HTML
-
The Baculoviridae is a family ofenvelopeddouble-strandedcircular DNA viruses. Baculoviruses are exclusively pathogenic to arthropods, especially insects of the order Lepidoptera, therefore have been widely used as commercial insecticides (Summers, 2006). According to the molecular phylogenetic studies, the family Baculoviridae can be divided into four genera. Alphabaculovirus and Betabaculovirus are lepidopteran-specific nucleopolyhedroviruses (NPVs) and granuloviruses (GVs), respectively. Gammabaculovirus and Deltabaculovirus, are NPVs infecting hymenopteran and dipteran hosts, respectively (Herniou, 2012). The alphabaculoviruses can be further divided into two subgroups: group Ⅰ and group Ⅱ (Bulach et al., 1999; Hayakawa et al., 2000; Herniou et al., 2003). Two different virion phenotypes are produced in baculoviral replication cycle : occlusion-derived virus (ODV) transmitting infection from insect to insect (oral infection) and budded virus (BV) mediating systemic infection within the infected insect (Volkman and Summers, 1977).
Two distinct types of envelope fusion proteins (EFPs), GP64 and F, have been identified in BV, which mediate the processes of virus attachment, low-pH dependent membrane fusion and virus budding. GP64 occurs only in group Ⅰ alphabaculoviruses, whereas F proteins are widely present in group Ⅱ alpha-and betabaculoviruses. It was proposed that an evolutionary event of the acquisition of GP64 by an ancestral group Ⅰ alphabaculoviruses virus and subsequent adaptive inactivation of the original F protein occurred in the evolution of baculovirus EFPs (Pearson et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2014).
GP64 and F protein are different in their structure and mode of action. In past decades, many investigations of the structure and function of GP64 have been undertaken (Monsma et al., 1996; Kadlec et al., 2008; Zhou and Blissard, 2008). The crystal structure of GP64 revealed that it belongs to Class Ⅲ EFPs. The post-fusion structure of GP64 consists of five domains or regions (I-V) with its fusion loop located in domain I of the protein (Kadlec et al., 2008). The transmembrane (TM) and pre-transmembrane (pre-TM) domains of GP64 are essential for membrane fusion and virus infectivity (Li and Blissard, 2008, 2009a, 2009b). The receptor binding domain of GP64 was mapped to the N-terminal 160 amino acids (aa) (Zhou and Blissard, 2008). Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are useful tools to investigate the function and structure of proteins. Two monoclonal antibodies AcV1 and AcV5 have been generated, and used to investigate the function of AcMNPV GP64. AcV1 was mapped to a conformational epitope of 24 aa in the central variable domain of GP64. AcV5 did not inhibit virus attachment but instead blocked the ability of BV virions to use the endocytic pathway (Hohmann and Faulkner, 1983; Volkman and Goldsmith, 1985; Zhou and Blissard, 2006). AcV5 targeted to 431-439aa of AcMNPV GP64 which was a linear epitope (Hohmann and Faulkner, 1983; Monsma and Blissard, 1995). These data greatly enriched the understanding of the GP64-mediated virus entry mechanism.
In contrast, F proteins have been less studied. The F protein of Helicoverpa armigera nucleopolyhedrovirus (HearNPV) is one of the best-studied F proteins. It is first synthesized as a precursor F0 and then cleaved by host proteinase furin into a disulfide-linked chains F1 (transmembrane subunit of 60 kDa) and F2 (surface subunit of 20 kDa) (Long et al., 2006; Yin et al., 2014). It contains abundant N-glycosylation modification, including N-glycosylations at N104, N293, N361, N526 and N571 (Long et al., 2007; Shen et al., 2016). A polyclonal antibody against HaF2 (anti-HaF2) effectively inhibited the infections of wild type (wt) HearNPV and a mutant HearNPV of which F protein retained only binding ability (vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64) (Wang et al., 2014), indicating that F2 includes important regions involved in receptor binding.
mAbs provide important tools for analysis of the structure and function of viral EFPs. Therefore, we generated mAbs using HaF2 as the antigen. Two kinds of mAbs, represented by 38F10 and 44D11, were characterized in this report. Both of these were able to recognize the native HaF protein expressed in HearNPV infected cells. One of the two mAbs, 44D11, showed a neutralizing effect on HearNPV infection and its mode of action was further explored.
-
HzAM1 cells were cultured at 27 ℃ in Grace's insect medium (Gibco-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) (pH 6.0), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco-BRL). HearNPV G4 strain has been preserved in "Chinese General virus collection centre" (CGVCC) (Chen et al., 2002). The recombinant viruses, vHaBac-egfp (Song et al., 2008) and vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64 (Wang et al., 2010) were generated previously. The expression vectors pET32a, and pGEX-KG, and the E.coli strains DH5α and BL21 were used for the expression of the recombinant F proteins.
-
The F2 fragment of HearNPV f gene, without signal peptide (SP) (encodes 34-173 aa of F), was amplified by PCR using HearNPV genomic DNA as template. For epitope mapping, four overlapping f2 fragmentsencoding the regions of F2 (34-76), F2 (47-123), F2 (85-148) and F2 (129-173) (Figure 1A) were amplified. F2 (129-173) was further truncated into two overlapping fragments: F2 (129-163) and F2 (148-173)(Figure 1A). The numbers indicate aa position of HaF2. All the primers were listed in Table 1. The PCR product encoding F2 (34-173) was digested with BamH I and Sac I and then cloned into the pGEX-KG vectors by fusion with a GST-tag (~25 kDa) for expression. The recombinant expression plasmids were transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells, cultured in LB medium and induced by 0.5 mmol/L IPTG at an optical density at 600 nm of 0.7 at 37 ℃. Then the cells were disrupted by sonication and the inclusion bodies were collected for repeated washing with 0.1% Triton X-100, 0.1 mmol/L EDTA and 2 mol/L urea, then dissolved in 8mol/L urea containing 0.1 mol/L dithiothreitol (DTT) for vaccination. Other six truncated f2 segments wereeach cloned into the BamH I/Sac I site of the pET32a vector with N-terminal tags (~20 kDa) for expression as describe above.Then cells were pelleted in PBS buffer for Western analysis.
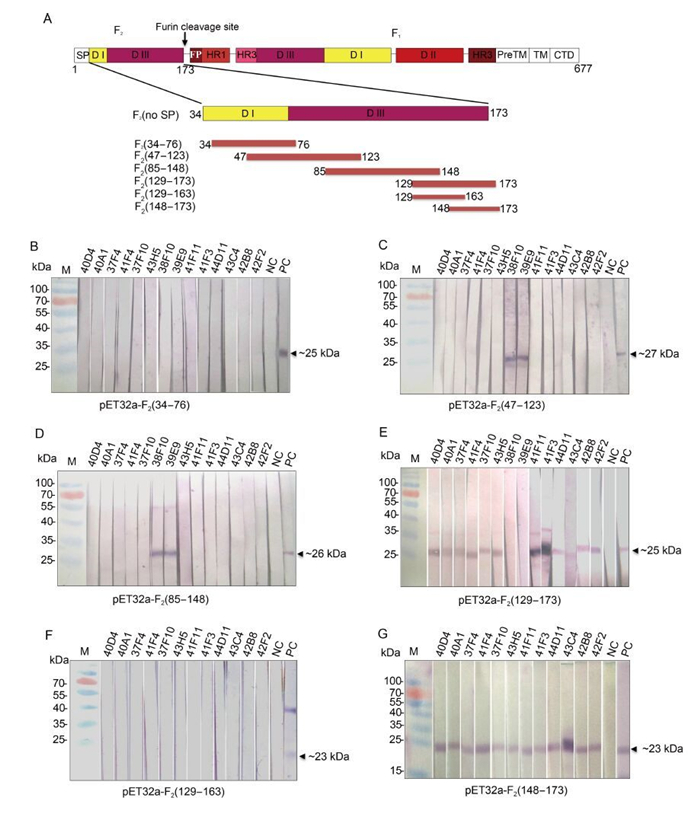
Figure 1. Mapping the recognition region of the mAbs against HaF2 protein. (A) Schematic diagram of HaF protein and truncation strategy. The structure of full length HearNPV F is shown at the top; the truncated HaF2proteins used for sequential mapping experiment are showed below. Numbers indicate amino acid positions. The domains (DI-Ⅲ) were defined according to Shen et al.(2016). (B) Epitope mapping experiment. The truncated HaF2 expressed by pET32a vector were presented as antigens. Fourteen hybridoma cells supernatants were used as the primary Abs for Western blot analysis. Anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody and pre-immune serum are as the positive control (PC) and negative control (NC), respectively. Upper numbers indicated the names of mAbs.
Primers Sequences (5′-3′) BamHI-F2-34-For CGGGATCCATTTTATTGTGTACTATATTAATTTC SacI-F2-76-Rev CGAGCTCTTCGATGACAAAATGCCAAACG BamHI-F2-47-For CGGGATCCTCAAATGAGATTCGTTGAAGTG SacI-F2-123-Rev CGAGCTCGTATATGTATGTTTGCAAATCG BamHI-F2-85-For CGGGATCCCAAGAATAAAAATTTAACCAGTTG SacI-F2-148-Rev CGAGCTCTACTAAGTCGGGATTCATTGC BamHI-F2-129-For CGGGATCCTGAAAAAAATAACGCCATTGATC SacI-F2-173-Rev CGAGCTCTCGTTTGTTGCGACTCGAG SacI-F2-163-Rev CGGAGCTCATCTGTGACTAAAGGTACGGG BamHI-F2-148-For CGGGATCCCAAATCGATGCTAACCGAAAATG Table 1. Primers for the PCR amplification of truncated HaF2 gene. Restriction enzyme sites are underlined.
-
The purified inclusion bodies of GST-HaF2 (34-173) protein were used to immunize BALB/cmice. The polyclonal antibodies were generated from theimmunized miceand detected byenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) by using the prokaryotical expressed F2 protein as antigen and neutralization assays. Then thespleen cells from positive mouse were fused with SP2/0 myeloma. Supernatants of hybridoma cells were screened by ELISA, Western blot and neutralization assay. Two selected hybridoma cells (38F10 and 44D11) were inoculated into mice to produce ascites fluids from which the mAbs were purified by a Protein A-SepharoseTM column column (Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany).
-
Truncated HaF2 proteins expressed in E.coli or the native F protein expressed in vHaBac-egfp infected HzAM1 cells (MOI = 5 TCID50 units/cell) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE and electro-transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane (Millipore). The blots were probed with the primary antibodies (hybridoma cell supernatants without dilution, and 1:5000 dilution for pre-immune mouse serum and anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody) and alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (1:5000 dilution). The final signals were detected with 4-Nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) and 5-Bromo-4-chloro-8-indolilphosphate (BCIP) (Amresco, Solon, USA).
-
HzAM1 cells were infected with vHaBac-egfp at MOI of 5 TCID50 units/cell. At 48 h post infection (p.i.), the cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde and incubated with the primary antibodies (purified mAbs 38F10 and 44D11, pre-immune mouse serum, and anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody, diluted at 1:500) at 37 ℃ for 2 h. After being washed for three times with PBS, cells were incubated with the secondary antibody, DyLight 594 conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG or Alexa Fluor 555 (Abcam, Hangzhou, China) labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG, at 37 ℃ for 1 h. Nuclei were stained using Hoechst 33258 dye (Beyotime, Haimen, China). The cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy.
-
Neutralization assay was conducted according to Wang et al.(2014) with slight modification. HzAm1 cells (1×105/well) were inoculated in a 24-well dish. vHaBac-egfp (MOI = 5 TCID50 units/cell) and vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64 (MOI = 20 TCID50 units/cell) were pre-incubated with purified mAbs, pre-immune antibody and anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody separately for 1 hat room temperature (RT). The doses of the antibodies were 0, 0.02, 0.1 and 0.5 μg per well for the purified mAb (38F10 or 44D11) or 0, 0.02, 0.1 and 0.5 μL per well for the serum (pre-immune antibody or anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody). Then the virus-antibody mixture was addedto HzAM1 cells for 2 h at 4 ℃ to allow virus binding, and then exchanged for fresh Grace'smediumcontaining 10% FBS. After 24 h, virusinfection was examined by fluorescence microscopy. Then, the cells were washed 3 times with 1 mL PBS and suspended in 200 μL PBS, and the infection rates (EGFP-positive cells) were quantified by flow cytometric analysis (FACS). Infection rates of vHaBac-egfp combined with the 3 antibodies at 3 concentrations were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. Fishers Least Signification Difference was used to compare the marginal means of the infection rates affected by the 3 antibodies.
-
Syncytium formation assay was conducted according to Wang et al.(2008) with slight modification. HzAM1 cellswere infected with vHaBac-egfp at an MOI of5 TCID50 units/cell. At 48hp.i., thecells were incubated with 38F10, 44D11, pre-immune mouse serum or anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody for 2 h at 4 ℃, washed with 1 mL Grace's medium and treatedwith low-pH Grace's medium (pH = 4.8) for 5 min at RT.The cells were washed threetimes with Grace's medium and incubated with Grace's medium containing 10% FBS (pH = 6.5). Twenty-four hours after pH shift, the inhibition of syncytium formation was detected by fluorescence microscopy.
-
The 3D structure of HaF pre-fusion form were modeled using the same method described by Shen et al.(2016). The pre-fusion structure of Simian virus 5 (SV5) F protein was used as template. The predicted structure was displayed by PyMOL software.
Cells, virus and plasmid
Expression of recombinant proteins
Generation of mAbs
Western blot analysis
Immunofluorescenceassay (IFA)
Neutralization assay
Syncytium formation inhibition assay
Prediction of three dimensional (3D) structure of HaF
-
HaF2 (34-173) fused with a GST tag was used to immunize mice to generate mAbs against HaF2. Totally 14 strains of positive hybridoma cells were selected by ELISA and Western analysis. Epitope mapping of these mAbs was determined using the expressed truncated HaF proteins, including F2 (34-76), F2 (47-123), F2 (85-148) and F2 (129-173), by Western blot analysis (Figure 1B-E). From the 14 mAbs, only 38F10 and 39E9 recognized both F2 (47-123) and F2 (85-148), therefore they were directed against an overlapping region (85-123 aa) of the two fragments (Figure 1C and 1D). 44D11 and the remaining 11 mAbs all recognized F2 (129-173), which locates in the C-terminus of HaF2 (Figure 1E). To further identify the epitopes of these 12 mAbs, F2 (129-173) was truncated into two segments: F2 (129-163) and F2 (148-173) (Figure 1A). The results of Western blot showed that all of the 12 mAbs reacted with F2 (148-173) segment, but none with F2 (129-163) (Figure 1F and 1G). Therefore, two kinds of mAbs, as represented by 38F10 and 44D11, with different linear epitopes against HaF2 were finally obtained.
-
To investigate whether 38F10 and 44D11 recognize F protein expressed by HearNPV infection, Western blot and IFA were performed. As shown in Figure 2A, 44D11, 38F10 and anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody (PC), but not pre-immune serum (NC) reacted with the HaF2 band (~20 kDa) in the sample of vHaBac-egfp infected HzAM1 cells. The IFA results demonstrated that both 38F10 and 44D11 detected the F protein located around the HearNPV infected plasma membrane, similar to the positive control anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody (Figure 2B). These results suggested that both 38F10 and 44D11 recognized the F protein in its native form during HearNPV infection (Figure 2B).
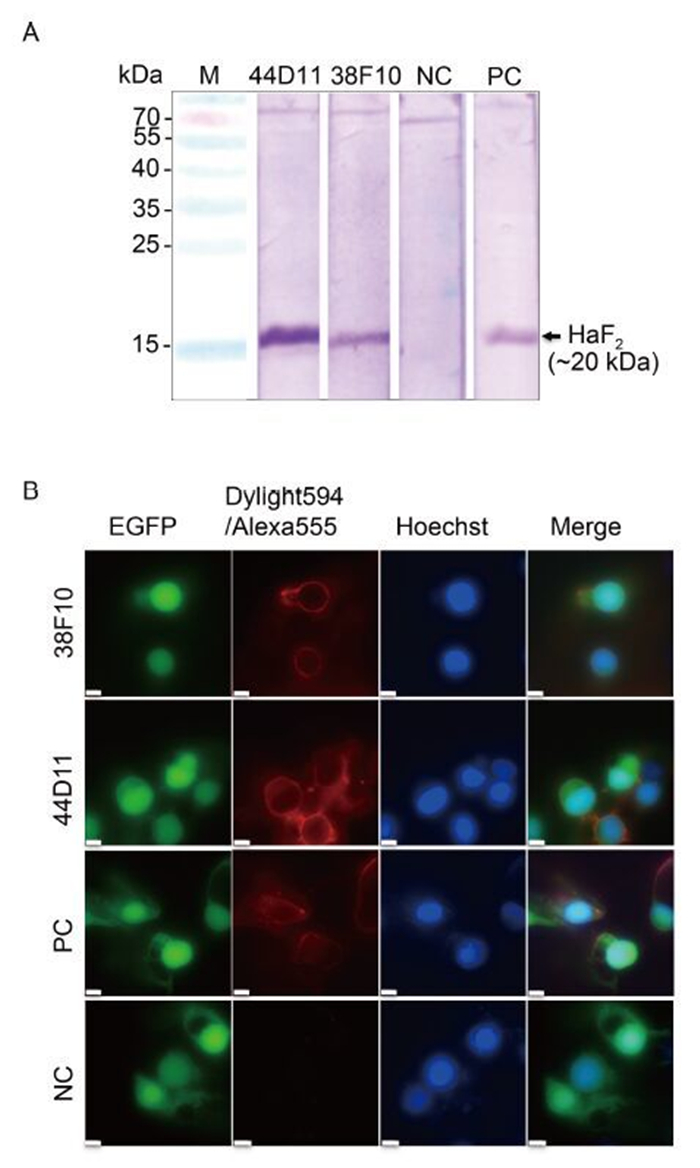
Figure 2. Characterization of mAbs 38F10 and 44D11. (A) Western blot analysis. HzAM1 cells were infected with vHaBac-egfp at an MOI of 5 TCID50 units/cell. At 48 h p.i., cells were harvested for Western blot analysis using 38F10 or 44D11 as the primary antibody. (B) Immunofluorescence assay. The cells were infected by vHaBac-egfp (green), and at 48 h p.i., cells were fixed and subjected for IFA using 38F10 or 44D11 as the primary antibody and DyLight594-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (red) or Alexa Fluor 555 labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG as the secondary antibodies. Hoechst 33258 (blue) was used for staining the nuclei. Anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody and pre-immune serum are as the positive control (PC) and negative control (NC), respectively. Bars represents 10 μm.
-
Neutralization assay was performed to test the neutralizing effect of 38F10 and 44D11. vHaBac-egfp was pre-incubated with 38F10, 44D11 and two control antibodies pre-immune serum as negative controls and anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody as a positive control, respectively, before infection into HzAM1 cells. Anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody could neutralize the vHaBac-egfp infection in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3A and 3C), which is consistent with our previous results (Wang et al., 2014). 44D11 could also neutralize virus infection in a dose dependent manner, with over 98% virus infection being inhibited in the presence of 0.5 μg mAb per well (Figure 3B and 3D); In contrast, 38F10 and pre-immune serum did not show obvious neutralizing effect even in the high antibody concentration (Figure 3B and 3D). Therefore, 44D11, but not 38F10, is a neutralizing mAb against HearNPV infection.
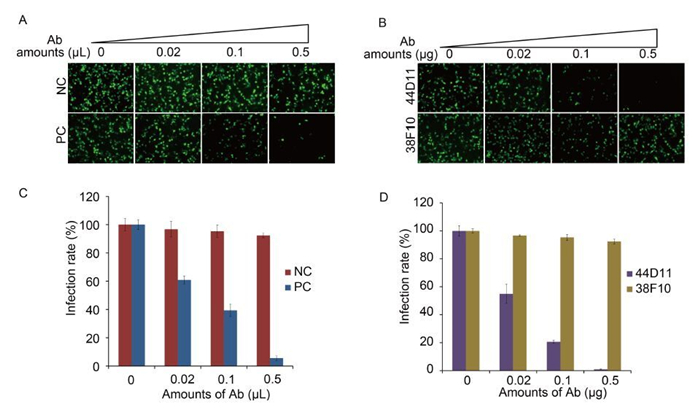
Figure 3. Neutralization assay. vHaBac-egfp (MOI = 5 TCID50 units/cell) was incubated with 44D11, 38F10, anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody (PC) or pre-immune serum (NC) for 1 h at 25 ℃ and then the virus-antibody mixture was added to the HzAM1 cells for 2 h incubation at 4 ℃. 24 h p.i., cells were detected by fluorescence microscopy (A and B) and FACS (C and D) (original magnification, 100×).
-
To further characterize the mode of action of 44D11, we analyzed whether this mAb can inhibit receptor binding and (or) membrane fusion, two major steps mediated by F proteins during baculovirus entry. A previous constructed recombinant virus vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64 contains a fusion-disabled HaF, only retaining the binding function of the F protein (Wang et al., 2014). Therefore, this virus was used in a neutralization assay. Consistent with our previous results, the neutralization assay showed that anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody significantly inhibited the infection of vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64 (F = 64.286, LSD-t = 9.776, P < 0.001) (Figure 4A) (Wang et al., 2014). In contrast, 44D11 didn't exhibit an obvious neutralizing effect on this virus (F = 64.286, LSD-t = 0.087, P = 0.931) (Figure 4A). This result suggested that 44D11 was not against the receptor binding domain within HaF2.
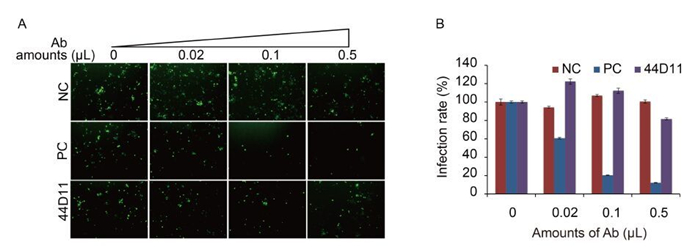
Figure 4. The neutralization mechanism of 44D11. vHaBacΔF-HaFdef-gp64 (MOI = 20 TCID50 units/cell) was incubated with 44D11, anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody (PC) or pre-immune serum (NC) for 1 h at 25℃, and then virus-antibody mixture was incubated with HzAM1 cells for 2 h at 4℃. At 48 h p.i., cells were detected by fluorescence microscopy (A) and FACS (B) (original magnification, 100×). The experiments were repeated twice.
The HaF protein mediates cell-to-cell fusion upon low-pH induction when it is expressed on the plasma membrane (Wang et al., 2008). We therefore wondered whether 44D11 could inhibit syncytium formation when added to the virus infected cells before low-pH triggering. As shown in Figure 5, in cells incubated with pre-immune serum, obvious syncytia with multi-nuclear cells were observed. Addition of 44D11 or anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody, but not the non-neutralizing mAb 38F10, could almost completely inhibit syncytium formation. Taking together the existing data, mAb 44D11 could inhibit membrane fusion rather than virus binding process.
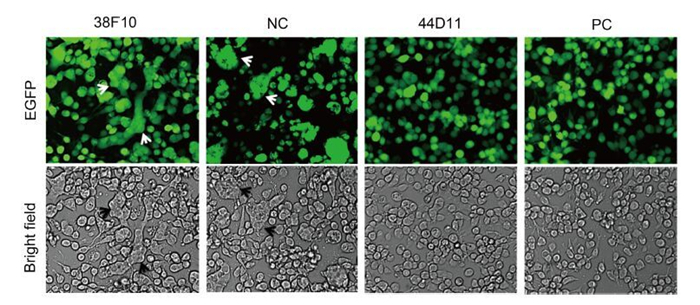
Figure 5. Syncytium formation inhibition assay. HzAM1 was infected with vHaBac-egfp at an MOI of 5 TCID50 units/cell. At 48 h p.i., cells were incubated with the 44D11, 38F10, anti-HaF2 polyclonal antibody (PC) or pre-immune serum (NC) for 2 h then triggered with pH 4.8 Grace's insect medium for 5 min (original magnification, 200×). Arrows indicated the multinuclear syncytia.
Generation and epitope mapping of mAbs against HaF2
Both 38F10 and 44D11 recognize native F protein during HearNPV infection
44D11 neutralizes the infection of HearNPV
44D11 recognizes a region within HaF2 involved in membrane fusion
-
Monoclonal antibodies represent a useful tool for the study ofvirus-host interaction, as well as for the development of promising therapeutic agents. In the past decades, a sweet of mAbs against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), influenza virus, herpesvirus, hepatitis C virus, Ebola virus, dengue virus, etc. has been described. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the generation and characterization of mAbs against baculovirus F protein, the major viral EFP essential for baculovirus entry into host cells.
Since a previous study showed that the F2 subunit of HearNPV contains important regions involved in virus binding and fusion, we decided to generate mAbs against some specific domains (Wang et al., 2014). Fourteen mAbs were produced and the epitope mapping was conducted against truncated HaF2 protein by Western analysis. HaF2 was first dissected into 4 overlapping peptide fragments, which were used for an initial round of screening. Two (38F10 and 39E9) out of the fourteen mAbs reacted with both F2 (47-123) and F2 (85-148), suggesting that they recognize a linear sequence (85-123aa) in the middle region of HaF2 (Figure 1E and 1F). In contrast, 44D11 and the remaining 11 mAbs clearly showed specific binding to the C-terminal fragment (129-173aa) of HaF2 (Figure 1G). In the second round of screening, the epitope regions of these 12 mAbs were further positioned between 48-173aa, the C-terminal end of HaF2 (Figure 1B). 38F10 and 44D11, as the representatives of the two different kinds of mAbs, were chosen for further investigation.
The ability of 38F10 and 44D11 to recognize native F protein in HearNPV-infected cells suggested that both region 85-123aa and 148-173aa might be naturally exposed on the surface of HaF protein (Figure 2 and Figure 6). However, only 44D11 showed virus-neutralizing activity (Figure 3). Neutralizing mAbs have the ability to neutralize virions via recognition of viral surface proteins essential for binding or fusion/entry of virus into host cells. A well-studied example is the neutralization of HIV by mAbs that inhibit the binding of gp120 to the CD4 receptor (Wibmer et al., 2015). Other mAbs that neutralize flaviviruses (He et al., 1995), rhinovirus (Smith et al., 1993), and papillomavirus (Booy et al., 1998), Newcastle disease virus (Iorio et al., 1989) may also by inhibiting cell attachment. For enveloped viruses, many mAbs have been identified to inhibit fusion between virus envelope with host membranes, as represented by two commercial mAbs Fuzeon (Enfuvirtide, T20) (Fung and Guo, 2004) and Synagis (Palivizumab) (Johnson et al., 1997), which are against HIV gp41 and respiratory syncytium virus F protein, respectively.
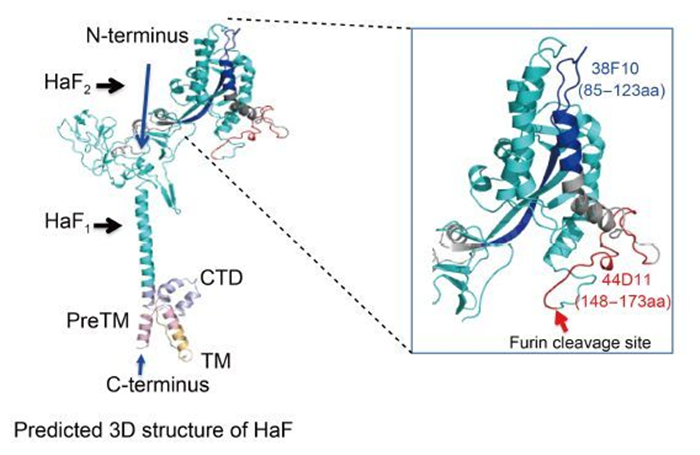
Figure 6. The recognition regions of the two mAbs in the predicted 3D structure of HaF. The predicted pre-fusion structure of HaF is presented on the left side. F2 subunit is colored by red, blue and gray and F1 subunit is shown in cyan. PreTM, TM and CTD are colored by light-pink, light-orange and light-blue, respectively. The N-terminus and C-terminus of HaF are indicated by blue arrowheads. The recognition regions of two mAbs are boxed. Right side represents an enlarged image of the boxed region. The recognition regions of 38F10, 44D11 are colored by blue and red, respectively. The furin cleavage site is indicated by a red arrowhead.
44D11 inhibited HearNPV infection probably via inhibiting the membrane fusion process during virus entry, since it significantly blocked low-pH induced cell-to-cell fusion mediated by F protein (Figure 5). The epitope of 44D11 localized to within the last 26 aa at the distal end of the C-terminus of HaF2, directly upstream of the fusion peptide at the N-terminus of HaF1 (Figure 6). For Class Ⅰ viral EFP, the fusion process is initiated by the exposure and insertion of the fusion peptide into the target host membrane. Single aa substitution at crucial residues within the fusion peptide of HaF and other baculovirus F proteins led to a significant reduction or even complete loss of fusogenicity (Westenberg et al., 2004; Tan et al., 2008). The binding of 44D11 to the C-terminus of HaF2 may thus result of sterichindrance of the release or membrane insertion of the fusion peptide. However, it is also possible that the nearby regions of the fusion peptide play a direct role in fusion process. There may exist another possibility that 44D11 is near to the N-glycosylation site (N104) within F2 subunit, which has been demonstrated to be crucial for HaF fusogenicity (Long et al., 2007). The detailed mechanism on how 44D11 inhibits membrane fusion of HaF needs further study.
In summary, we have characterized two different mAbs against the F2 subunit of the HearNPV F protein. Both of these can detect linear epitopes, which are likely exposed on the surface of the native F protein. 38F10 is a non-neutralizing mAb, while 44D11 is a neutralizing one inhibiting the fusion process. These mAbs provide valuable tools to further research the structure and function of baculovirus F proteins, as well as the F-mediated virus entry mechanism.
-
This work was supported by the grants from the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31370191 and 31621061), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant XDB11030400), and Open Research Fund Program of the Key Laboratory of Agricultural and Environmental Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. We acknowledge the Core Facility and Technical Support of Wuhan Institute of Virology for technical assistance. The authors would like to thank Dr. Xiulian Sun for the great help in statistical analysis.
-
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest. This study was approved of the Ethics Committee of Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
-
TZ, MW and ZH designed the experiments. ZZ, JL, ZW performed the experiments. ZZ, FD and HW analyzed the data. ZZ, ZH, MW and TZ wrote the paper. All the authors approved the final manuscript.













 DownLoad:
DownLoad: