HTML
-
Approximately one third of the world's population live in areas endemic for hepatitis E virus (HEV) and are at risk for infection (Perez-Gracia et al. 2013). Although the majority of HEV infections is asymptomatic, some of them cause acute and chronic hepatitis E (HE), fulminant liver failure and even extrahepatic symptoms (Kamar et al. 2012). HE may be particularly severe in pregnant women and immunocompromised patients (Kumar et al. 2004; Dalton et al. 2009). HEV is responsible for numerous outbreaks of viral hepatitis in many tropical countries. It is estimated that the number of symptomatic HEV infections in these countries exceeds three million annually, causing up to 70, 000 deaths each year (Rein et al. 2012).
The virions of human HEV are icosahedral and spherical particles with a diameter of approximately 27–34 nm (Smith et al. 2014). The viral genomes are positive-sense single-stranded RNA molecules of 6.4–7.2 kb containing three open reading frames (ORFs: ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3), 5'- and 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs), and a poly (A)-tract at the 3'-end. ORF1 encodes the non-structural proteins and functional domains including methyltransferase (Met), Y-domain (Y), papain-like protease (PCP), hypervarible region (HVR), macro-domain (X), RNA helicase (Hel) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) required for RNA replication. ORF2 expresses the capsid protein. ORF3 overlaps with ORF2 and encodes a multifunctional phosphoprotein (Cao and Meng 2012; Kamar et al. 2012; van Tong et al. 2016). An additional ORF4, overlapping the 50 end of ORF1, has been described recently for rat and ferret HEV strains. However, the functional role of ORF4 is not clear (Johne et al. 2014).
According to the latest consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae from the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), it is divided into two genera: Orthohepevirus including all mammalian and avian HEV strains, and Piscihepevirus including cutthroat trout virus. Currently, four species (Orthohepevirus A, B, C and D) have been assigned in the genus Orthohepevirus. Within the species Orthohepevirus A, seven HEV genotypes (HEV-1 to HEV-7) are recognized based on the criterion of amino acid (aa) distances (> 0.088) of concatenated ORF1 and ORF2 (lacking hypervariable regions) (Smith et al. 2014, 2016). HEV-1 to HEV-4 are human pathogens, HEV-1 and HEV-2 infect exclusively humans and are typically associated with large waterborne epidemics in some countries of Asia and Africa as well as in Mexico, while HEV-3 and HEV-4 are detected in humans and a number of other animal species and the main cause of sporadic cases of HE in many industrialized countries (Pavio et al. 2015). HEV-5 and HEV-6 have been identified only in wild boars, and the HEV-7 from dromedary camels has been reported to infect humans and cause chronic HE, as observed in a liver transplant patient (Woo et al. 2014; Lee et al. 2016). Recently, putative HEV-8 is identified in Bactrian camels with an unknown zoonotic potential (Woo et al. 2016; Sridhar et al. 2017). The species Orthohepevirus C contains two genotypes: genotype C1 (HEV-C1), including strains derived from rat and shrew, and HEV-C2, including strains derived from ferret and possibly mink (Smith et al. 2014). Of note, the current newly discovered HEV-related viruses from moose, fox, kestrel and little egret are waiting for further classification (Purdy et al. 2017).
Rodents are highly abundant and diversified in various terrestrial habitats and harbour a variety of viruses closely related to human diseases (Koch et al. 2007). Currently, a number of HEV-related viruses have been detected from Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) and Black rats (Rattus rattus) at different sites including China, Vietnam, Indonesia, the USA and eleven European countries (Johne et al. 2010a; Purcell et al. 2011; Li et al. 2013; Mulyanto et al. 2014; Ryll et al. 2017; Wang et al. 2017c). Furthermore, rat HEV sequences have been detected also in the greater bandicoot rat (order: Rodentia) and Asian musk shrew (order: Soricomorpha) (Guan et al. 2013; Li et al. 2013). The zoonotic transmission potential of rat HEV to humans is still controversial (Johne et al. 2014). Sera of rats that are infected with rat HEV are known to cross-react with human HEV antigens (Dong et al. 2011). Moreover, rat HEV was shown to replicate in a human-derived cell line with a reverse genetics system (Li et al. 2015). However, experimental infection of monkeys and domestic pigs with rat HEV failed (Cossaboom et al. 2012).
In this study, we have investigated the presence and prevalence of HEV-related viruses (orthohepeviruses) in 278 small mammal specimens pertaining to 7 species sampled in Yunnan province, China, and report the discovery of novel orthohepeviruses from Chevrier's field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) and Père David's vole (Eothenomys melanogaster).
-
278 small mammals (rodents, shrews, and carnivore), which comprised three orders, four families, and seven species, were captured by mouse traps in Luxi city and Lijiang city, Yunnan province, China, from September 2014 to November 2015 (Table 1). All animals live-trapped were anaesthetized to minimize suffering. Different tissues (liver, heart, intestine, spleen, kidney, and lung) were collected separately and used for analysing virus tissue tropism. Samples were transported by nitrogen canister and stored at -80 ℃ until thawed for RNA extraction. The animal species were firstly identified by trained field biologists and then confirmed by DNA sequencing of the mitochondrial cytochrome (CytB) gene following previously described methods (Ge et al. 2013; Wang et al. 2017b). RNA was extracted from tissue using the High Pure Viral RNA Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) following the manufacturer's instructions, and cDNA was synthesized using Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus (M-MLV) Reverse Transcriptase (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The extracted RNA was eluted, aliquoted and stored at -80 ℃.

Table 1. Detection of orthohepevirus in small mammals from Yunnan province, China between 2014 and 2015
-
The extracted RNA was tested by broad-spectrum heminested reverse-transcription (RT)-PCR using degenerate primers based on the conserved domain of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)-encoding gene of viruses within the genus Orthohepevirus. PCR products comprised 291 nucleotides (nt) (Drexler et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2017b). The amplicons underwent gel purification with MinElute Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden; Germany) and they were sequenced with both forward and reverse primers using the 3100 Sequencer (ABI, Waltham, MA, USA) or cloned using the pGEM-T Easy vector system (Promega, Madison, WI, US) for sequencing if the direct sequencing failed.
Based on the sequences obtained in this study, we designed primers and probes that specifically targeted the novel rodent orthohepeviruses detected in China. Probes were labelled at the 5' end with 6-carboxyfluorescein (6-FAM) and at the 3' end with Black Hole Quencher 1 (BHQ1) (Supplementary Table S1). The standard curves of the template RNA were constructed as previously described (Wang et al. 2017b; Yang et al. 2017). Samples were characterized by a well-defined exponential fluorescence curve that crossed the cycle threshold (Ct) within 36 cycles. Specimens with a Ct > 36 were repeated to exclude operational faults. The viral genome copy number was calculated in each sample using the standard curves of the template RNA. Virus loads of 4 representative orthohepevirus-positive specimens (RdHEVAc18, RdHEVAc53, RdHEVAc55, and RdHEVAc70) of different tissues (liver, heart, intestine, spleen, kidney, and lung) were measured.
-
The complete genomic sequences of four rodent orthohepevirus strains were amplified by PCR using degenerate and strain-specific primers (Supplementary Table S1) (Drexler et al. 2012). Genome ends were amplified by using 5'/3'-Full rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) kit (Clontech, Takara Bio, USA). PCR products were gel purified with a MinElute Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and sequenced with both forward and reverse primers using a 3100 Sequencer (ABI, Waltham, MA, USA). The sequencing chromatograms were inspected carefully for overlapping multicolour peaks, which are an indicator of sequence heterogeneity. The PCR products were cloned using the pGEM-T Easy Vector System (Promega, Germany) and at least three clones for each PCR fragment were sequenced to obtain a consensus sequence.
-
Sequence analysis and genome assembly were carried out with Geneious version 10.0.5 (Biomatters Limited, Auckland, New Zealand) as previously described (Wang et al. 2017a; b). Pairwise distances of complete genome nt and concatenated ORF1/ORF2 aa sequences were analysed using SSE as recommended by ICTV Hepeviridae Study Group (Simmonds 2012; Smith et al. 2014). Sequence similarity comparisons were implemented using the BLASTn search engine (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). Homology to known protein domains was identified using Motif Scan (http://myhits.isb-sib.ch). To identify possible recombination, bootscanning analyses of full-length sequences were performed in the SimPlot software program, version 3.5.1 with a sliding window size of 200 and a step size of 20 aa increment (Lole et al. 1999; Drexler et al. 2012). All orthohepevirus sequences reported in this study were submitted to GenBank under Accession Numbers: MG019963–MG020021 for orthohepevirus partial RdRp gene sequences and MG020022–MG020025 for orthohepevirus full-length genome sequences.
-
The preliminary sequence alignment and editing were performed using MAFFT (Katoh et al. 2002). Phylogenetic reconstructions were performed using MEGA version 7 with 1000 bootstrap replicates (Kumar et al. 2016). The neighbour-joining trees of p-distances among aligned partial RdRp-coding gene sequences comprised 291 nt corresponding to positions 4300–4590 within Orthohepevirus A reference strain (GenBank Accession No. M73218) and aligned complete genome sequences of the newly detected rodent orthohepeviruses were built, respectively. The maximum-likelihood trees were reconstructed from aa sequences for ORF1, ORF2, ORF3, and putative ORF4-encoding proteins respectively, using the Jones–Taylor– Thornton model with frequencies, and gamma distribution with invariant sites according to the previous study (Smith et al. 2014). The reference HEV strains within the family Hepeviridae and complete genome sequences derived from rat and ferret within the species Orthohepevirus C were used for phylogenetic analyses. The branches are labelled with the strain designation, the host species, and the GenBank accession number. The classification of the respective species or genotypes is indicated on the right.
-
GraphPad Prism Software version 7.03 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) was used for data analysis using a Student t test. All results were presented as mean ± standard errors of the means (SEM). P values of less than 0.05 (single asterisks in figures) were considered statistically significant; whereas P values less than 0.01 (double asterisks) and 0.001 (triple asterisks) were considered highly significant.
Sampling and RNA Extraction
Orthohepevirus Detection and Quantification
Full-Length Genomic Sequencing
Sequence Analysis
Phylogenetic Analysis
Statistical Analysis
-
A total of 278 small mammals, belonging to three orders, four families, and seven species, were captured between 2014 and 2015 from two geographical locations: Lijiang city and Luxi city in Yunnan province, China. Blood and tissue samples harvested from these animals were examined for the presence and prevalence of orthohepevirus using broad-spectrum hemi-nested RT-PCR as previously described (Drexler et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2017b). As illustrated in Table 1, 63 samples produced fragments of the expected size and were confirmed to be positive for orthohepevirus RNA by direct sequencing or clone sequencing. The orthohepevirus-positive samples originated from two species: Chevrier's field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) belonging to the family Muridae from Lijiang city and Père David's vole (Eothenomys melanogaster) belonging to the family Cricetidae from Luxi city, with the infection rates of 29.20% (59/202) and 7.27% (4/55), respectively (Table 1). Based on 291 nt of partial RdRpencoding gene, the sequences of the samples had nt identity of 73%–84% with Orthohepevirus C strains. The 59 orthohepevirus strains from Chevrier's field mouse from Lijiang city reflected remarkable diversity within the group (71%–99% nt identity). Above all, 56 strains had the highest nt identity of 74% to ferret HEV strain F63 (GenBank Accession No. LC177792) and three strains had the highest nt identity of 86% to rat HEV strain rat/Mu09/ 0434/DEU/2010 (GenBank Accession No. JN167538). The four orthohepevirus strains from Père David's vole from Luxi city shared nt identity of 77%–99% within the group and had the highest nt identity of 72% to kestrel HEV strain kestrel/MR16/2014/HUN (GenBank Accession No. KU670941). While other small mammal samples, including Rattus tanezumi, Mus caroli, and Eothenomys chinensis (order: Rodentia), Anourosorex squamipes (order: Soricomorpha), and Mustela sibirica (order: Carnivora) were negative for orthohepevirus RNA detection (Table 1).
-
Since complete genome sequences are required for new orthohepevirus assignment (Smith et al. 2014, 2016), and in order to further characterize the novel orthohepevirus strains from the different wild rodent samples, we generated four full-length genome sequences from selected samples, two each from Chevrier's field mouse (designated RdHEVAc: RdHEVAc14 and RdHEVAc86) and Père David's vole (designated RdHEVEm: RdHEVEm40 and RdHEVEm67). The lengths of the whole-genome sequences were 6967 nt for RdHEVAc14; 6966 nt for RdHEVAc86; 6961 nt for RdHEVEm40; and 6964 nt for RdHEVEm67, respectively, excluding the poly(A)-tail. The G + C contents of RdHEVAc14 and RdHEVAc86 were 55.0 and 54.7%, but only 50.5 and 50.3% for RdHEVEm40 and RdHEVEm67. The genomic features and putative domains of these newly detected rodent orthohepevirus strains were characterized in Table 2. A similar genomic organization including 3 ORFs of the family Hepeviridae was observed for these novel rodent orthohepevirus strains, 4 putative functional domains including Met, X, Hel, and RdRp could be predicted in the ORF1 (Table 2). Surprisingly, the putative ORF4 overlapping ORF1 as postulated to exist in the HEV-C1 and HEV-C2 was found at genomic position 35–553 of RdHEVAc, but was absent in RdHEVEm (Johne et al. 2010b, 2014). No putative ORF5 and ORF6 were observed for these novel strains (Johne et al. 2010b; Raj et al. 2012).

Table 2. Genomic features and putative domains of novel rodent orthohepevirus strains
-
Complete genome nt identity between RdHEVAc14 and RdHEVAc86 was 92.3, and 89.8% between RdHEVEm40 and RdHEVEm67. However, RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm were highly divergent with only 56.4%–56.8% nt identity in the genomic sequences. Comparisons of the wholegenome nt sequences and aa sequences of deduced ORFs of newly detected rodent orthohepevirus strains with representative orthohepevirus reference strains are shown in Tables 3 and 4. All the novel rodent orthohepevirus strains in this study had a highest nt identity to the strains within the species Orthohepevirus, HEV-C1 (65.5%) and HEVC2 (62.8%) for RdHEVAc, and HEV-C1 (56.8%) and HEV-C2 (56.1%) for RdHEVEm. Similar results were obtained using the coding regions for comparison: RdHEVAc strains shared higher percentage of aa sequence similarity to HEV-C1 or HEV-C2 than other species and genotypes within the family Hepeviridae, HEV-C1 (ORF1, 68.0%; ORF2, 74%; ORF3, 46.2%; and ORF4, 50.8%) and HEV-C2 (ORF1, 68.6%; ORF2, 71.6%; ORF3, 36.3%; and ORF4, 54.1%). Likewise, identities of three ORFs from RdHEVAc to HEV-C1 (ORF1, 53.4%; ORF2, 62.8%; ORF3, 24.8%; and ORF4, 50.8%) to HEV-C2 (ORF1, 54.3%; ORF2, 58.8%; and ORF3, 26.3%) (Tables 3, 4). Compared to other orthohepevirus strains within the species Orthohepevirus C, the genomic organization of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm also demonstrated genetic variability. As shown in Fig. 1, HEV-C1 had the two distinct translational frames for ORF1 and ORF2, and ORF3 and ORF4, respectively. However, HEV-C2 and RdHEVAc implemented three different translational frames for ORF1 and ORF3, ORF2, and ORF4, respectively. Importantly, RdHEVEm used three translational frames for ORF1, ORF2, and ORF3, which is the same as for HEV-1 to HEV-3 (Sridhar et al. 2017). Moreover, the overlaps of ORF1, ORF2, and ORF3 for HEV-C1, HEVC2, RdHEVAc, and RdHEVEm vary length and location (Fig. 1). In addition, the 5'-UTR region of RdHEVAc carried a 10 nt motif GCAACCCCCG reported to be uniquely present in the rat HEV strains, yet RdHEVEm lacked this motif despite having a longer 5'-UTR region (Mulyanto et al. 2014).

Table 3. Identities of complete genome and ORFs between RdHEVAC and representative orthohepevirus reference strains

Table 4. Identities of complete genome and ORFs between RdHEVEm and representative orthohepevirus reference strains
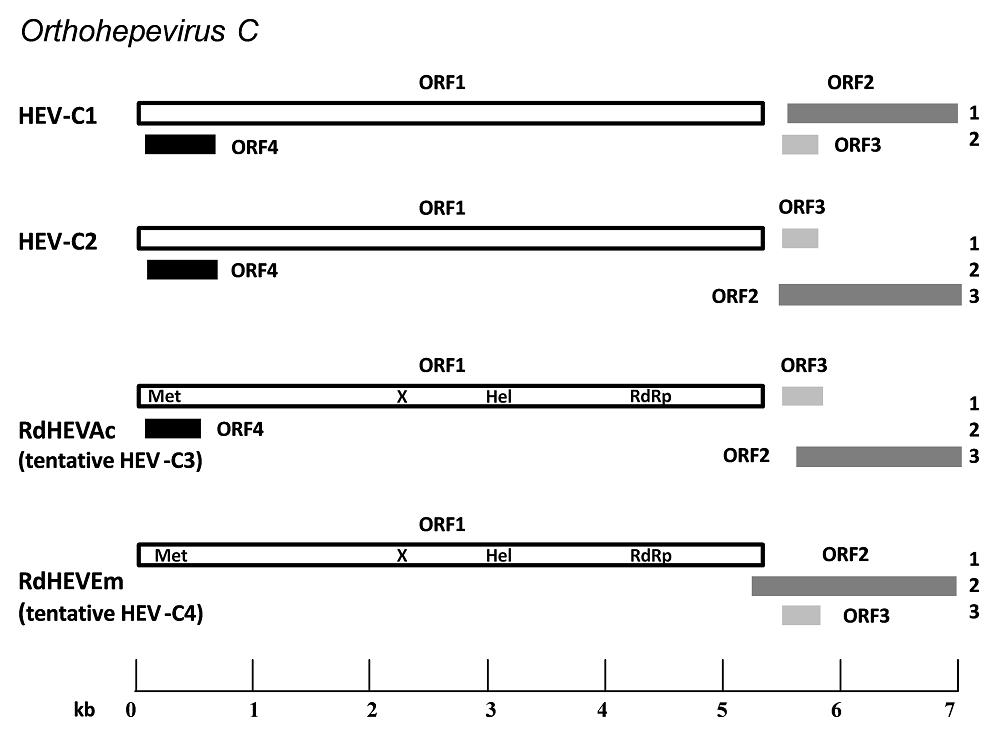
Figure 1. Schematic description of the species Orthohepevirus C genomes and viral proteins. Different reading frames are denoted on the right, ORF1 is considered as frame 1. HEV-C1 is relative to the reference strain R63 (GenBank Accession No. GU345042); HEV-C2 is relative to the reference strain FRHEV4 (GenBank Accession No. JN998606). ORF1 encodes the non-structural polyprotein, and putative domains of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm including methyltransferase (Met), macrodomain (X), RNA helicase (Hel) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) are indicated. ORF2 encodes the capsid protein. ORF3 encodes a small multifunctional protein. The function of particular ORF4 is still unknown (adapted from Sridhar et al. 2017).
-
A neighbour-joining tree of pairwise distances among alignments of partial RdRp-coding sequences showed that the detected orthohepevirus strains from the two rodent species in this study were highly diverse within the genus Orthohepevirus (Fig. 2A). Intriguingly, three orthohepevirus sequences derived from Chevrier's field mouse clustered into the HEV-C1 cluster. Conversely, the other 56 orthohepevirus sequences derived from the same species formed a separate group (RdHEVAc) (Fig. 2B). Meanwhile, four orthohepevirus strains derived from Père David's vole formed a separate clade (RdHEVEm) and seemed to be more divergent within the family Hepeviridae. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete genome sequences indicated that the RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm from the order Rodentia formed two independent branches within the clade of the species Orthohepevirus C, which reflected even higher divergence from HEV-C1 (order: Rodentia) than HEV-C2 (order: Carnivora) (Fig. 3A). Similar phylogenetic topologies were observed when the deduced ORF1 and ORF2 were analysed separately (Fig. 3B, C). Although the phylogenetic topologies of ORF3 and ORF4 seemed to be more complex, RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm were remarkably divergent from other assigned species or genotypes within the family Hepeviridae (Fig. 3D, E),
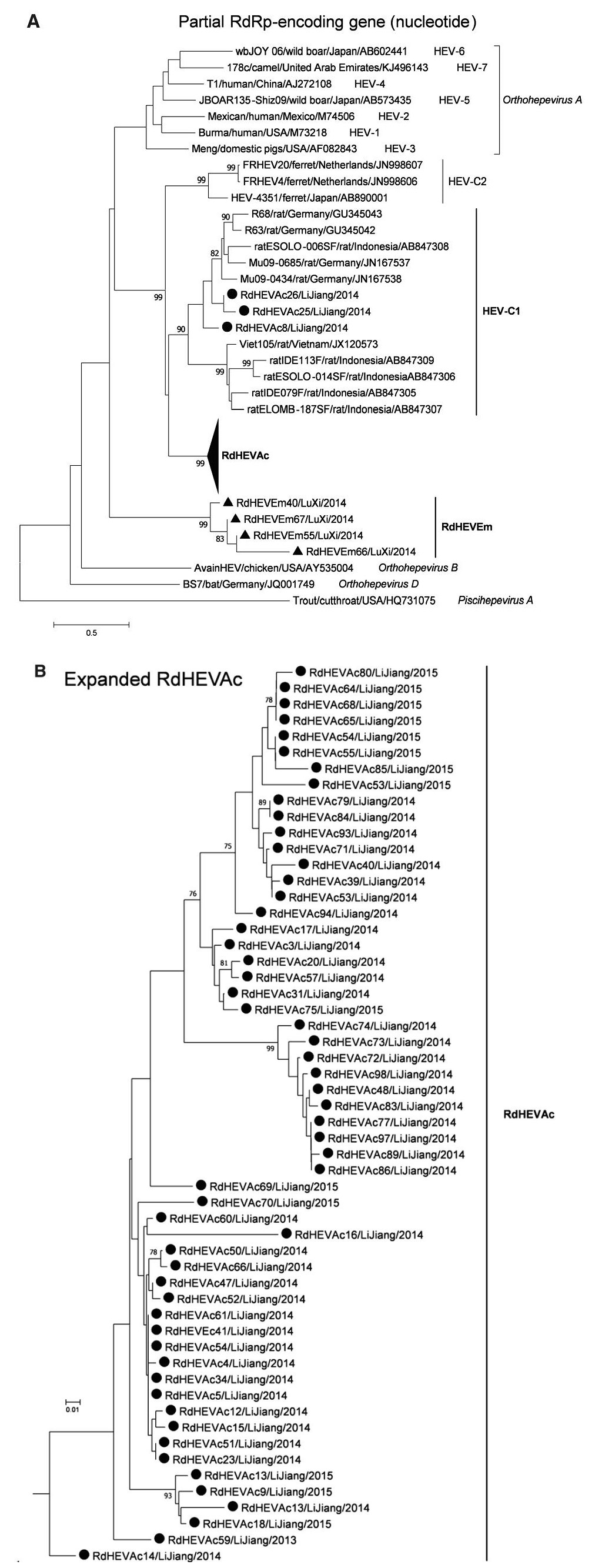
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of partial RdRp gene sequences. Branches supported by > 75% of bootstrap replicates are indicated. The branches are labelled with the strain designation, the host species, location, and the GenBank accession number. The classification of the respective species or genotypes is indicated on the right. Newly detected orthohepevirus sequences in this study are highlighted in bold. A Partial RdRp gene alignment comprising 291 nucleotides corresponding to positions 4300–4590 within the Orthohepevirus A reference strain (GenBank Accession No. M73218). To allow better legibility, RdHEVAc is collapsed. B Expansion of RdHEVAc from A.
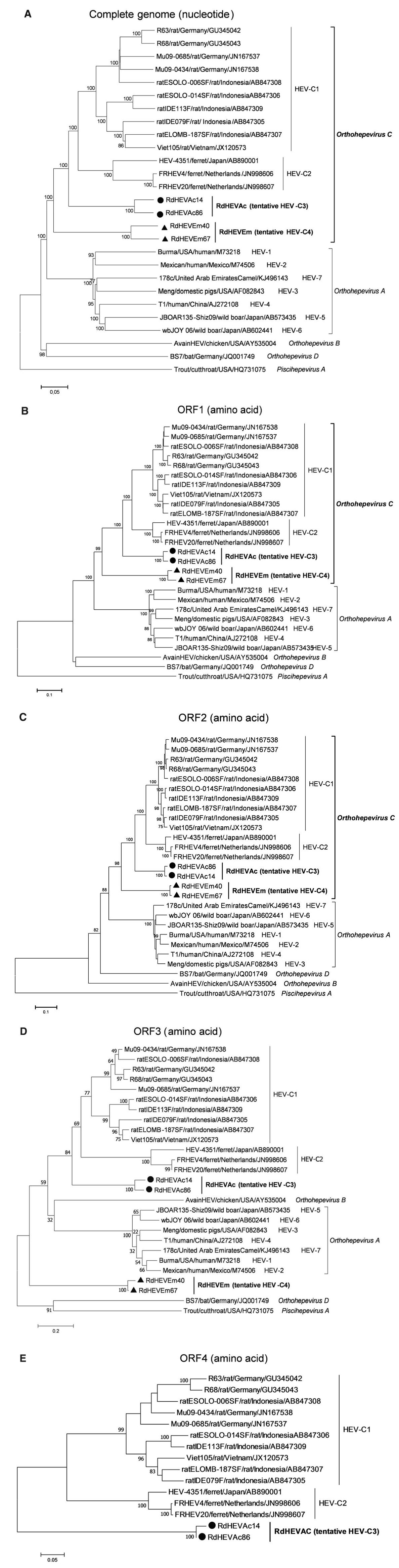
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm. Branches supported by > 75% of bootstrap replicates are indicated. The branches are labelled with the strain designation, the host species, location, and the GenBank accession number. The classification of the respective species or genotypes is indicated on the right. RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm are highlighted in bold. A Complete genome nucleotide sequences. B Amino acid sequences of ORF1-encoded proteins. C Amino acid sequences of ORF2-encoded proteins. D Amino acid sequences of ORF3-encoded proteins. E Amino acid sequences of ORF4-encoded proteins.
The aa identity plot from bootscan analyses with Simplot V3.5 (Lole et al. 1999) demonstrated that the novel rodent orthohepevirus strains had no evidence of recombination between ORF1- and ORF2-encoded aa sequences compared to reference strains of Orthohepevirus A to Orthohepevirus D (Supplementary Figure S1). Pairwise distances of complete genome nt and concatenated ORF1/ORF2 aa sequences were analysed using SSE (Simmonds 2012) (Supplementary Table S2). The mean pairwise distance results were indicative that HEV-C1 and HEV-C2 differed from each other by a distance of 0.311 (nt) or 0.229 (aa). However, the pairwise distances between RdHEVAc and HEV-C1 was 0.340 (nt) or 0.298 (aa), and between RdHEVAc and HEV-C2 was 0.351 (nt) or 0.286 (aa). Similarly, the pairwise distance between RdHEVEm and HEV-C1 was 0.405 (nt) or 0.411 (aa), and between RdHEVEm and HEV-C2 was 0.409 (nt) or 0.412 (aa). Lastly, the pairwise distance between RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm was 0.405 (nt) or 0.416 (aa). Thus, the divergences between RdHEVAc, RdHEVEm, HEV-C1 and HEV-C2 were comparable to or even higher than the divergence between HEV-C1 and HCV-C2.
-
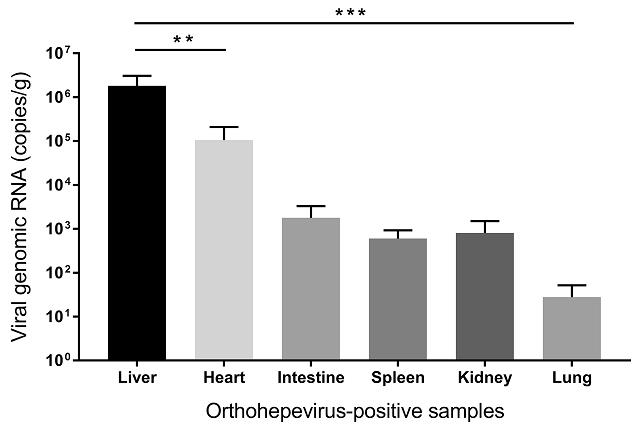
Viral load detected by qPCR in different rodent tissues are presented in Fig. 4. The overall viral titres were significantly higher in liver than in other tissues (heart, intestine, spleen, kidney, and lung) (P < 0.01). Specifically, the viral concentration for two specimens of the liver reached 5.4 × 106 and 1.8 × 106 genomic RNA copies per gram of tissue, respectively. In contrast, viral titres from other tissues were lower than 4.3 × 105 copies per gram. Moreover, several samples from intestine, spleen, heart, kidney, and lung were under detection limit.
Presence and Prevalence of Orthohepeviruses in Rodents
Complete Genome Characterization of Newly Discovered Orthohepeviruses
Comparative Analysis of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm
Phylogenetic Relationship and Pairwise Distance Analysis of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm
Quantification of Novel Orthohepeviruses
-
In this study, we discovered diverse novel orthohepevirus strains in two rodent species from Yunnan province, China, including Chevrier's field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) belonging to the family Muridae from Lijiang city and Père David's vole (Eothenomys melanogaster) belonging to the family Cricetidae from Luxi city, with the infection rates of 29.20% (59/202) and 7.27% (4/55), respectively. These novel orthohepeviruses shared limited nt and aa sequence identities to known orthohepevirus strains within the family Hepeviridae. In the previous studies, HEV-related viruses in rodents have been molecularly detected in the species R. norvegicus, R. rattus, R. flavipectus, R. rattoides losea, and R. exulans, which exclusively belong to the family Muridae and then formed HEV-C1 (Johne et al. 2010a, b; 2012; Lack et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2017c). Therefore, this is, to the best of our knowledge, the first report of divergent HEV-like viruses in another two rodent species: A. chevrieri (Family: Muridae) and E. melanogaster (family: Cricetidae). It is expected that there are many more orthohepeviruses circulating in other rodent species and in various geographic regions.
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of partial nt sequences of the RdRp-encoding gene showed that novel orthohepevirus strains in this study were highly diverse within the genus Orthohepevirus, 56 orthohepevirus strains from Chevrier's field mouse and four orthohepevirus strains from Père David's vole were classified into two separated clusters, namely RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm, notably, three orthohepevirus strains from Chevrier's field mouse clustered into HEV-C1 clade. Whether they are spillover infections from rat HEV strains needs to be further determined. Although rats were found to be infected with human pathogenic HEV-3 or rabbit HEV-3 in other studies, no zoonotic mammalian orthohepeviruses were detected in Chevrier's field mouse or Père David's vole (Kanai et al. 2012; Lack et al. 2012; Ryll et al. 2017). Phylogenetic analyses of complete genome nt sequences and aa sequences of deduced separate ORF1 and ORF2 reflected that RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm fell within the cluster of the species Orthohepevirus C. However, RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm clustered into two separate monophyletic branches among the Orthohepevirus C strains, which were divergent from HEV-C1 and HEV-C2. Notably, RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm from the oder Rodentia reflected even higher divergence from HEV-C1 (order: Rodentia) than HEV-C2 (order: Carnivora), which supports the significance of host switches evolution while opposing the co-evolutionary theory associated of the species Orthohepevirus C.
Putative ORFs and functional domains were predicted to exist in RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm, however with slight differences in the length and location. Comparative analysis of RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm with other Orthohepevirus C strains indicate that there are some unique features: firstly, a putative ORF4 overlapped with ORF1 as postulated to exist in the species Orthohepevirus C was also observed for both RdHEVAc, whereas it was absent in RdHEVEm (Johne et al. 2010b; Raj et al. 2012); secondly, the G + C content of RdHEVAc14 and RdHEVAc86 were 55.0% and 54.7%, a little less than other rat HEV strains (56.0%–57.8%), whereas those for RdHEVEm40 and RdHEVEm67 were only 50.5% and 50.3%, comparable with lowest mammalian HEV G + C content from bat HEV strains BS7 (51.6%) and BtHEVMd2350 (50.4%) within the species Orthohepevirus D (Drexler et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2017b); thirdly, RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm, HEV-C1, and HEV-C2 used distinct translational frames and the overlaps of ORF1, ORF2, and ORF3 are irregular; finally, the 5'-UTR region of RdHEVAc carried a 10 nt motif GCAACCCCCG reported to be uniquely present in the rat HEV strains (Mulyanto et al. 2014), yet RdHEVEm despite having a longer 5'-UTR region lacked this motif (Mulyanto et al. 2014).
As expected, novel rodent orthohepevirus strains in this study have considerable diversity compared to other known orthohepevirus strains, complete genome sequence identities range from 34.6% (cutthroat trout virus) to 65.5% (HEV-C1). Similar results were obtained using the coding regions, which indicated RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm had the highest aa sequence identity to HEV-C1 or HEV-C2. Pairwise distances of complete genome nt sequences and concatenated ORF1/ORF2 aa sequences between representative HEV prototype strains within the genus Orthohepevirus were calculated as recommended in recent studies (Smith et al. 2013, 2014, 2016). The divergences between RdHEVAc, RdHEVEm, HEV-C1 and HEV-C2 are comparable to or even higher than the divergence between HEV-C1 and HEV-C2. Above all, in accordance to the guidelines provided by the latest consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae for assigning new HEV strains, phylogeny and pairwise distance based taxonomy consistently suggested that two putative novel genotypes could be designated, preliminarily named HEVC3 and HEV-C4, within the species Orthohepevirus C.
HEV causes a systemic disease affecting the liver predominantly. According to the results of in-house orthohepevirus-specific qRT-PCR, the concentration of viral genome copies in orthohepevirus RNA-positive rodent are distinct in different tissues, which may be related to different infection stages. Importantly, virus titres in liver samples are significantly higher than other tissues, demonstrating the hepatotropism of these viruses, which is analogous to rat HEV strains (Johne et al. 2010b, 2012).
In summary, here we have described the detection of diverse orthohepeviruses in Chevrier's field mouse (Apodemus chevrieri) and Père David's vole (Eothenomys melanogaster), which expands the knowledge of orthohepevirus infection in the order Rodentia. We hypothesize that RdHEVAc and RdHEVEm may represent two putative novel genotypes within the species Orthohepevirus C. The present work supports data for the epidemiology and genetic diversity of orthohepevirus in Chinese wild rodents, and gives new insights into the origin, evolution, and host range of HEV. Future investigations on field samples, experimental infection trials and epidemiological studies are essential to clarify the distinct host range and zoonotic potential of these novel viruses.
-
This work was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81660558, 81260437, and 81290341), a Scientific and Technological Basis Special Project grant (2013FY113500) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of PR China, and Yunnan Provincial Collaborative Innovation Centre for Public Health and Disease Prevention and Control (2015YNPHXT05). B.W. is supported by the China Scholarship Council (CSC), Beijing, China. We thank Dominik Harms for critical reading of our manuscript.
-
YZZ and XLY designed and coordinated the study. YZZ, JHZ, WHY, HP and LXW collected samples. XLY, BW, LW, BL and WZ performed molecular studies. BW and XLY analysed the data. XLY, BW, ZLS, YZZ and CTB drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Yunnan Institute of Endemic Diseases Control and Prevention. Sampling procedures were performed following the guidelines and protocols for the Laboratory Animal Use and Care from the Chinese Centres for Disease Control and the Rules for the Implementation of Laboratory Animal Medicine (1998) from the Ministry of Health, China.
Conflict of interest
Animal and Human Rights Statement
-
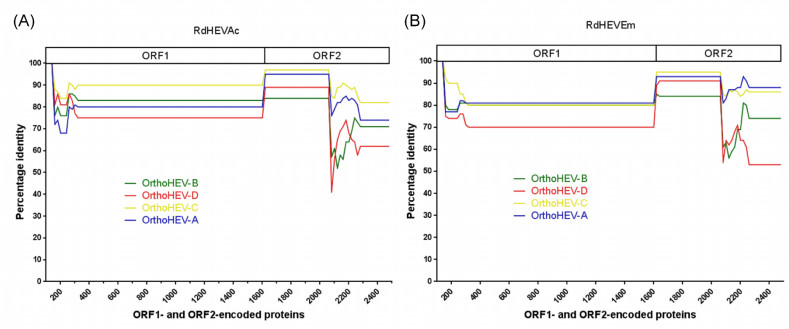
Figure S1. Amino acid identity plot. The complete ORF1 and ORF2 were translated, concatenated, and compared to reference strain of Orthohepevirus A to D. The GenBank accession numbers are as follows: M73218, M74506, AF082843, AJ272108, AB573435, AB602441, and KJ496143 for Orthohepevirus A; AY535004 for Orthohepevirus B; GU345042 and JN998606 for Orthohepevirus C; and JQ001749 for Orthohepevirus D. The uncorrected amino acid identity was plotted with a sliding window size of 200 and a step size of 20 amino acids. A schematic representation of concatenated ORF1 and ORF2 is shown at the top. (A) RdHEVAc. (B) RdHEVEm.

Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for orthohepevirus detection, complete genome sequencing, and viral quantification
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: