HTML
-
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a highly contagious viral disease caused by foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), which seriously affects cloven hoofed animals such as cattle, pigs and sheep, causing huge economic losses to animal husbandry (Jamal and Belsham 2013). It has been classified as a World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE)-listed disease. The causative agent FMDV is a single-stranded positive RNA virus of the genus Aphthovirus within the family of Picornaviridae. The viral genome consists of about 8,500 nucleotides, including a 5′-UTR, a large open reading frame (ORF), and a 3′-UTR. The single ORF encodes a polyprotein of about 250 kDa, which is then cleaved by the viral proteases to produce four structural proteins (VP1, VP2, VP3 and VP4) and eight non-structural proteins (Lpro, 2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, 3B, 3Cpro and 3Dpol) (Zhu et al. 2019).
FMDV has seven serotypes, including O, A, C, Asia 1, SAT 1, SAT 2 and SAT 3 types, and there is no cross-protection between different serotypes. Therefore, multiple serotypes of FMDV can spread in one region simultaneously, which results in the difficulty to prevent and control FMD (Diaz-San Segundo et al. 2017). Although the commercial vaccines against FMDV are effective up to now, as an RNA virus, FMDV evolves quickly, and new vaccines and antiviral drugs remain required for control and eradication of the disease in future.
Peroxiredoxin-6 (PRDX6) is a bifunctional protein with the activity of glutathione peroxidase and phospholipase A2 (PLA2) (Fisher 2011). The expression and activity of PRDX6 are regulated by various factors or stimulations. Oxidative stress effectively stimulates the expression of PRDX6, and the expression of PRDX6 is also regulated by hormones. The PLA2 activity of PRDX6 is regulated by its phosphorylation. The T177 of PRDX6 is phosphorylated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and this phosphorylation increases its PLA2 activity (Hall et al. 2011). PRDX6 plays an important role in antioxidant defense, which depends on its ability to reduce the peroxidation of membrane phospholipids, and in maintaining the balance of phospholipid metabolism (Pak et al. 2016). Besides, PRDX6 includes an anti-apoptotic function, which interferes with the apoptosis induced by excessive oxidative stress, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), or endoplasmic reticulum stress (Kim et al. 2013).
In this study, we investigated the function of PRDX6 during picornaviral infection, and identified the antiviral function of PRDX6 against porcine picornavirus. We found the PLA2 activity of PRDX6 was required for suppression of the viral replication. Meanwhile, a significant decrease of PRDX6 was triggered by FMDV infection, and the viral protease 3Cpro was determined to be the factor responsible for degradation of PRDX6. 3Cpro-induced degradation of PRDX6 was also identified in another porcine picornavirus Senecavirus A (SVA). This is the first report of the direct antiviral function of PRDX6 and unveils a novel role of 3Cpro of porcine picornavirus on antagonizing host antiviral response.
-
HEK293T cells, IBRS-2, PK-15 and EC-4 cells were maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, Gibco) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Hyclone), 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. All the cells were cultured at 37 ℃ in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator. Foot-and-mouth virus (FMDV) strain O/BY/CHA/2010 (GenBank number: JN998085) was propagated and titrated in PK-15 cells and stored at¬80 ℃ until use as previously described (Zhu et al. 2016). Senecavirus A (SVA) CH-FJ-2017 (GenBank number: KY747510) was propagated and titrated in IBRS-2 cells as previously described (Zhu Z. et al. 2017). Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) strain CV777 was stored in our laboratory. The virus was propagated in Vero cells. Sendai virus (SeV) was reproduced in chicken embryo cultures, and was used as a model RNA virus to activate type Ⅰ interferon pathway.
-
The monolayer PK-15 cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 3 times to remove the medium and FBS, and then infected with FMDV or SVA at the multiplicity of infection of 0.5 (MOI = 0.5). A fetal bovine serum-free medium was used to dilute the virus stock proportionally. The cells were then incubated with the diluted virus for 1 h at 37 ℃. The unabsorbed virus was then removed, and a maintenance medium containing 1% fetal bovine serum was used to maintain the cells for different hours. The collected cells were used for subsequent analysis.
-
To construct porcine PRDX6 expression plasmid, a full-length CDS fragment was amplified from the cDNA synthesized from PK-15 cells and inserted into the pcDNATM3.1/myc-His(-) A vector. The constructed plasmids were verified by DNA sequencing analysis. The Flag-tagged viral protein expressing plasmids were constructed by our lab previously (Zhu et al. 2016; Xue et al. 2018). The inhibitors MJ33 (1-hex-adecyl-3-(trifluoroethyl)-sn-glycero-2-phosphomethanol) and Mercaptosuccinate were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. The siRNA targeting porcine PRDX6 was designed and synthesized by Shanghai GenePharma biotechnology company. The siRNA sequences were listed in Supplementary Table S1. The plasmids and siRNA transfection experiments were performed using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instruction.
-
Total RNAs were extracted using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen). About 2 μg of total RNA were reverse transcribed into cDNA using a reverse transcription system (Invitrogen). Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qPCR) was performed using TaKaRa TB Green Premix Ex Taq II on the ABI QuantStudio 5 Real-Time PCR Systems. The mRNA levels of PRDX6, FMDV, SVA and GAPDH were measured by qPCR under the following thermal cycling condition: 95 ℃ for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 ℃ for 15 s and 60 ℃ for 1 min. Fluorescence signals were collected by the machine during the extension phase of each PCR cycle. The threshold cycle (CT) value was normalized to that of GAPDH. The primers used in this study were listed in Supplementary Table S1. All samples were run in triplicate, and the experiment was repeated for three times.
-
The Western blotting was performed as previously described (Zhu et al. 2016). The expression of Flag-tagged or Myc-tagged exogenous proteins was detected by anti-Flag (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc) and anti-Myc (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) antibodies respectively. Antibody for endogenous PRDX6 detection was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. FMDV-positive serum (prepared by our lab previously) was used as the primary antibody to detect FMDV proteins. Rabbit anti-SVA-VP2 and SVA-3Cpro antibodies were prepared by our lab. The anti-rabbit, anti-mouse or anti-pig secondary antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase were used for detection of the antigen–antibody complexes. Specific bands were visualized with enhanced chemiluminescent substrate (ECL). Each blot was stripped and reblotted with anti-β-actin (Sigma) antibody for loading control. Each immunoblot assay was carried out at least three times and one of them was presented.
-
All the data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA) and expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) obtained from the experiments repeated at least three times. P value < 0.05 (*) was considered statistically significant, P value < 0.01 (**) was considered highly statistically significant, ns represented not significant.
Cell Lines and Viruses
Virus Infection
Plasmids, Inhibitors, siRNA (Small Interfering RNA) Oligos and Transfection
Reverse Transcription and qPCR
Western Blotting and Antibodies
Statistical Analysis
-
A previous proteomic study showed that porcine circovirus type 3 (PCV3) infection resulted in a decrease of PRDX6 protein abundance in the lungs of specific-pathogen-free piglets (Jiang et al. 2020). However, what is the state of PRDX6 during RNA virus infection remains unknown. To investigate the state of PRDX6 protein in FMDV-infected porcine cells, PK-15 cells were incubated with FMDV for 0, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 or 14 h. The expression of PRDX6 protein and FMDV viral protein was detected by Western blotting. As shown in Fig. 1A, the protein levels of total PRDX6 was dramatically down-regulated as infection progressed. The PRDX6 protein almost vanished at 12 hpi, and no cleaved bands were detected during the infection. In contrast, in the mock-infected cells, no remarkable change of PRDX6 protein was observed at different time (Fig. 1B). This was consistent with the PCV3 infection induced reduction of PRDX6, which implied a potential role of PRDX6 during viral infection.
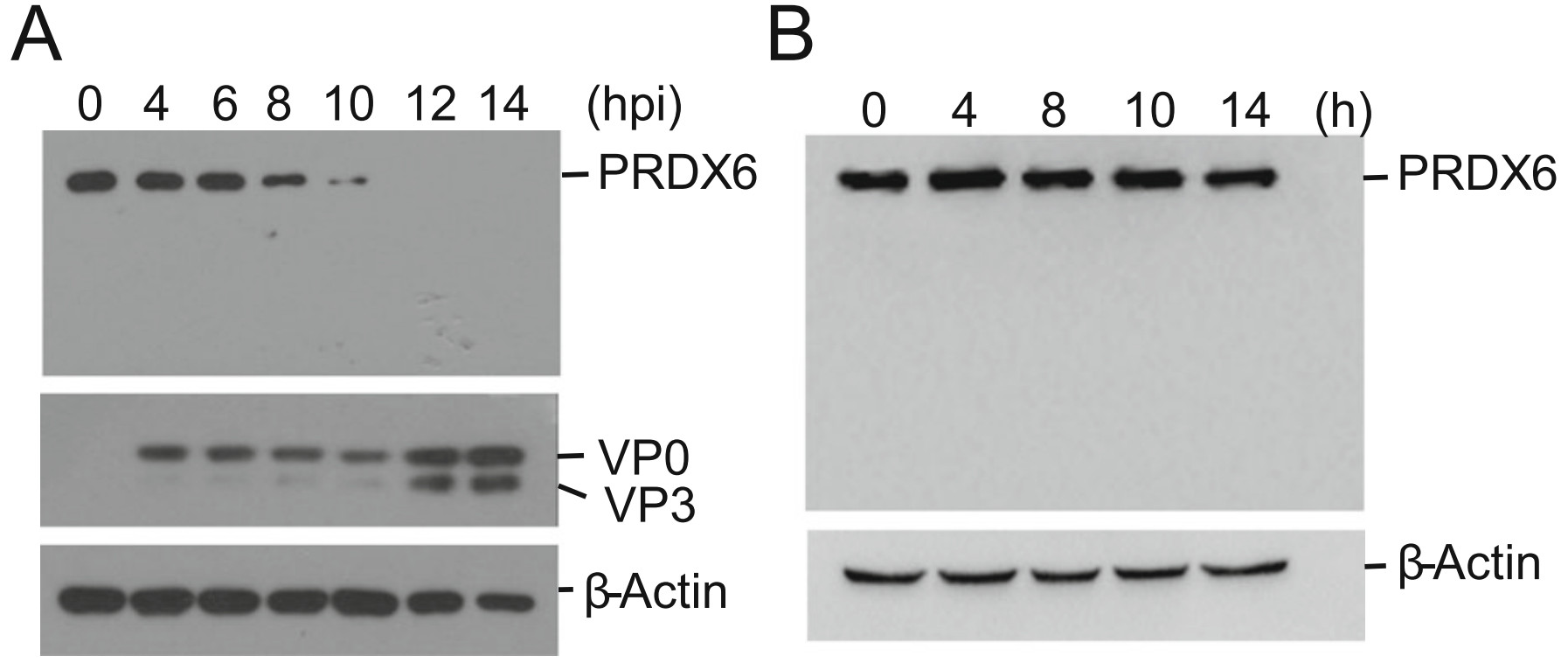
Figure 1. FMDV infection induced the decrease of PRDX6 protein abundance. A PK-15 cells were infected with FMDV (0.5 MOI) for 0, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 or 14 h. The cells were collected and the expression level of PRDX6 protein was determined by Western blotting analysis. B PK-15 cells were parallelly cultured for 0, 4, 8, 10 or 14 h. The cells were collected and the expression level of PRDX6 protein was determined by Western blotting analysis.
-
To explore whether PRDX6 affect FMDV infection, PK-15 cells were transfected with increasing amount of PRDX6 expressing plasmids, and the transfected cells were then infected with FMDV. The viral proteins, viral RNA and virus yields were evaluated respectively. Overexpression of PRDX6 dramatically suppressed FMDV replication, the viral proteins (Fig. 2A), viral RNA (Fig. 2B) and virus yields (Fig. 2C) levels were all decreased in PRDX6 overexpressing PK-15 cells, showing a dose dependent manner. We also evaluated the replication of FMDV in another porcine epithelial cell line (EC-4), which also indicated that overexpression of PRDX6 suppressed FMDV replication (Fig. 2D). To confirm the antiviral role of PRDX6, three pairs of siRNAs were designed and synthesized. The knockdown efficiency of the siRNAs was evaluated through both qPCR and Western blotting analysis, which showed that the siRNA-329 had the highest knockdown efficiency (Fig. 2E). Therefore, PRDX6 siRNA-329 was used for the subsequent knockdown assays. As expected, knockdown of cellular PRDX6 clearly promoted FMDV replication. The viral proteins (Fig. 2F), viral RNA (Fig. 2G) and virus yields (Fig. 2H) levels were all enhanced in PRDX6 knockdown cells. These results indicated that PRDX6 plays an important antiviral function during FMDV replication.
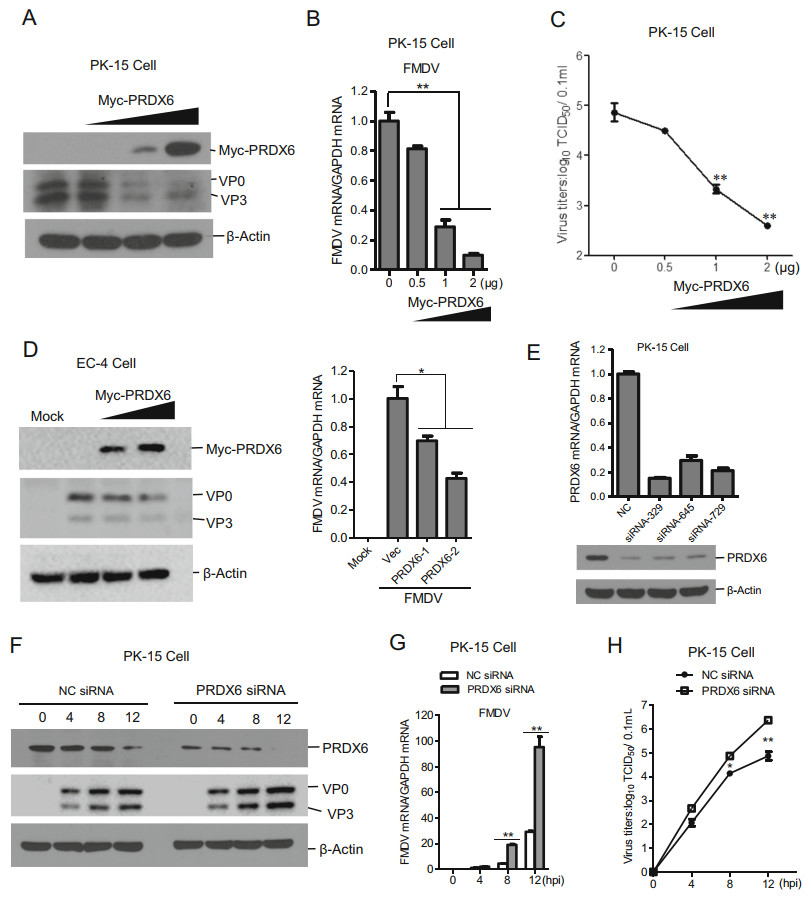
Figure 2. PRDX6 inhibited FMDV replication. A–C PK-15 cells were transfected with 0, 0.5, 1 or 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids for 24 h. The cells were then infected with FMDV (MOI = 0.5) for 12 h. The expression of viral proteins (A) and viral RNA (B) were detected by Western blotting and qPCR respectively. The virus yields were measured by TCID50 assay (C). D EC-4 cells were transfected with 0, 1 or 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids for 24 h. The cells were then mock-infected or infected with FMDV for 12 h. The expression of viral proteins and viral RNA were detected by Western blotting and qPCR respectively. E PK-15 cells were transfected with 120 nM of nontargeting control NC siRNA or PRDX6 siRNA (siRNA-329, siRNA-645 siRNA-729) for 36 h, the knockdown efficiency of each siRNA was then evaluated by qPCR and Western blotting analysis respectively. F–H PK-15 cells were transfected with 120 nM of NC siRNA or PRDX6 siRNA (siRNA-329) for 36 h, the cells were then infected with FMDV (MOI = 0.5) for 0, 4, 8 or 12 h. The expression of viral proteins (F) and viral RNA (G) were detected by Western blotting and qPCR respectively. The virus yields were measured by TCID50 assay (H).
-
PRDX6 is a bifunctional protein with the activities of glutathione peroxidase and PLA2, and the different functional sites are involved in the two kind of catalytic activities which play the regulatory functions independently. In order to investigate whether the catalytic activity of PRDX6 was associated with PRDX6-mediated antiviral effect against FMDV, the specific inhibitors of the glutathione peroxidase and PLA2 were used in the present study. MJ33 (1-hex-adecyl-3-(trifluoroethyl)-sn-glycero-2-phosphomethanol), which has no inhibitory effect on the peroxidase activity but only suppresses the PLA2 activity, was used as the inhibitor of the PLA2 activity of PRDX6 (Chen et al. 2000). Mercaptosuccinate, which does not interfere with the PLA2 activity, was used as a specific inhibitor of glutathione peroxidase of PRDX6 (Wang et al. 2019). PK-15 cells were pretreated with MJ33 or mercaptosuccinate and then infected with FMDV, the replication of FMDV was then evaluated. Pretreatment of the cells with the MJ33 significantly enhanced FMDV replication (Fig. 3A), while incubation of the cells with the mercaptosuccinate did not affect the replication of the virus (Fig. 3B). These results indicated that the PLA2 activity but not the glutathione peroxidase was involved in PRDX6-mediated FMDV inhibition. To investigate the effect of PRDX6 on type I interferon (IFN) and NF-κB signaling, HEK293T cells were transfected with IFN-β or NF-κB reporter plasmids and were subsequently infected with Sendai virus (SeV) or uninfected. The results showed that overexpression of PRDX6 slightly promoted type I IFN signaling but not NF-kB signaling (Fig. 3C and 3D).
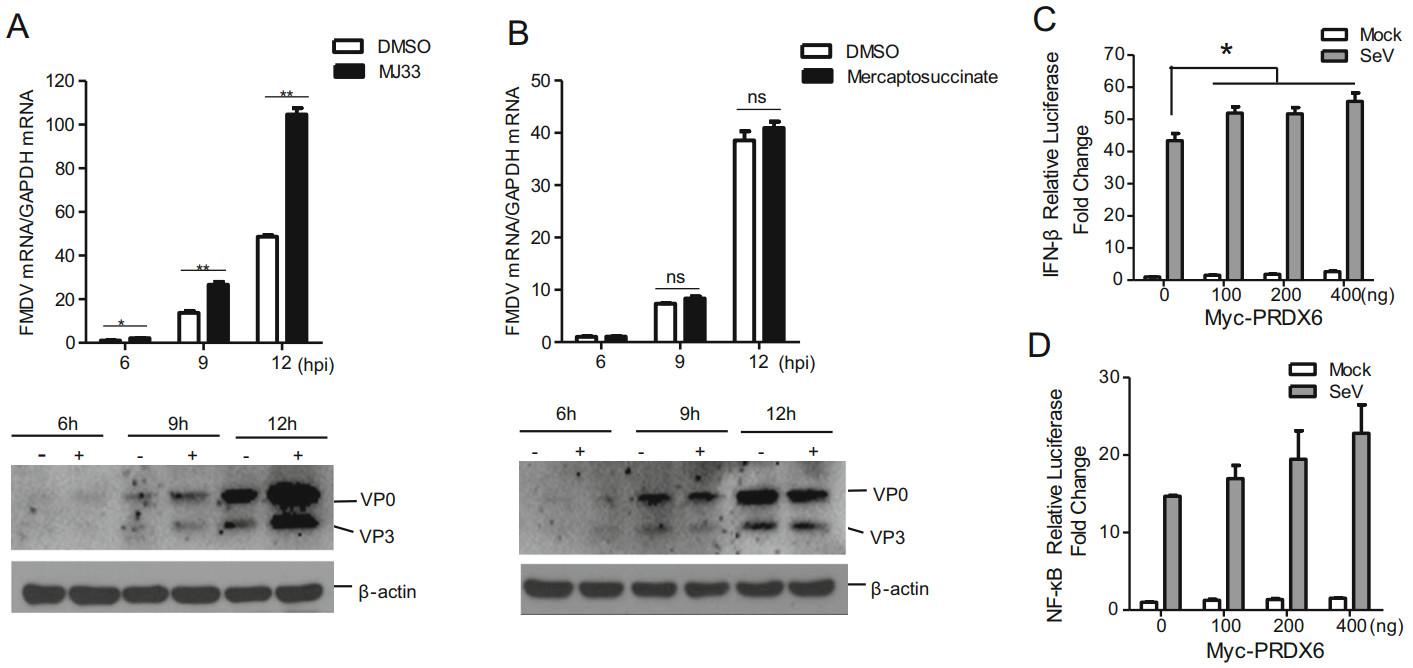
Figure 3. The PLA2 activity of PRDX6 was critical for suppression of FMDV. A PK-15 cells were treated with DMSO (solvent control) or 200 nmol/L of MJ33 for 2 h, and the cells were then infected with FMDV (0.5 MOI) for 6, 9 or 12 h. The cells were collected and the expression levels of viral RNA and viral proteins were determined by qPCR and Western blotting analysis respectively. B PK-15 cells were treated with DMSO (solvent control) or 50 pmol/L of mercaptosuccinate for 2 h, and the cells were then infected with FMDV (0.5 MOI) for 6, 9 or 12 h. The cells were collected and the expression levels of viral RNA and viral proteins were determined by qPCR and Western blotting analysis respectively. C–D HEK293T cells were transfected with 0, 100, 200 or 400 ng of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids together with 100 ng of IFN-β-promoter- (C) or NF-κB-promoter-driven (D) luciferase reporter plasmids and 10 ng of the internal control plasmid pRL-TK for 24 h, and the cells were mock-infected or infected with SeV for another 10 h. The luciferase activity was determined by the dual-luciferase assay.
-
PRDX6 showed an antiviral effect against FMDV, which explained why FMDV induced the decrease of PRDX6 during viral infection. To investigate which viral proteins were involved in induction of PRDX6 reduction, HEK293T cells were co-transfected with Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and the plasmids expressing various FMDV proteins. The expression levels of Myc-PRDX6 and viral proteins were then evaluated. Overexpression of Flag-tagged 2B protein and 3Cpro dramatically inhibited the expression of Myc-PRDX6 (Fig. 4A). The regulatory effect of FMDV proteins on the endogenous PRDX6 protein expression was subsequently evaluated. PK-15 cells were transfected with the plasmids expressing various FMDV proteins, the expression of endogenous PRDX6 protein was detected by Western blotting. However, we only found 3Cpro inhibited the expression of PRDX6 protein (Fig. 4B). Therefore, we further investigated the regulatory effect of 3Cpro on PRDX6 protein expression. The dose-dependent assays of 3Cpro-induced reduction of both exogenous and endogenous PRDX6 were further performed. The expression of both exogenous and endogenous PRDX6 was decreased by overexpression of 3Cpro, showing a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 4C and 4D). Meanwhile, no cleaved bands were detected in 3Cpro overexpressing cells. The mRNA level of PRDX6 in 3Cpro overexpressing cells was measured as well, which showed that 3Cpro did not affect the mRNA expression of PRDX6 (Fig. 4E). These data indicated that 3Cpro induced the reduction of PRDX6 at protein level but not the transcriptional level.
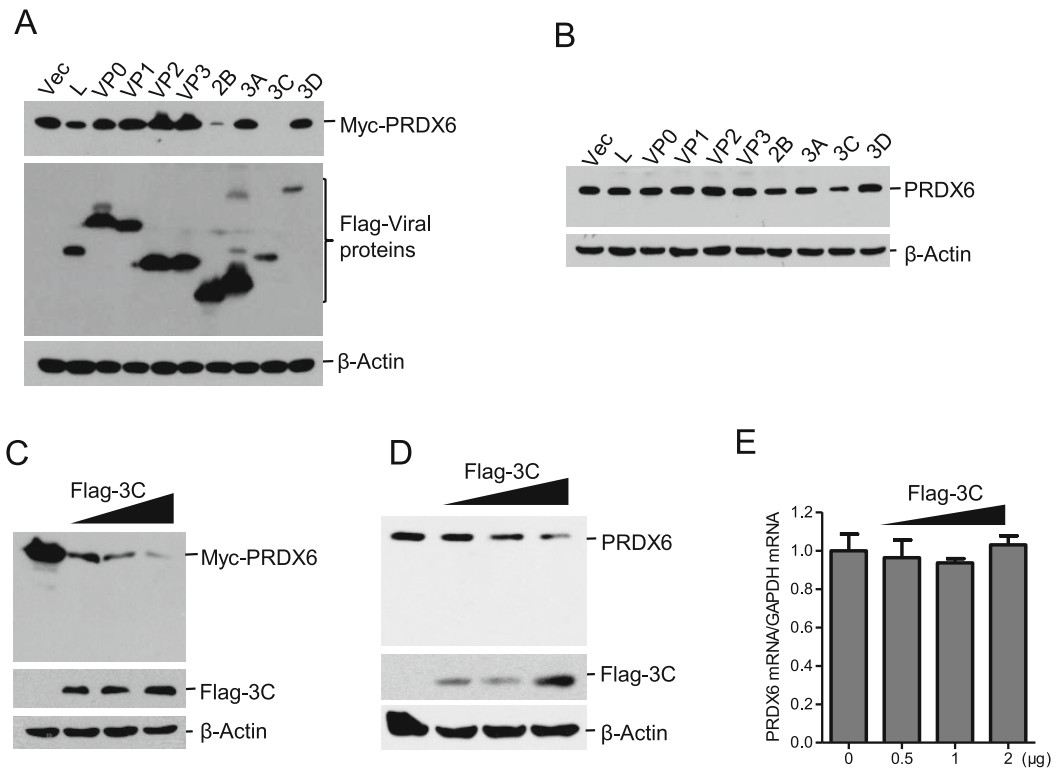
Figure 4. FMDV 3Cpro was responsible for inducing the reduction of PRDX6 protein expression. A HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 2 μg of plasmids expressing various Flag-tagged viral proteins. The cells were collected at 24 hpt and subjected to Western blotting analysis. The expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-tagged viral proteins was detected using anti-Myc and anti-Flag antibodies respectively. B PK-15 cells were transfected with 2 μg of plasmids expressing various Flag-tagged viral proteins. The cells were collected at 36 hpt and subjected to Western blotting analysis. The expression of endogenous PRDX6 was detected using the anti-PRDX6 antibody. C HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 0, 0.5, 1 or 2 μg of Flag-3C expressing plasmids. The cells were collected at 24 hpt and subjected to Western blotting analysis. D–E PK-15 cells were transfected with 0, 0.5, 1 or 2 μg of Flag-3C expressing plasmids for 24 h. The expression levels of PRDX6 protein (D) and PRDX6 mRNA (E) were detected by Western blotting and qPCR respectively.
-
3Cpro did not affect the mRNA expression of PRDX6 while it induced the reduction of PRDX6 protein abundance. The involved mechanism was further investigated. 3Cpro and Lpro of FMDV could induce the cleavage of eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4G and results in shut-off of host proteins (Belsham et al. 2000). To explore whether 3Cpro-induced reduction of PRDX6 was related to the host protein shut off response, PK-15 cells were treated with DMSO (solvent control) or cycloheximide (CHX, a widely used protein synthesis inhibitor in eukaryotes), the abundance of PRDX6 was then detected by Western blotting. It showed that the PRDX6 was very stable (Fig. 5A), having a long half-life (> 12 h). Another host protein IRF7 which has a short half-life was used as a control. The expression of PRDX6 in FMDV infected cells could not be detected at 12 hpi (Fig. 1A). This suggested that the decrease of PRDX6 was not related to the host protein shut off response. To investigate whether the proteasomes, lysosomes, autophagy-associated proteolysis or caspase-dependent pathways were involved in 3Cpro-induced reduction of PRDX6, the proteasome inhibitor MG132, lysosome inhibitor CQ, autophagy-associated proteolysis inhibitor NH4Cl and a general caspases inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK were used to evaluate the inhibitive effects. The 3Cpro-induced reduction of PRDX6 could not be impaired by any of these inhibitors (Fig. 5B). To investigate whether 3Cpro degraded PRDX6 through its proteolytic activity, the mutants of 3Cpro with the disrupted catalytic activity (3C-H46Y, 3C-D84N and 3C-C163G) or intact catalytic activity (3C-H205R) were used to evaluate their regulatory effect on PRDX6. The disruption of the proteolytic activity of 3Cpro significantly rescued the abundance of PRDX6, and the mutant with intact enzyme activity remained effective to induce the reduction of PRDX6 protein (Fig. 5C). These results indicated that 3Cpro degraded PRDX6 through its proteolytic activity.

Figure 5. FMDV 3Cpro degraded PRDX6 through its proteolytic activity. A) PK-15 cells were treated with DMSO (solvent control) or 100 μg/mL of CHX for the indicated time. The abundance of IRF7 and PRDX6 proteins was detected by Western blotting. B HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 2 μg of Flag-3C expressing plasmids and maintained in the presence or absence of MG132 (2 μmol/L or 20 μmol/L), CQ (50 μmol/L or 100 μmol/L), NH4Cl (2 mmol/L or 20 mmol/L) or Z-VAD-FMK (10 μmol/L or 50 μmol/L) for 36 h. Expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-3C proteins was detected by Western blotting. C HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 2 μg of plasmids expressing Flag-tagged 3Cpro or the mutants of 3Cpro. Expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-3C or 3C mutants was detected by Western blotting.
-
To investigate whether PRDX6 also plays a significant role in the antiviral defense against other porcine picornavirus, PK-15 cells were transfected with an increasing amount of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids, and another porcine picornavirus SVA was used to infect the PRDX6 overexpressing cells. The results showed that overexpression of porcine PRDX6 also suppressed SVA replication (Fig. 6A). We also evaluated the expression of PRDX6 in SVA-infected cells, and found that SVA infection could also decrease the abundance of PRDX6 protein (Fig. 6B). The viral proteins of SVA that were responsible for induction of PRDX6 reduction was also evaluated, and we found that overexpression of SVA 3Cpro inhibited exogenous expression of PRDX6 (Fig. 6C). The dose-dependent experiment was also performed and showed that 3Cpro induced the degradation of PRDX6, revealing a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 6D). The endogenous expression of PRDX6 in 3Cpro overexpressing cells was further detected, which suggested that 3Cpro decreased the endogenous expression of PRDX6 (Fig. 6E). To investigate whether 3Cpro of SVA also degraded PRDX6 through its proteolytic activity, the mutants of SVA 3Cpro with disrupted catalytic activity (3C-H48A, 3C-C160A or double-site mutation H48A–C160A (3Cdm)) were used to evaluate their regulatory effect on PRDX6. The results showed that disruption of the proteolytic enzyme activity of SVA 3Cpro rescued the abundance of PRDX6 (Fig. 6F). These results indicated that SVA 3Cpro degraded PRDX6 through its proteolytic enzyme activity as well. We also evaluated the effect of PRDX6 on a porcine coronavirus (PEDV, Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus) replication. Unexpectedly, overexpression of PRDX6 promoted PEDV replication (Fig. 6G). This implied that PRDX6 played a unique role in inhibiting picornavirus replication.
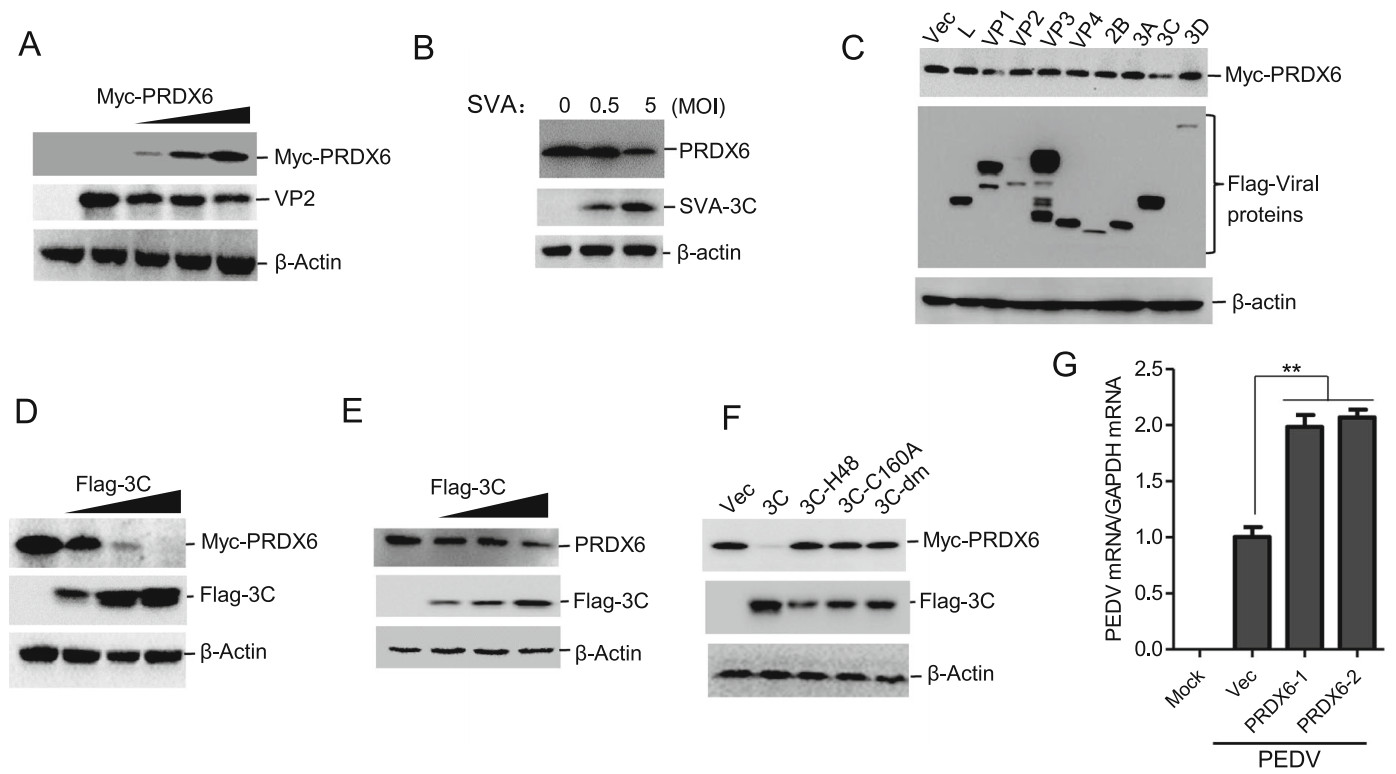
Figure 6. SVA 3Cpro induced reduction of PRDX6 to impair PRDX6-mediated antiviral effect. A PK-15 cells were transfected with 0, 0.5, 1 or 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids for 24 h. The cells were then infected with SVA (MOI = 0.5) for 12 h. The expression of SVA VP2 protein and Myc-PRDX6 was then detected by Western blotting. B PK-15 cells were infected with 0.5 or 5 MOI of SVA for 10 h, the expression of PRDX6 and SVA 3Cpro was detected by Western blotting. C HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 2 μg of plasmids expressing various Flag-tagged viral proteins. The cells were collected at 24 hpt and subjected to Western blotting analysis. The expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-tagged viral proteins was detected using anti-Myc and anti-Flag antibodies respectively. D HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 0, 1, 2 or 4 μg of Flag-3C expressing plasmids. The expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-3C protein was detected by Western blotting. E PK-15 cells were transfected with 0, 1, 2 or 4 μg of Flag-3C expressing plasmids. The expression of PRDX6 and Flag-3C protein was detected by Western blotting. F HEK-293 T cells were transfected with 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids and 2 μg of Flag-3C or the mutants of 3Cpro expressing plasmids. Expression of Myc-PRDX6 and Flag-3C or 3C mutants was detected by Western blotting. G PK-15 cells were transfected with 0, 1 or 2 μg of Myc-PRDX6 expressing plasmids for 24 h. The cells were then mock-infected or infected with PEDV for 18 h. The viral RNA level was then measured by qPCR.
FMDV Decreased PRDX6 Expression as Infection Progressed
PRDX6 Played an Antiviral Role Against FMDV
The PLA2 Activity of PRDX6 Was Essential for its Antiviral Effect Against FMDV
FMDV Proteinase 3Cpro Induced the Reduction of PRDX6 Protein Expression
FMDV 3Cpro Induced PRDX6 Reduction Through Its Proteolytic Activity
The 3Cpro of Another Porcine Picornavirus SVA Also Induced Degradation of PRDX6
-
Foot-and-mouth disease is highly contagious and economically important. FMDV facilitates its own replication by manipulating the expression of various host proteins. The virus could upregulate several host proteins to establish a more favorable environment for its replication (Zhu et al. 2015; Yang et al. 2020). Meanwhile, the virus could also downregulate several host proteins to impair host antiviral response (Zhu ZX et al. 2017; Medina et al. 2020). A large amount of host proteins have been identified to be regulated by FMDV or directly interact with FMDV proteins during viral infection that affect the replication of the virus. Such as, FMDV 2B protein achieves immune escape by inducing RIG-I reduction (Zhu et al. 2016). FMDV induces the expression UBE1 to promote viral replication (Zhu et al. 2015). FMDV VP1 targets sorcin to inhibit the production of IFNs (Li et al. 2013). The interaction between VP0 and PCBP2 promotes the replication of the virus (Li et al. 2019). The interaction between DCTN3 and 3A has a certain relationship with the host tropism of FMDV (Gladue et al. 2014). DNAJA3 and Sam68 are closely related to the replication of FMDV (Zhang et al. 2019).
As a bifunctional protein with the activities of glutathione peroxidase and PLA2, the expression and activity of PRDX6 are regulated by various factors (Nelson et al. 2011). Oxidative stress and hormones effectively stimulate the expression of PRDX6 (Gao et al. 2016). Here, we determined that FMDV infection negatively regulate expression of PRDX6, which was consistent with the results of a previous proteome study of PCV3 infection in pigs that showed PRDX6 could be downregulated by PCV3 infection (Jiang et al. 2020). Classical swine fever virus (CSFV) infection could induce the expression of PRDX6 (Sun et al. 2008). These data suggest that PRDX6 plays important function during viral infection. Different virus infection could result in different fate of PRDX6.
PRDX6 plays an important role in antioxidant defense, which depends on its activity to reduce the peroxidation of membrane phospholipids, and it also maintains the balance of phospholipid metabolism through the phospholipid remodeling pathway (Fisher et al. 2016). The PLA2 activity of PRDX6 is regulated by its phosphorylation, which is phosphorylated by MAP kinase at T177 (Hall et al. 2011). PRDX6 is involved in regulation of inflammatory response. It can be upregulated in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages treated with LPS (Diet et al. 2007; Knoops et al. 2016). PRDX6 suppresses the inflammation to prevent multiple sclerosis (Yun et al. 2015). In addition, PRDX6 has anti-apoptotic function, and has resistance to oxidative stress, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and cell apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum pressure (Walsh et al. 2009). FMDV infection promotes inflammation and cellular apoptosis to favor viral replication (KU et al. 2005; Wang et al. 2012; Kang et al. 2020). PRDX6 has an inhibitory effect on inflammation and apoptosis, these results imply an antiviral function of PRDX6 against FMDV, and PRDX6 might play antiviral function through regulation of inflammation or apoptosis. Overexpression of PRDX6 partly activated type I IFN pathway. This might be associated with its antiviral function during FMDV replication as well.
Previous study shows CSFV infection increases the expression of PRDX6, and CSFV NS5A significantly induces the expression of PRDX6. This implicates that PRDX6 relieves cellular oxidative stress induced by CSFV NS5A (He et al. 2012). Besides, iridovirus can up-regulated the PRDX6 mRNA in liver, which may play an important role in regulating oxidative stress by scavenging of ROS, involving immune reactions and minimizing the DNA damage in rock bream (De Zoysa et al. 2012). Here we found that PRDX6 inhibits the replication of FMDV through its PLA2 enzyme activity but not the the activities of peroxidase. In addition, overexpression of PRDX6 promoted PEDV replication, which showed an opposite effect compared to its role on FMDV. Therefore, PRDX6 might play different functions during different virus infections. PLA2 plays important roles in phospholipid digestion and metabolism (Murakami et al. 2017). The phospholipid biosynthesis and metabolism is related to the virus release process. Whether PRDX6 suppresses the release of FMDV from the infected cells should be investigated further.
FMDV infection induced downregulation of PRDX6, and viral 3Cpro was responsible for this effect. We also identified the antiviral function of PRDX6 against SVA, and SVA 3Cpro also induced degradation of PRDX6. 3Cpro has been determined to be an important viral factor to facilitate FMDV and SVA replication through disruption of host defense system and impairing host antiviral response (Grubman et al. 2008; Qian et al. 2017; Xue et al. 2018). In the present study, we determined that both FMDV and SVA 3Cpro induced the degradation of PRDX6 through its proteolytic enzyme activity, however, we did not observe any cleaved bands. How did 3Cpro induce the degradation of PRDX6 and which regions included the cleavage sites remains unknown. We supposed that 3Cpro efficiently degraded PRDX6 into many small fragments that resulted in the absence of visible cleaved bands. Comparing with 3Cpro-induced degradation of exogenous PRDX6, the endogenous level of the PRDX6 protein did not appear to be surprisingly "regulated" by 3Cpro. We thought that overexpression of PRDX6 might provide more chance to let 3Cpro move to PRDX6, while the endogenous PRDX6 might have partly decreased chance to contact with viral 3Cpro.
Taken together, we show here for the first time that PRDX6 suppresses porcine picornavirus replication, the PLA2 enzyme activity is associated with PRDX6-mediated antiviral effect. Both FMDV and SVA infection induces PRDX6 protein expression, and the viral 3Cpro was responsible for induction of PRDX6 degradation to impair PRDX6-mediated antiviral effect against porcine picornaviruses. This study provided new findings for the function of PRDX6 and also identified a novel antagonistic mechanism for porcine picornavirus.
-
This work was supported by grants from the National Key R & D Program of China (2017YFD0501103), the Key Development and Research Foundation of Yunnan (2018BB004), the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project (Y2017JC55), and Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund (1610312016013 and 1610312017003).
-
ZZ and HZ conceived the study and designed the experiments. CW, HF, XZ, KL, FY, WC, HL and LG carried out the experiments. XZ, KL, ZX, WC and CW analyzed the data. ZZ, HZ and CW wrote the paper, HF and XL revised the manuscript. ZZ and HZ finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: