HTML
-
EBOV Zaire ebolavirus CH2 domain Constant domain 2 C-sdAb C-based single domain antibody GP Glycoprotein IFL Internal fusion loop SUDV Sudan ebolavirus BDBV Bundibugyo ebolavirus TAFV Taı¨ Forest ebolavirus RESTV Reston ebolavirus RBD Receptor binding domain MLD Mucin-like domain GPCL Cleaved GP NPC1 Niemann-Pick C1 ADCC Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity FDA Food and Drug Administration EVD Ebola Virus Disease sdAb Single domain antibody V-sdAb V-based single domain antibody RSV Respiratory syncytial virus GPt GP1 truncation 293F FreeStyle 293-F PEI polyethylenimine sGP Soluble GP HA Hemagglutinin CDRs Complementarity-determining regions
-
Ebola virus belongs to the Filoviridae family and causes the majority of hemorrhagic fever diseases, including the pandemics in West Africa during 2014-2016 which led to more than 28, 600 cases and 11, 325 deaths (https://www.cdc.gov/). Six species of Ebolavirus genus have been identified: Zaire ebolavirus (EBOV or ZEBOV), Sudan ebolavirus (SUDV), Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BDBV), Taï Forest ebolavirus (TAFV), Reston ebolavirus (RESTV), and Bombali ebolavirus (Emanuel et al. 2018; Karan et al. 2019). Among these, EBOV and SUDV are lethal and have been associated with large outbreaks in Africa with high human case fatalities (Negredo et al. 2011). EBOV glycoprotein (GP) is the key target of neutralizing antibodies (Lee et al. 2008). The precursor GP is cleaved by furin protease to form GP1 and GP2. These two subunits form a heterodimeric monomer through a disulfide bridge, and three GP1 form a chalice-shaped trimer, cradled by three GP2 fusion subunits. GP1 contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which is wrapped with glycan cap region and head region, while a mucin-like domain (MLD) is linked to the side of each monomer. The GP2 subunit contains the hydrophobic internal fusion loop (IFL), two heptad repeats (HR1 and HR2), a CX6CC disulfide bond motif, a membrane-proximal external region, and a transmembrane anchor (Lee et al. 2008). After virion internalization, GP is cleaved by cathepsin B & L to form cleaved GP (GPCL) which allows binding a receptor Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) (Wang et al. 2016). Subsequently, the structural rearrangement of GP2 enables IFL to be exposed and inserted into the host-endosomal membrane, thereby promoting membrane fusion (Gregory et al. 2011).
Significant advances have been made towards developing potent therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) for the treatment of EBOV infection. For example, ZMapp, a cocktail composed of three mAbs, is the first therapeutic antibody drug for emergency use in treatment of EBOV-infected patients during the 2014-EBOV outbreak in Liberia (Davey et al. 2016). Its components, 2G4 and 4G7, bind to epitopes in the GP base region and neutralize EBOV by preventing conformational rearrangements of GP during the fusion process. The third component of ZMapp, 13C6, recognizes the glycan cap region to facilitate antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) (Qiu et al. 2011, 2012, 2014). Following the discovery of ZMapp, another cocktail Inmazeb (REGN-EB3) containing three mAbs developed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of EBOV infection in adult and pediatric patients, including newborns of infected mothers (Markham 2021). Besides these cocktails, a human monoclonal antibody mAb114 (Ebanga) developed by Ridgeback Biotherapeutics has also been authorized by the FDA for treating EBOV infection, which was isolated from Ebola virus disease (EVD) survivors (Corti et al. 2016). MAb114 mainly binds to the GP1 core (RBD region) and still associates with it after proteolytic removal of the glycan cap, thus inhibits the binding of the cleaved GP to its receptor NPC1 (Misasi et al. 2016). In clinical trials, REGN-EB3 and mAb114 could reduce the mortality rate to 33.5% and 35.1%, respectively (Mulangu et al. 2019). Although the approval of antibody drugs is a remarkable achievement in treating EBOV infection, it is still highly desirable to identify more potent neutralizing antibodies which could further decrease the mortality.
Over the past decade, great efforts have been devoted to the development of single domain antibodies (sdAbs) based on heavy chain variable domains (V-based sdAbs, V-sdAbs) such as VHHs (termed nanobodies) from heavy chains of camelid immunoglobulins (Gong and Xiao 2013). Caplacizumab is the first approved bivalent humanized nanobody targeting Von Willebrand factor for the treatment of acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (Duggan 2018). In addition, the sdAbs show great potentials for the treatment of infectious diseases. For instance, ALX-0171 is a trivalent nanobody that can inhibit respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), which has been clinically evaluated (Detalle et al. 2016). Recently, the human IgG1 heavy chain constant domain 2 (CH2) has been proposed as a scaffold for the development of C-based sdAbs (C-sdAbs) (Dimitrov 2009; Gong and Xiao 2013). Besides the antigen-binding activity as V-sdAds, the scaffold itself might offer additional advantages since it contains binding sites or portions of binding sites for Fc receptors and complement C1q on the framework regions, which might naturally extend the serum half-life, and mediate stability and effector functions in vivo.
In this study, we identified a novel C-sdAb M24 targeting EBOV GP that could neutralize pseudotyped and authentic EBOV in vitro. This C-sdAb might be further developed as a therapeutic candidate against EBOV infection. Our results also provide clues for the improvement of antibody-based therapy against EVD.
-
The Codon optimized EBOV glycoprotein GP ectodomain (GPe, Zaire ebolavirus strain Mayinga, GenBank: EU224440.2) was cloned into pSectag2A vector for mammalian cellular expression. The protein lacks the transmembrane domain and the carboxy-terminal amino acids from 637 to 676, with T42V/T230V mutations for the elimination of glycosylation (Lee et al. 2008). GPe△muc is GPe without mucin-like domain (amino acids 312–463). The C-termini of both GPe and GPe△muc contain T4 trimerization domain (Zhao et al. 2016; Agnolon et al. 2020) and StrepTagII for purification. GP1 truncation (GPt) contains residues from 54 to 222 of GPe△muc and carries an IgG1 Fc fragment at C-terminus. The construct for sGP was truncated at residue Y311 and cloned into the vector pSectag2A with a 6-histidine (His) tag (Pallesen et al. 2016). The endotoxin-free plasmids were transiently transfected into FreeStyle 293-F (293F) cells using polyethylenimine (PEI) (Sigma). Five days after transfection, the supernatant was clarified by centrifugation at 8000 × g for 15 min and passed through a 0.22 μm filter. Protein sGP was purified using Ni2+-NTA Agarose (Qiagen) according to the instructions. Strep-tagged proteins were purified using Strep-Tactin® XT Superflow® (IBA) as the manufacturer's protocol. Proteins with Fc fragment were purified from the culture medium by protein-A sepharose (GE Healthcare). The purified proteins were concentrated using Amicon Ultra (Millipore) centrifugal filter units and were prepared in PBS.
-
A CH2-based phage display library was constructed in house as previously described (Gong et al. 2012). This library was used for panning against EBOV GPe△muc. After five rounds of panning, polyclonal phage ELISA was performed to identify candidate clones (Kazemi-Lomedasht et al. 2015). Briefly, a 96-well plate (Corning) was coated with 2 µg/mL of GPe△muc at 4 ℃ overnight. BSA was incubated in the same condition as control. After blocking and washing, 1012 cfu of input phage from each round after panning were added and incubated for 1 h at 37 ℃. Then wells were washed with PBS and incubated with HRP-conjugated anti-M13 (Sino Biological Inc.) for 1 h at 37 ℃. Substrate ABTS (Life technology) was added subsequently, and the intensity of absorbance signals was measured at 405 nm. For monoclonal phage ELISA, 200 colonies were randomly picked from the fifth round of panning, and then performed as previously reported (Gong et al. 2012). Finally, one enriched clone S5 was selected for further characterization.
-
S5 was expressed and purified following previously published protocols (Gong et al. 2012). In brief, the plasmid of S5 for expression was transformed into E. coli HB2151 bacterial culture. The expression was induced by IPTG at 37 ℃ overnight. The bacterial cells were harvested and lysed by polymyxin B (Sangon) in 150 mmol/L Tris and 450 mmol/L NaCl buffer. The supernatant was clarified by centrifugation and purified by Ni2+-NTA Agarose (Qiagen) according to the instructions.
-
Heavy and light chains of KZ52, 13C6, 2G4 were synthesized (Sangon) according to previous reports (Lee et al. 2008; Pallesen et al. 2016) and cloned into pVITRO2-neo-mcs (InvivoGen). These IgGs were expressed in 293F cells and purified from the culture medium with protein A column (GE Healthcare) as described above. An EBOV neutralizing antibody mAb114 single-chain format scFv-114 with His tag and HA tag (for competitive ELISA) was cloned into pComb3XSS vector (Addgene) for expression and purification. Another version of scFv-114 with His tag and FLAG tag (for measurement of binding) was also constructed. The proteins were expressed using E. coli HB2151 and purified by Ni2+-NTA Agarose (Qiagen) as described above.
-
ELISA was performed for the evaluation of binding. Briefly, 96 half-well plates (Corning) were coated overnight with GPe△muc at 4 μg/mL. The next day, plates were washed with PBS, and then blocked for 1 h at 37 ℃. Next, Serially-diluted antibodies were added and incubated for one hour at 37 ℃. Then, 1:3000 diluted HRP-conjugated anti-flag (Sigma) was used as the secondary antibody and incubated for 1 h at 37 ℃. The intensity of absorbance signals was measured as described above. The binging ability of matured S5 (termed M24, see below) with GPe, GPt, and sGP was also tested by ELISA with the same method.
-
For affinity maturation, the phage display library based on S5 with random mutations was constructed by error-prone PCR as previously described (Zhang et al. 2004). Candidate C-sdAbs were expressed as described above, and culture supernatant was used directly for binding test by ELISA.
-
Purified S5 and M24 were loaded into the Superdex 75 10/300 GL column (GE Healthcare) running on ÄKTA pure system to assess possible oligomer formation. The standard markers are BSA (67 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), ribonuclease A (13.7 kDa), aprotinin (6.512 kDa), and vitamin B12 (1.355 kDa). The volume of samples was 100 μL and eluted with 150 mmol/L Tris and 450 mmol/L NaCl buffer, pH 7.4 at room temperature. UNICORN 7.0 software was used for data collection and analysis.
-
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) G was replaced by expressing both eGFP and EBOV GPe△muc (rVSV-EBOV) as described previously (Wong et al. 2014). For neutralization assay, BHK-21 cells were seeded at 2.0 × 104 cells per well and cultured overnight in Eagle's minimal essential medium (EMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 I.U./mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin at 37 ℃ in an incubator containing 5% CO2. After about 24 h, rVSV-EBOV was incubated with serial two-fold diluted S5 at an initial concentration of 5 μmol/L in serum-free EMEM for 1 h at 37 ℃ before infection. An EBOV neutralizing antibody mAb114 single-chain format scFv-114, and the C-sdAb scaffold were used as positive control and negative control, respectively. The amount of viruses used for infection was determined to achieve approximately 70% final infection in the control well without antibody (MOI = 0.2 infectious units per cell). The virus-antibody mixture with equal volume was incubated with cells in EMEM supplemented with 2% FBS at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2 for 24 h before cells were fixed. Images were captured by a fluorescence microscope (Leica). The neutralization ability of M24 was also tested with the same method at the initial concentration of 1.5 μmol/L, and the dilution was performed with a three-fold gradient. The percentages of infected cells were measured using Operetta High Content Imaging System (Perkin-Elmer). Data for neutralization were presented with the percentage of inhibition relative to control cells treated with rVSV-EBOV.
-
Neutralization assays involving infectious viruses were performed at the BSL-4 facility in Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Authentic EBOV (Zaire ebolavirus) was used to test the neutralization activity of M24. Vero E6 cells were seeded at 1.5 × 104 cells per well in the inner 60 wells of 96-well plates (Biofile) for 24 h prior to virus infection. Serial three-fold diluted antibodies were mixed with equal volume of authentic EBOV (1500 ffu), and incubated at 37 ℃ for 1 h before being adding to cells. Cells were fixed at 48 h post infection, and determined by indirect immunofluorescence assay using rabbit polyclonal antibody against EBOV NP protein (gift from Professor Zheng-Li Shi, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Science) and Alexa Fluor 488 labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG as the secondary antibody (Proteintech). Data were analyzed using Operetta High Content Imaging System (Perkin-Elmer) as described above.
-
GPe△muc was immobilized at 8 μg/mL in 96 half-well plates (Corning) at 4 ℃ overnight. Serial ten-fold dilutions of competitive antibodies beginning at 2 μmol/L were mixed with 1 nmol/L of M24 with equal volumes, and the mixture was then added to wells. HRP-conjugated anti-flag (Sigma) was used as the secondary antibody and subsequent work was performed in standard methods.
-
Amino acid sequences of M24 and EBOV GP (PDB 5JQ3) (Zhao et al. 2016) in FASTA format were put into SWISS-MODEL (Waterhouse et al. 2018) server as a query to search for relative protein structures. Next, data of templates were ranked according to QMEAN scoring. Top-ranked templates were compared and selected according to their three-dimensional structures, sequence similarity, and quaternary structural features. 3D protein model was automatically generated through the target-template alignment. Subsequently, contact and blocking residues were picked and the chosen templates were submitted to the server. Finally, ten samples with best interface-energy were returned from the server, and the docking model was chosen from the top three for analysis.
-
GPe△muc mutations with alanine substitutions: E523A, I527A/G528A, I532A, and G541A were constructed and expressed using 293F cells as described above. 96-well Strep-Tactin® Coated microplate (IBA) was coated with cultural supernatant of GPe△muc and its four mutations overnight at 4 ℃ respectively. The next day, diluted antibodies (scFv-114, KZ52, and C-sdAb M24) at final concentration of 200 nmol/L were added into wells for binding ELISA followed the standard method.
-
96 half-well plates (Corning) were coated with GPe△muc at 4 ℃ overnight. After blocking with 3% milk, the wells were treated with acidic buffer (150 mmol/L Tris, 450 mmol/L NaCl buffer, pH 5.5) for 1 h, and with neutral buffer (150 mmol/L Tris, 450 mmol/L NaCl buffer, pH 7.5) as control. Next, antibodies were serially diluted with acidic buffer and neutral buffer, respectively. Diluted antibodies were added to wells for binding ELISA as the standard method.
-
All experiments were performed as triplicate. The data were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Student's t-test and one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey's test were used to compare the data from different groups. P < 0.01 was considered statistically significant.
Expression and Purification of EBOV GP and GP Truncations
Screening of C-sdAbs Targeting EBOV GP
Expression and Purification of sdAbs
Expression and Purification of IgG Antibodies
Measurement of Binding
Affinity Maturation
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Pseudovirus Neutralization Assay
Authentic Virus Neutralization Assay
Competitive ELISA
Molecular Modeling and Docking
Alanine Scanning
Measurement of Binding at Low pH
Statistical Analysis
-
Panning against EBOV GPe△muc was performed from the C-sdAb based phage display library constructed as previously reported (Gong et al. 2012). Polyclonal phage ELISA shows the enrichment of positive clones after the fifth-round panning (Fig. 1A). We then randomly picked up single colonies for the monoclonal phage ELISA. Clones with positive signals were sent for sequencing, which led to the identification of an enriched clone S5. After expression and purification, S5 exhibits specific but weak binding to EBOV GPe△muc (Fig. 1B). Consistent with the binding activity, S5 shows modest neutralizing activity against the pseudovirus rVSV-EBOV (Fig. 1C).

Figure 1. Screening of C-sdAb candidates against EBOV GP. A Polyclonal phage ELISA. Phage specifically binding to EBOV GPe△muc (black bar) was enriched in the fifth round. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 by student's t-test. B Binding of C-sdAb S5 to EBOV GPeΔmuc measured by ELISA. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. C Neutralization of S5 against replicative rVSV-EBOV. Scaffold and scFv-114 were used as negative and positive controls respectively. D Affinity maturation of S5. The single clones were screened from culture supernatant directly by ELISA.
To improve neutralization potency, the affinity maturation of S5 was performed. As a result, a total of 200 specific single colonies were selected for evaluation and optimization, which resulted in the identification of one candidate clone M24 (Fig. 1D).
-
M24 binds to EBOV GPe△muc with EC50 of 0.1 nmol/L (1.5 ng/mL), which increases by over 104 times compared to parental clone S5 (Fig. 2A). The binding activity is comparable to that of scFv-114 (EC50 of 0.4 nmol/L or 10 ng/mL) (Fig. 2B). Meanwhile, M24 exists as a monomer, whereas S5 forms an oligomer in the solution (Fig. 2C). Therefore, the affinity maturation process not only increases affinity, but also improves the physicochemical property.
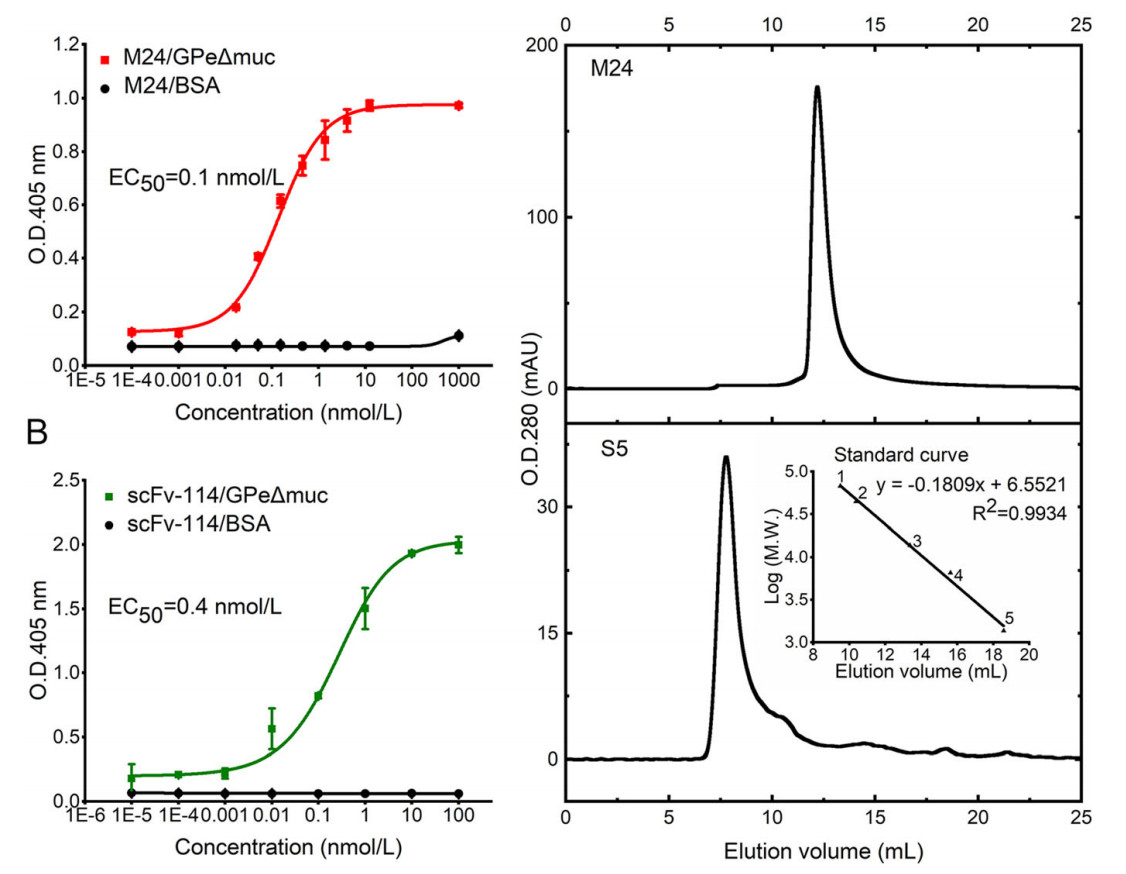
Figure 2. Characterization of purified C-sdAb M24 against EBOV GP. A Binding activity of M24 (matured C-sdAb S5) to EBOV GPeΔmuc measured by ELISA. B Binding activity of scFv-114 to EBOV GPeΔmuc measured by ELISA. ELISA data are shown as mean ± SEM. C Evaluation of oligomer formation of M24 and S5 measured by SEC. A standard curve was determined based on the elution volumes of the protein standards. 1. BSA, 67 kDa; 2. Ovalbumin, 43 kDa; 3. Ribonuclease A, 13.7 kDa; 4. Aprotinin, 6.512 kDa; 5. Vitamin, 1.355 kDa.
We then tested the neutralization ability of M24 against rVSV-EBOV. As shown in Fig. 3A, M24 effectively neutralized rVSV-EBOV with IC50 of 0.8 nmol/L (12 ng/mL). Similarly, the positive control scFv-114 inhibited rVSV-EBOV with IC50 of 2.8 nmol/L (70 ng/mL), which was consistent with the previous study (Corti et al. 2016).
Figure 3. Neutralization of M24 against rVSV-EBOV (A) and authentic EBOV (B). Scaffold and scFv-114 were used as negative and positive controls respectively. Data for neutralization are shown in the percentage of inhibition relative to control cells infected by EBOV alone. Results are shown as mean ± SEM, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test.
The neutralization activity of M24 was then further evaluated with authentic EBOV (Zaire ebolavirus). We found that M24 modestly neutralized authentic EBOV with a maximum inhibition efficacy of 31.6%. By contrast, scFv-114 could efficiently neutralize authentic EBOV (Fig. 3B). Since M24 strongly neutralized the pseudotyped EBOV but weakly inhibited live EBOV, we tried to perform more studies to find out the possible reasons.
-
To determine the epitope recognized by M24, we constructed different GP truncations (Fig. 4A) and evaluated the binding of M24 to them. Firstly, we found that M24 could still efficiently bind to GPe with EC50 of 4.8 nmol/L (72 ng/mL) and scFv-114 could bind to GPe with EC50 of 5.0 nmol/L (125 ng/mL) (Fig. 4B). However, their binding to GPe significantly decreased compared to their binding to GPe△muc. One concern is that although MLD is dispensable for M24 binding, it may hinder the binding of M24, thus leading to the modest neutralization of M24 against live EBOV. However, scFv-114 also significantly lost the binding to GPe since the coverage of RBD by MLD, but it efficiently neutralized live EBOV due to tightly binding to GPCL. Therefore, the loss of binding of M24 to GPe might not be the major reason for the weak inhibition against live EBOV. Next, a GP truncation was tested to determine the binding regions for M24. GPt is a truncated GP1 containing RBD but lacks glycan cap and MLD (Fig. 4A). M24 and the glycan cap binder 13C6 could not bind to GPt, while scFv-114, the RBD binder, bound to the GPt (Fig. 4C). M24 and 2G4 could not bind to soluble GP (sGP), a sGP that shares 295 residues with the GPe (Fig. 4A), while 13C6 bound strongly to it (Fig. 4D). These data indicate that MLD and RBD are unnecessary for the binding of M24 to GP, and M24 does not bind to sGP alone.
Figure 4. Binding region determination. A Construction of different EBOV GP truncations. GPe includes receptor-binding domain (RBD, 54–201), Glycan cap (227–310), mucin-like domain (MLD, 314–462), internal fusion loop (IFL, 511–556). GP truncation (GPt) is from 55 to 222. sGP is from 33–311 residues. B–D Binding of M24 and different control antibodies to different GP constructs. E Competitive ELISA between M24 and scFv-114, KZ52, 13C6, and 2G4. Biotinylated-M24 (M24-bio) was a positive control. All data are shown as mean ± SEM.
To confirm these findings, we further performed a competitive ELISA. M24 had no competition with the glycan cap binder 13C6, the RBD binder mAb114, or the base binder KZ52 and 2G4 (Fig. 4E). These results indicate that the epitope of M24 is distinct from the antibodies tested in this study.
To refine the epitope of M24, we firstly used molecular modeling and docking for prediction. The computationally predicated GPe/M24 complex indicated that M24 might recognize residues in the IFL region of GP2, which differed from KZ52 and mAb114 (Fig. 5A). To refine the critical residues in GP for M24 binding, we next evaluated the binding of M24 against GP mutations, including GP E523A, GP I527A & G528A, GP I532A, and GP G541A (Fig. 5B) in the IFL of GP2 according to the results of docking. As a result, the binding of M24 to these mutations has dramatically decreased compared to its binding to wild-type GP. In contrast, the binding of mAb114 and KZ52 to these mutants was unaffected (Fig. 5C). Notably, alanine substitution in I532 residue reduced the binding of KZ52 and M24 by 54.7% and 73.2% respectively but did not affect the mAb114 binding. Overall, these epitope mapping analyses indicate that residues E523, I527 & G528, I532, and G541 within IFL of GP2 may be critical for M24 binding. What's more, these four residues are highly conserved among GPs of Zaire ebolavirus (Fig. 5D). In conclusion, these results prove further evidence that IFL is an effective target for the development of anti-EBOV agents.
Figure 5. Epitope mapping and analysis of M24. A Epitope presentation in trimeric EBOV GPe△muc. Predicted M24 epitope, blue; KZ52 epitope, purple; mAb114 epitope, green. B M24 and GP2 complex by molecular docking. M24 scaffold is colored yellow and its binding regions are colored orange. IFL in GP is colored blue. The critical residues (E523, I527 & G528, I532, and G541) in IFL involved in binding are shown in red spheres. Other GP regions are colored grey. C Binding of M24 (blue) to different GP mutants. All the mutants could still bind to mAb114 (green) while only one mutation affects the binding to KZ52 (purple). Mock reflects GP binding of untransfected cell supernatant. Results are shown as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. D Sequence alignment of IFL regions in different EBOV GPs. In general, these five residues (red) are conserved while variations have been found between EBOV and SUDV.
-
Receptor interaction and membrane fusion of filovirus occur in the acidified endosomes, and acidic pH could shift the GP2 conformational equilibrium to an intermediate state in favor of NPC1 binding (Das et al. 2020). We next examined whether M24 could bind to GP at acidic pH by ELISA (Fig. 6). As a result, M24 binds to GPe△muc with EC50 of 9.6 nmol/L (144 ng/mL) at pH 5.5, which has been decreased about 100 times than the binding at natural pH (Fig. 6A). However, the binding of scFv-114 and KZ52 is independent of pH (Fig. 6B and 6C). Therefore, the decrease of binding to GP at acidic condition might be a crucial factor for the weak neutralization activity of M24 against authentic EBOV.
Figure 6. Binding of M24 (A), scFv-114 (B), and KZ52 (C) to GPe△muc at neutral and acidic pH conditions. In the case of M24, the binding at pH 5.5 (red) decreases dramatically compared to the binding at pH 7.5 (black). In contrast, the binding of scFv-114 and KZ52 at pH 5.5 (red) has no significant change compared to the binding at pH 7.5 (black). Data are shown as mean ± SEM.
Screening of C-sdAb Candidates Against EBOV GP
Characterization of M24
Identification of the Putative M24 Epitope
Binding of M24 to GP at Acidic pH
-
The current antibody-based treatment for EVD has indeed been an unprecedented success. However, over 30% of antibody-treated patients still died of high viral loads according to clinical trials. Hence, better effective anti-EBOV agents are required to meet more medical needs.
Since all approved antibodies against EBOV infection are full-length format currently, we have attempted to use the sdAb technique platform to select potential candidates. A great deal of work has been devoted towards the development of binding domains based on novel scaffolds from altered protein folding domains with much smaller size compared to conventional full-length antibodies. The sdAbs are quite attractive candidates for the treatment of various diseases, including infectious diseases (Schepens et al. 2011; Wu et al. 2020). However, to our knowledge, no sdAb against EBOV infection has been reported. In our previous work, the antibody CH2 domain was engineered to make it more suitable as a scaffold for the development of C-sdAbs (Gong et al. 2009, 2011; Gao et al. 2019; Cao et al. 2020) and showed the potentials of functional C-sdAbs as therapeutic candidates (Xiao et al. 2009; Gong et al. 2012). In this study, we screened C-sdAb phage display libraries against EBOV GP and identified one C-sdAb that has shown strong neutralizing activity against pseudotyped EBOV but modest inhibition to authentic EBOV. To further reveal the mechanism of the neutralization, we performed experiments to refine the epitope.
Based on the truncated GP binding analysis and computational prediction, we found that the binding region of M24 is located within the IFL of GP2. A mouse-derived mAb 6D6 and a macaque-derived mAb CA45 recognize the IFL (Zhao et al. 2017; Milligan et al. 2019). Interestingly, the epitopes of these identified antibodies targeting IFL more or less span the base region that shares with the epitope of KZ52. In contrast, M24 appears to be a novel epitope targeting IFL without spanning the base region according to the result of competitive ELISA. Notably, it has been pointed out that the contact of IFL-targeting antibodies to residues in both IFL and GP1 is essential for neutralizing activity (Wec et al. 2017; Zhao et al. 2017; Milligan et al. 2019). In consistence with this point, FVM02, an IFL mAb that binds to the tip of IFL with no GP1 contact lacks neutralizing activity in vitro although it could provide 30% protection in mice due to Fc-mediated effector functions (Keck et al. 2016). Despite the low efficacy, M24 targeting the IFL epitope without GP1 contact still has neutralizing activity in vitro. The difference may provide novel understanding of the IFL epitope. In addition, M24 recognizing epitope is relatively conserved among Zaire ebolavirus, which could be a broad-spectrum target for drug and vaccine development.
When the virion is internalized, the GP2 is rearranged to form a fusion core termed the six-helix bundle, which promotes membrane fusion in the endosome under an acidic condition. In this process, a low-pH condition triggers a reversible conformational change in GP, which results in the state for NPC1 binding (Wang et al. 2016; Das et al. 2020). Under acidic pH, antibodies such as mAb114 and CA45 remain the binding ability to GP (Misasi et al. 2016; Zhao et al. 2017), suggesting that reservation of GP binding in the acidic condition may play a significant role in neutralizing activity. On the contrary, the decreased binding of M24 under the acidic condition probably attributes to some uncertain conformational changes caused by instability of itself, which leads to modest neutralizing activity against authentic EBOV. These findings suggest that further engineering of M24 for the increase of its stability, including the stabilization of the complementarily-determining regions (CDRs) may lead to higher binding affinity to EBOV GP under both acidic and neutral conditions, thus may increase the neutralizing efficacy.
In summary, we identified and characterized a novel C-sdAb M24 against EBOV GP, a potential inhibitor for neutralizing EBOV. It offers a proof-of-concept that sdAbs could be therapeutic candidates against EBOV infections. Also, our findings provide useful epitope information on functional epitopes for the development of anti-EBOV drugs and vaccines, which might strengthen our capacity to tackle the EBOV outbreak in the future.
-
We thank the Core Facility and Technical Support, Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Wuhan Institute of Biotechnology; Wuhan Key Laboratory on Emerging Infectious Diseases and Biosafety; Center for Biosafety Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences; and the National Virus Resource Center for resource support. We are grateful to the Wuhan National Biosafety Laboratory support team, including the engineering, biosafety, biosecurity, and administrative staff. This work was jointly supported by the Advanced Customer Cultivation Project of Wuhan National Biosafety Laboratory, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2021ACCP-MS01, 2019ACCP-ZD03), the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province of China (2019CFA076), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31870926).
-
RG contributed to the conception of the study, data analysis, and manuscript preparation. RW performed the experiment, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. HZ, CP, and JS helped to perform the experiment. HZ helped experimental analysis with constructive discussions. RG finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
-
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: