-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the patho-gen of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Now AIDS is epidemic all over the world. Establish-ment of the non-human primate models for AIDS research has been a major focus of vaccine develop-ment and pathogenesis researches since the discovery of AIDS (7, 8). Although chimpanzees are susceptible to HIV-1 infection, it is generally acknowledged that they are less suitable for AIDS research because they rarely develop disease after HIV infection (4). Natural simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) infection is widespread in feral populations of African monkeys, but this infection does not result in immunodeficiency (14). SIV and Simian/human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) infect macaques and result in an immunodeficiency syndrome that is remarkably similar to that in HIV infected humans. Thus, SIV/macaques and SHIV/ macaques models have been usually used to study the pathogenesis of HIV/AIDS as well as evaluation of drugs and vaccines (6, 15).
SIVmac239 and SIVmac251 are commonly used SIV strains. Both strains are originally isolated from breeding rhesus monkeys, and they are pathogenic to rhesus macaques (3, 11). SIVmac239 is an important immunodeficiency virus strain, because SIVmac239 is used to construct SHIVs as backbone. And many attenuated SIV strains are also constructed by deleting the pathogenic gene of SIVmac239 (12, 13). SIV-mac251 is usually used in China (5, 10). To further understand HIV-1 pathogenesis and find better vaccine and drug, two Chinese rhesus macaques were inoculated with SIVmac239 to establish non-human primate AIDS animal model in the present study.
HTML
-
Three Chinese rhesus macaques from Kunming Primate Research Center, Chinese Academy of Sci-ences (CAS), were housed at an Animal Biosafety Level 3 (ABSL-3) laboratory and used in this study. All animals were screened and found to be negative for simian type D retrovirus (SRV) and SIV by antibody ELISA and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) prior to use. Macaques were restrained with ketamine hydrochloride (10 mg/kg of body weight) before virus inoculation and blood collection. Housing, mainte-nance and care of the animals were performed in accordance with the regulations and recommendations of the Animal Care Committee of Kunming Institute of Zoology, CAS.The clones p239SpSp5' and p239-SpE3' kindly donated by Prof. Gao Bin of Institute of Microbiology, CAS, were used for generating the infectious pathogenic SIVmac239. The Virus stocks were propagated in CEMx174 cells and stocked at -80 ℃. The frozen aliquots of the titered virus were quickly thawed before intravenous inoculation.
Both macaques (#99003 and #99083) were ino-culated intravenously with 5000 TCID50 of cell-free SIVmac239, and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was injected in macaque #98081 as the negative control. The whole blood was collected from all monkeys in EDTA-K2 tubes at days 0, 7, 14, 21, 35, 64, 78, 92, 99, 106, 113, 121 thereafter. Infected animal were euthanized on day 121 after infection.
-
The number of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes in peripheral blood was determined using the Tru-CountTM (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) method by flow cytometry. In briefly, blood samples were stained with the fluorochrome-conjugated mono-clonal antibodies to CD3-PE, CD4-PerCP (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) for analysis on a Becton Dickinson FACSCalibur flow cytometery (New Jersey, United States) according to manufac-turer's protocols.
-
Plasma viral load were determined by TaqMan real-time RT-PCR. The RNA copy number was determined by using an external standard curve based on in vitro transcripts representing 1624 to 1985 nt of the SIVmac239 genome with primer A (Table 1) (Genbank Accession Number M33262). The assay had a sensitivity of 180 RNA copies per mL of plasma and the linear dynamic range was from 102 to 108 copies/mL (R2 = 0.99). Viral RNA was purified from 0.3 mL of plasma with TRIzol (MRC, Cincinnati, US) and finally dissolved in 30 μL of RNase free dH2O. Viral RNA was then converted to cDNA using PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit according to the manufacture' instruction (TAKARA, Dalian, China). The 149-bp SIVmac239 gag gene fragment primer was primer B, and probe C was used in real-time PCR (Table 1). SIV gag gene amplification was carried out using Premix Ex TaqTM (Perfect Real Time) kit (TAKARA, Dalian, China), and the amplication condition was as follows: one cycle of 10 seconds at 94 ℃ and 40 cycles in two steps each (94 ℃ for 5 s, 60 ℃ for 30 s).

Table 1. PCR Primer pairs and probe
-
Cell-associated infectious viruses were isolated by co-cultivation of rhesus macaque peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) with 2×105 CEMx174 cells in RPMI 1640 containing 10% FBS in 24-well plates. The cultures were observed for cytopathic effect (CPE) under a light microscope, and virus production was monitored by PCR using primer A (Table 1).
-
Proviral DNA in PBMCs of inoculated monkeys was detected by nested PCR as described previously (2). Briefly, the first PCR round using primer D has the following cycle profile: 95 ℃ for 10 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 ℃ for 55 sec, 56 ℃ for 30 sec, 72 ℃ for 28 sec, and 72 ℃ for 10 min. For the second round, 0.5 μL products from the first round were amplified using the same profile of the first round, primer E was used (Table 1). PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide.
-
SIV specific antibodies were assayed by ELISA method. Briefly, PEG purified and TNE solution disolved SIV antigen were coated in ELISA plates, and plasma antibody was then detected according to ELISA procedure.
Macaques and virus inoculum
Lymphocyte phenotyping
Plasma virus load measurement
Virus isolation
Detection of proviral DNA in PBMCs
SIV-specific antibodies assay
-
The kinetics of CD4+ T lymphocytes is an indicator for the demonstration of clinical course. The changes in the numbers of CD4+ cells were assayed during the 121-day period of infection. The numbers of CD4+ T cell in negative control rhesus #98081 had relatively steady throughout the period of observation at early stage. While the CD4+ cell numbers of both the infected rhesus monkeys #99083 and #99003 dropped within the first two-week post challenge and remained at a relatively low level (Fig. 1). The lower CD4+ cell number was consistent with higher viral load.
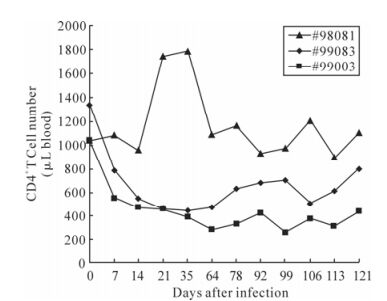
Figure 1. The numbers of CD4+ T cells in SIVmac239 infected Chinese rhesus macaque. The three curves represented variation during the 121 days of CD4+ T lymphocytes. Monkey #99083 and #99003 had been SIV challenged. And monkey #98081 was used as the negative control. The CD4+ cell number was counted by flow cytometry.
-
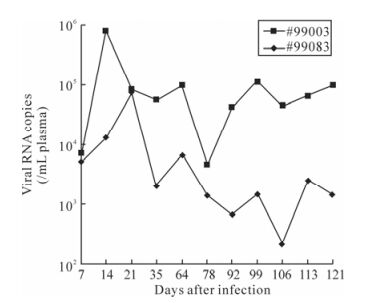
Quantification of SIV viral RNA load in plasma was determined by TaqMan real-time RT-PCR. Peak viremia occurred at day 14 in macaque #99003 (7.9×105 copies / mL plasma) and declined thereafter. Interestingly, it consistently had higher viral loads throughout the course of the study (average 6.5×104 copies/mL), and another macaque #99083 had lower viral loads (2.0×103 copies/mL on an average) and peak viremia occurred on day 21 (7.4×104 copies / mL plasma) (Fig. 2).
-
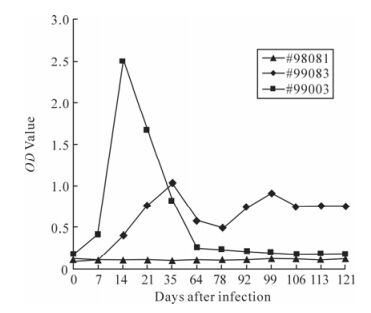
Plasma from the two infected monkeys was used to detect SIV antibodies production by ELISA. Both rhesus monkeys mounted detectable antibody response against SIV antigens. Interestingly, two infected monkeys had significantly different antibody response. The antibody in Macaque #99003 reached a peak level at week 2 after infection and the curve rapidly dec-lined down to undetectable level. The antibody in macaque #99083 had a peak level at week 5 and consistently maintained at this level throughout the course of research, though the peak level was lower than that of macaque #99003 (Fig 3). These finding are consistent with their relatively higher viral loads.
-
Proviral DNA in the PBMCs was measured by nested PCR. Even at the early stage of infection, proviral DNA had been detected in the PBMCs of two infected monkeys, and remained positive throughout the observation period (Fig. 4 and Fig. 5).
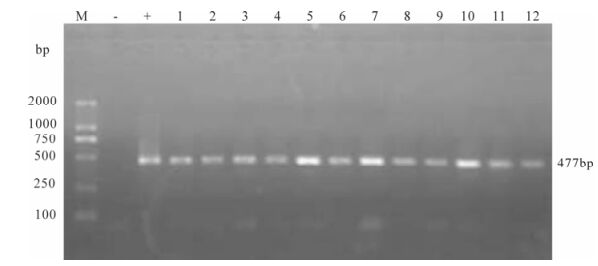
Figure 4. Proviral DNA in PBMCs of SIVmac239 infected Chinese rhesus #99003. Shown is the gel electrophoresis profile of nested PCR products amplified from DNA extracted from PBMCs of different days postinfection. Lane 1, 2 represent 7 day post-infection, lane 3-5 represent 14, 21, 35 day post-infection, lane 6, 7 represent 64 day post-infection and Lane 8-13 represent 78, 92, 99, 106, 113, 121 day post-infection.
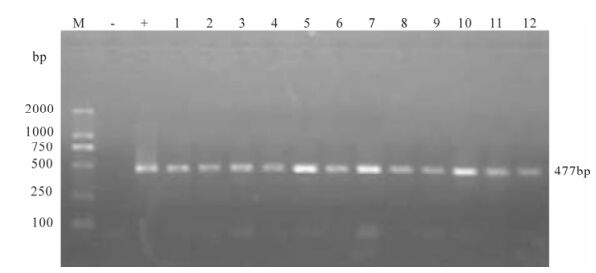
Figure 5. Proviral DNA in PBMCs of SIVmac239 infected Chinese rhesus #99083. Shown is the gel electrophoresis profile of nested PCR products amplified from DNA extracted from PBMCs of different days post-infection. Lane 1, 2 represent 7 day post-infection, lane 3, 4 represent 21, 35 day post-infection, lane 5, 6 represent 64 day post-infection, lane 7-12 represent 78, 92, 99, 106, 113, 121 day post-infection.
-
The cytopathic effect (CPE) could be seen in co-cultivation of infected rhesus macaque PBMCs with CEMx174 cells under a normal light microscope at week 2 post-challenge (Fig. 6). The constant suc-cess of SIV isolation indicates that viral replication persistently occurs in infected monkeys. The success of virus isolation is in good accordance with our results on nested PCR for provirus in peripheral blood cells. Since that time point, the PBMCs of the mon-keys remained virus-positive throughout the obser-vation period (Fig. 7).
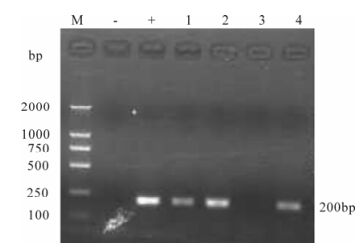
Figure 7. Detection of SIVmac239 in supernatant from macaque PBMCs and CEMx174 cells co-cultures. RT-PCR products were assayed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, 2 represent isolated viruses from macaque #99003 day 7 and 14 post-infection, respectively; Lane 3, 4 represent isolated viruses from macaque #99083 day 7 and 14 post-infection, respect-tively.
CD4+ T lymphocytes in macaques
Plasma viral load in SIV-infected macaques
SIV-specific antibody responses
Proviral DNA assay
Virus isolation from PBMCs
-
The non-human primate AIDS models are impor-tant for studying HIV/AIDS pathogenesis, evaluating vaccines and anti-HIV drugs. HIV and SIV are related lentiviruses that cause a similar syndrome in their res-pective hosts. Because of these similarities, SIV and SHIV infection in macaques have been used extensively for studying HIV-1 infection. In this study, two Chinese rhesus macaques were followed up for 121 days after intravenous inoculated with SIVmac239. The results showed that both the Chinese macaques developed rapid systemic infection. Viremia could be detected seven days post-challenge, and viral load reached the peak at week 2 or week 3 post-challenge. The CD4+ T lymphocytes began to decrease two weeks after challenge. We also isolated infectious SIVmac239 and screened out SIV-specific antibodies in the serum of those two infected macaques. All these results demonstrated that SIV-mac239 caused HIV-1-like pathologic effects in Chinese rhesus macaque after inoculation by the intravenous route.
In our study, macaque #99003 had higher viremia with the peak of viral load up to 7.9×105 copies/mL plasma and a lower CD4+ T lymphocytes of 259 cells/μL blood. Macaque #99083 had a viral load of 7.4×104 copies/mL plasma and its CD4+ T lym-phocytes remained at a higher level than that of #99003, even though the number decreased to 442 cells/μL blood. In other words, the peak of viral load was 7.9× 105 copies/mL blood, and the CD4+ T lymphocyte decreased to its bottom of 259 cells/μL blood with a retrieve up to 497 cells/μL blood thereafter in two infected macaques. During the four-month period, the monkeys had not developed AIDS and had not shown any pathologic symptoms.
According to previous study (9), the humoral im-mune response and cellular immune response of Chinese rhesus macaque infected with SIVmac239 were more similar to human immune responses to HIV in comparison with SIV-infected Indian macaque. The pathogenetic process develops much faster in SIV-infected Indian macaques. And the blood viremia is higher in Indian monkeys (1). The viral load could grow up to 107-108 copies/mL in plasma. The CD4+ T lymphocytes decreased greatly even down to 200-cells/μL blood. When the CD4+ T lymphocytes depletion goes on, the monkeys would have more opportunity infections. But this process is slower in SIV-infected Chinese rhesus macaques. The viral load is about 105 to 107 copies/mL in plasma. It needs even several years for the AIDS to develop. The Chinese macaques and Indian macaques have similar phy-logenesis, but their pathogenetics processes are so different to SIV infection.
Both macaques seroconverted with anti-viral anti-bodies detected early at 1 week after infection. In general, macaques infected with SIVmac239 exhibited relatively high antibody titers to virus. This finding may be related to the fact that macaques infected contained high virus loads. However, two infected monkeys had different viremia and different immune response in present study. The SIV-specific antibody of macaque #99003 increased greatly in a short period and then decreased to the negative level. Meanwhile, the SIV-specific antibody level of macaque #99083 was higher than that of macaque #99003, and the antibody kept at a steady level in the period. The levels of anti-viral antibodies correlate with viral load in both animals. So, the antibody might be related with the control of infectious virus. More compre-hensive research with more macaques to confirm this phenomenon is needed.
In summary, this study shown that pathogenic SIVmac239 caused productive infection and the loss of CD4+ T cells in inoculated Chinese macaques. This animal model can be applied for studying the patho-genic mechanisms of AIDS, evaluating antiviral drugs and vaccine.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: