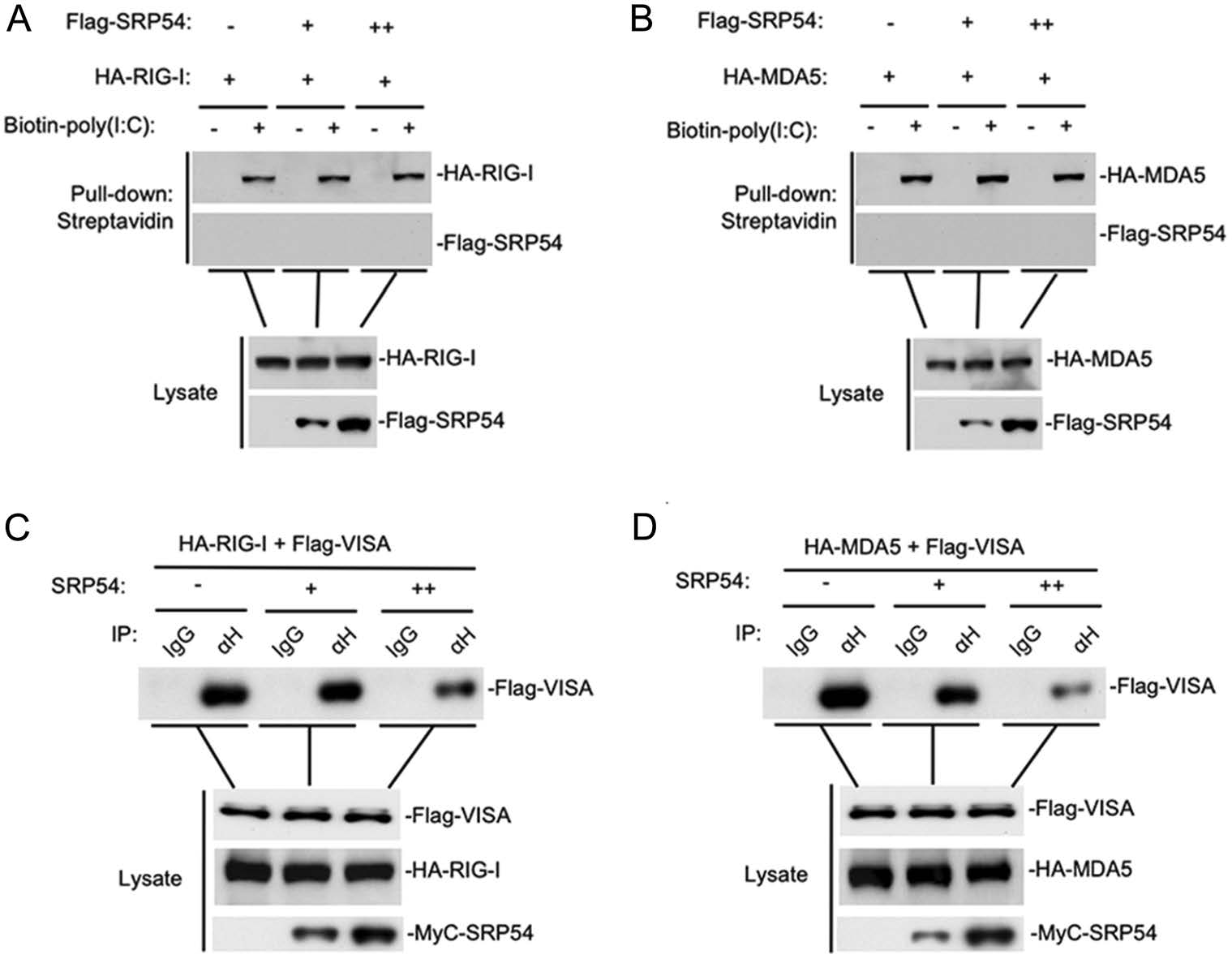
Figure 5. SRP54 impairs the interaction of RIG-I or MDA5 with VISA. A, B HEK-293T cells (1 × 107) were cotransfected with indicated mounts SRP54 and MDA5 or RIG-I, 24 h after transfection cells were harvested and treated with NP40 lysis buffer. Cell lysates were incubated with biotinylated-poly(I:C) and streptavidin-Sepharose. Bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. C, D HEK-293T cells (1 × 107) were co-transfected with increased amounts of Mcy-tagged SRP54 (6 μg or 12 μg), Flag-tagged VISA (3 μg) and HA-tagged RIG-I or MDA5 (6 μg each). Coimmunoprcipitation and immunoblotting were performed with the indicated antibodies.
-
SRP54 has the GTPase activity. Previously, it has been reported that three kinds of loss-of-function mutations (G226E, T115A, T117del) was found in Shwachmandiamond-like syndrome (SDS) patients (Carapito et al. 2017). Therefore, we further investigated whether the GTPase activity of SRP54 is required for its function in innate immune response. In reporter assays, the SRP54 mutants (G226E, T115A, T117del) also inhibited SeV-trigged activation of IFN-β promoter to comparable levels with that of the wild type SRP54 (Fig. 6). These data indicate that the function of SRP54 in SeV-induced signaling pathway does not rely on its GTPase activity.
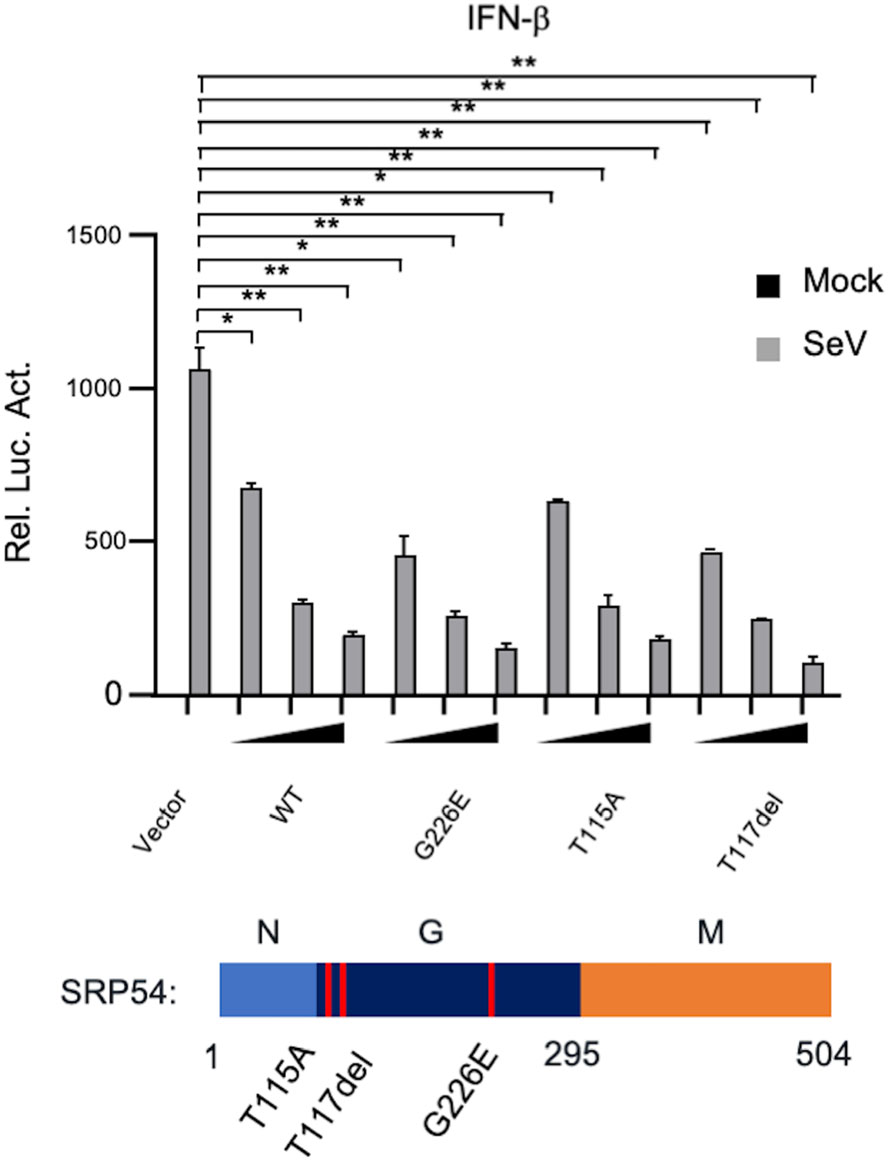
Figure 6. The GTPase activity of SRP54 is dispensable for its ability to inhibit virus-induced signaling. HEK-293T cells (1 × 105) were cotransfected with IFN-β reporters (0.05 μg) together with indicated mutations of SRP54. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before luciferase assays were performed. Graphs show mean ± SD. n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
Overexpression of SRP54 Inhibits RLR-Mediated Signaling
Knockdown of SRP54 Potentiates RLR-Mediated Signaling
SRP54 Inhibits Cellular Antiviral Responses
SRP54 Targets RIG-I and MDA5
SRP54 Impairs the Interaction of RIG-I/MDA5 with VISA
The GTPase Activity of SRP54 is Dispensable for Its Ability to Inhibit Virus-Induced Signaling
-
Recent studies have revealed multiple regulatory mechanisms of RLR signaling for maintenance of immune homeostasis. In this study, we found that SPR54 functions as a negative regulator of innate immune response to RNA viruses. Overexpression of SRP54 inhibited RNA virus induced expression of antiviral genes and facilitated viral replication, whereas knockdown of SRP54 had an opposite effect. Further investigation revealed that SRP54 interacted with RIG-I and MDA5 and disrupted the recruitment of VISA to these RLRs.
It has been reported that SRP54 could bind to 7SL RNA although the affinity is relatively low (Akopian et al. 2013). However, in our pull-down assays, SRP54 did not bind to poly(I:C) or affected binding of RIG-I and MDA5 with poly(I:C). Therefore, the RNA-binding activity of SRP54 is not required for its inhibitory function in RLR-signaling.
In addition to RNA-binding, SRP54 has also been demonstrated to function as an important GTPase in the cotranslational process (Bacher et al. 1996). However, reporter assays showed that the GTPase-deficient mutant of SRP54 inhibited RLR-signaling as well as the wild type SRP54, suggesting such activity is dispensable. These results indicate that the inhibitory function of SRP54 on innate immune response was not mediated by SRP-dependent protein translocation but is a novel role of SRP54.
Taken together, our findings suggest that SRP54 negatively regulates the RIG-I/MDA5-VISA-mediated antiviral innate immune signaling and reveal the mechanism of how SRP54 negatively regulates this signaling pathway from molecular and cellular levels. These findings are the first to reveal the role of SRP54 in innate immune system and provide important theoretical basis and potential molecular targets for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
-
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770946, awarded to Y.Y.) and Key Research Programs of Frontier Science (awarded to Y.Y.W.) funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
-
DPW, YYW and YY designed the experiments. DPW, HYZ, BWL and TZ carried out the experiments. DPW, ZSX, YYW and YY analyzed the data. DPW wrote the paper. YY and YYW checked and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they no conflict interest.
-
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: