HTML
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the etiological agent of COVID-19, has become a catastrophe to the entire mankind and society causing incalculable damage (Bai et al. 2020). Since its first outbreak in 2019, it has caused more than 188 million infections with over 4.06 million deaths until July 17, 2021, according to WHO (https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019), and those numbers are still rising (Yip et al. 2020). As a global pandemic, SARS-CoV-2 has become the focus of researchers. Efforts are being made to find effective drugs and therapeutics to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2 as much as possible.
As a member of the Nidovirales order in the Coronaviridae family, SARS-CoV-2 is one of the largest positive-stranded RNA viruses with an approximately 30 kb genome in length with a 5′ cap and a 3′ poly A tail (Wang et al. 2020; Clark et al. 2021). The ORF1a and ORF1ab locate in the 5′ terminal viral genomes coding for polyproteins, including pp1a and pp1ab by ribosome shifting, and then the proteases hydrolyze and cleave polyproteins into 16 distinct nonstructural proteins (nsps) (Al-Qaaneh et al. 2021). The nsps that participate in viral genome replication and transcription are essential for the survival of the SARS-CoV-2. The nsps related to viral pathogenesis would stimulate effective immune responses, which were potential vaccine candidates (Ong et al. 2020). For example, 142 T cell epitopes were mapped across the SARS-CoV-2 genome, and 6 from the nsp2 (Mateus et al. 2020).
The unknown structure and function of nsp2 have hindered our understanding of its role in SARS-CoV-2 infection. The study of viral-host protein interaction found that SARS-CoV nsp2 could interact with host proteins widely including prohibitin 1 (PHB1) and PHB2, which were implicated in a number of cellular functions, including cellular migration, differentiation, apoptosis, and so on (von Brunn et al. 2007; Cornillez-Ty et al. 2009; Justo Arevalo et al. 2021). Deletions of the nsp2 in MHV and SARS-CoV resulted in attenuating of viral growth and RNA synthesis, but not death (Graham et al. 2005). Although nsp2 exists in SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), there are relatively large sequence differences among three coronavirus pathogens that have posed great threats to human health (Singh et al. 2020). Sequence alignment found that the identity of nsp2 between SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV was 76.8%, while between SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV was 24.2% (Supplementary Fig. S1). Mutation and evolutionary analysis of SARS-CoV-2 revealed that nsp2 Thr85Ile reached a high frequency in North America (> 60%) in March 2020. But no structural information is available to determine the specific function of this site (Zhao et al. 2020). What role nsp2 plays in the process of SARS-CoV-2 infection remains to be explored. The acquisition of high-resolution structures is an effective and critical method in understanding the function of SARS-CoV-2 nsp2.
Here, we report the high-resolution crystal structure of the N-terminal of SARS-CoV-2 nsp2 with a resolution of 1.96 Å. The structure consists of three zinc fingers (ZnFs). The large area of positive charge on the surface and experiments reveal the ability of binding with nucleic acids. Residues K111, K112, and K113 are key sites for binding nucleic acids. Combined with the structure, the epitopes might be mapped better to understand the immune responses to SARS-CoV2 and possible implications for vaccines.
-
The full-length gene SARS-CoV-2 nsp2 (nsp2full-length) of 638 amino acid residues was obtained from Prof. Bo Zhang (Wuhan Institute of Virology, Chinese Academy of Sciences). Construct of nsp2full-length was subcloned into the EcoR I/Kpn I sites of a modified pPICZ expression vector with a C-terminal GFP-6 × His tag under the AOX1 promoter for eukaryotic expression. The plasmids were transformed into P. pastoris X-33 cells. The expression was detected by GFP fluorescence in a small scale. After screening the strains with high expression, they were cultured in BMM medium (100 mmol/L potassium phosphate pH 6.0, 1.34% YNB, 1% methanol) at 28 ℃ for 72 h, and methanol was added every 24 h.
Using nsp2full-length as a template, the N-terminal of 276 amino acid residues (nsp21-276) was inserted into pGEX expression vector (Novagen). The mutant of nsp21-276 was created using site-directed mutagenesis and verified by DNA sequencing. The GST fusion tags are cut from the nsp21-276 constructs by a tobacco etch virus (TEV) protease cleavage site. The plasmids were transformed into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells. Cells were incubated in Luria–Bertani medium at 37 ℃ until the OD600 reached 0.8–1.0 and then supplemented with 100 μmol/L ZnCl2, meanwhile induced with 0.2 mmol/L isopropyl-D-thiogalactoside for an additional 12 h at 18 ℃.
-
Both yeast and E. coli cultures were harvested by centrifugation at 4,000 ×g for 10 min at 4 ℃, and resuspended in a lysis buffer (20 mmol/L Tris pH 7.5, 500 mmol/L NaCl, 2 mmol/L β-mercaptoethanol, 5% glycerol, 30 mmol/L imidazole), then added with 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100 and 1 mmol/L PMSF (Invitrogen). Cells were disrupted by high pressure (1,800 bar, P. pastoris) or sonication (E. coli), then clarified by centrifugation at 18,300 ×g for 45 min to remove cell debris. The supernatant was applied to a Ni2+-chelating column or GST affinity column (GE Healthcare). The GFP or GST fusion tag of the proteins was cleaved using TEV protease at 4 ℃ for 6–8 h. The protein sample was then loaded onto a Q Sepharose (GE Healthcare), and eluted with a NaCl gradient. The proteins were further purified by size exclusion chromatography using Superdex 200 10/300, (GE Healthcare) in SEC buffer (20 mmol/L Tris pH 7.5, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 2 mmol/L TCEP). The peak fractions were collected and checked by SDS-PAGE (Fig. 1A). The protein with a purity of 95% was concentrated to 5.5 mg/mL and stored at 4 ℃ for further use.

Figure 1. The overall structure of nsp2. A. The nsp21-276, nsp2full-length, and nsp21-276 mutant1 (K111A/K112A/K113A) samples after size exclusion chromatography purification, respectively. B The overall structure of nsp21-276 consists of four chains in the asymmetric unit. A, B, C, D four chains are shown in pink, yellow-orange, cyan, and green, respectively. C The stereo structure of nsp21-276. The α-helices and β-sheets are colored cyan and magenta, respectively, and the three zinc atoms are shown as red, blue, and yellow spheres, respectively. The diagram of Zn2+ binding site is illustrated under the stereo structure of nsp21-276.
-
Initial crystal screening was performed at 4 ℃ with multiple commercial screens (Hampton Research). Using the sitting-drop vapor diffusion method, 1 μL of purified protein was mixed with 1 μL reservoir solution in 48-well plates. Initial nsp21-276 crystals were grown in a reservoir solution containing 20% PEG 8000, 0.1 mol/L HEPES pH 7.0 at 4 ℃. Unfortunately, the crystal of nsp2full-length was not obtained after many attempts. Crystals of nsp21-276 were further refined by the hanging-drop vapor diffusion method, and the protein was mixed with reservoir solution in different volume ratios.
After precipitant concentration and pH optimized, well-diffracted crystals were finally obtained in 18% PEG 8000, 0.1 mol/L HEPES pH 7.5 at a 2.5:2 (v/v, protein/reservoir solution) at 4 ℃ (Supplementary Fig. S2A, S2B). The crystals were flash-cooled in liquid nitrogen in mother liquor containing 20% glycerol as a cryoprotectant. Data were collected on beamlines BL17U1 at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF). Data were indexed, integrated, and scaled by autoPROC and XDS (Yu et al. 2019). The statistics are summarized in Table 1.
Parameters Value Data collection Wavelength (Å) 0.9793 Space group P21 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 57.93, 159.6, 63.55 α, β, γ (°) 90, 91.2, 90 Resolution (Å)a 50.0–1.96 (2.06–1.96) I/σ 17.9 (2.7) Rmerge 0.062 (0.673) Completeness (%) 99.8 (99.7) Total No. of reflections 555, 159 Unique reflections 82, 763 Redundancy 6.7 (5.8) Refinement Resolution (Å) 50.0–1.96 No. of reflections 75, 133 Rwork/Rfree (%) 19.97/22.56 No. of atoms Protein 8406 Ligand/ion 18 Water 925 B-factors (Å2) Protein 34.26 Ligand/ion 39.12 Water 42.08 r.m.s. deviationsb Bond lengths (Å) 0.003 Bond angles (º) 1.29 Ramachandran Plot (%)c 96.8/3.2/0.0 aStatistics for highest resolution shell.
bRoot mean square deviations
cResidues in favored, allowed, and outlier regions of the Ramachandran plot.Table 1. Data collection and refinement statistics of SARS-CoV-2 nsp21-276 (PDB: 7EXM)
-
The structure of nsp21-276 was solved by the single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) method. The anomalous signals in the data were strong as analyzed by SHELX C program (Sheldrick 2008), indicating the existence of zinc atoms. There initial Zn sites were found by the program SHELX D with a CCweak/CCall of 20.8/28.9 in space group P21. Twelve initial Zn sites were found and the phases were generated. The crude partial model with 19 β-sheets and 27 α-helices in 787 residues was built by program SHELEX E and figure of merit reached 0.626 (Sheldrick 2008). The initial model was further adjusted by manual model building using COOT (Emsley et al. 2010) and refinement using REFMAC5 (Murshudov et al. 2011). The structure was refined finally to 1.96 Å resolution with an Rwork of 19.97% and an Rfree of 22.56%.
-
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) data were performed at the beamline BL19U2 of the SSRF. Briefly, proteins were subjected to size exclusion chromatography with buffer (20 mmol/L HEPES pH 7.5, 150 mmol/L NaCl). Various concentrations of protein samples were tested, and the data were collected at 1.03 Å with 20 frames and a distance of 1 m from the detector. Individual data were used to process by using Software RAW (Nielsen et al. 2009). The scattering data from the buffer alone were measured before and after each sample, and the average of the scattering data before and after each sample was used for background subtraction. The scattering data and the structure PDB file for fitting were submitted to the FoXS online server (http://modbase.compbio.ucsf.edu/foxs/) (Pelikan et al. 2009).
-
Single or double-stranded DNAs (ssDNA or dsDNA) were used for EMSA. The ssDNA sequence is: 5'-GATGTGATTTTAATAGCTTCTTAGGAGAATGACAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA-3', which is similar to the 3'-UTR RNA sequence of SARS-COV-2. Double-stranded DNAs were prepared by annealing two oligonucleotides (the above ssDNA and its complementary DNA) slowly. In short, the mixture of the two complementary oligos was incubated at 95 ℃ for 5 min and then annealed two degrees per minute to 4 ℃. Different amounts of full length and nsp21-276 were incubated with 5 μmol/L ssDNA or dsDNA in a 20 μL reaction volume for 2 h at 25 ℃ and the mixture was then separated on a 6% native polyacrylamide gel in 1 × TG buffer (45 mmol/L Tris pH 8.0, 45 mmol/L glycine pH 8.9) and 1 × TB buffer (45 mmol/L Tris pH 8.0, 45 mmol/L boric acid, pH 8.0) at 180 V for about 45 min, respectively. The incubation molar ratios of full length and nsp21-276 to nucleic acid were shown in the figures. In order to investigate whether the zinc finger structures were involved in interacting nucleic acid, the zinc ions of nsp21-276 were chelated with gradient EDTA concentration (0–200 mmol/L). The nsp21-276 mutant 1 (K111A/K112A/K113A) was incubated with DNA at a 15:1 molar ratio to study the effect of residues K111, K112, and K113 on binding nucleic acids. The DNAs were visualized by staining with GelRed.
Protein Expression
Protein Purification
Crystallization and Data Collection
Structural Determination
SAXS Experiments
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays (EMSA)
-
Since the full-length nsp2 didn't get crystals eventually, we tried to express a series of truncated nsp2 proteins. After many attempts, only one fragment of nsp2 (residues 1–276) was finally obtained crystals. After crystal screening and optimization, well-diffracted crystals were acquired at 4 ℃ (Supplementary Fig. S2). The expressions of nsp21-276 and nsp2full-length proteins are shown in Fig. 1A. By SAD method and manual model building in COOT combined with refinement in REFMAC5, the final nsp21-276 structure in the space group P21 was refined to 1.96 Å resolution with an Rwork of 19.97% and an Rfree of 22.56% (Table 1).
The structure of nsp21-276 consists of four chains in the asymmetric unit and the overall conformation looks like a four-leaf clover (Fig. 1B). Chain A is symmetric to chain B, and chain C is symmetric to chain D. Each chain contains ten α-helices (α1–α10) and fourteen β-sheets (β1–β14) with three ZnFs to form a complete domain (Fig. 1C). Each chain binds three zinc atoms, arranged in symmetrical triangles.
The side chains of Cys20 in α1, Cys51, His54, and His56 in the loop coordinate the zinc ion Zn1 within a stable fold to form the classical C2H2 zinc finger structure (ZnF1) (Eom et al. 2016) (Fig. 2A). The ZnF2 coordinated by the Cys143, Cys146, Cys161, and Cys165 belongs to a C4 type zinc finger, and four reversed β-sheets form a clamped structure with zinc ions Zn2 nested inside (Fig. 2B). Zn3 ion is tetrahedrally coordinated by three cysteines (C190, C193, C236) in β11, α8, and β13 respectively, and one histidine H202 in loop to form a C2HC type ZnF (Fig. 2C, 2D).
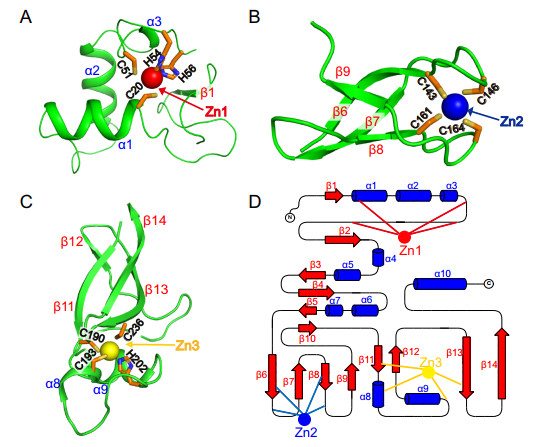
Figure 2. Close-up view of three zinc finger structures. A The first Zn1 ion (red) is engaged by residues C20, C51, H54, and H56. B The second Zn2 ion (blue) is engaged by residues C143, C146, C161, and C164. C The third Zn3 ion (yellow) is engaged by residues C190, C193, H202, and C236. All the residues are the same color (C, orange; N, blue; S, yellow; O, red). D The topology of these three zinc fingers. Blue cylinders and red arrows represent helices and β-sheets, respectively.
-
It is worth exploring whether the oligomeric state of nsp21-276 in solution is monomer or tetramer since the overall structure consists of four chains. We have performed gel filtration analyses and SAXS experiments to analyze the oligomeric states of nsp21-276 in solution. The single peak in the size exclusion chromatography suggests that it is a monomer in solution (Fig. 3A). Furthermore, SAXS results also indicated that monomer fitted best in solution, while tetramer fitted worse (Fig. 3B, 3C). SAXS data and analysis are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Therefore, four nsp21-276 solved in the asymmetric unit were not analyzed because it was formed by crystal packing.
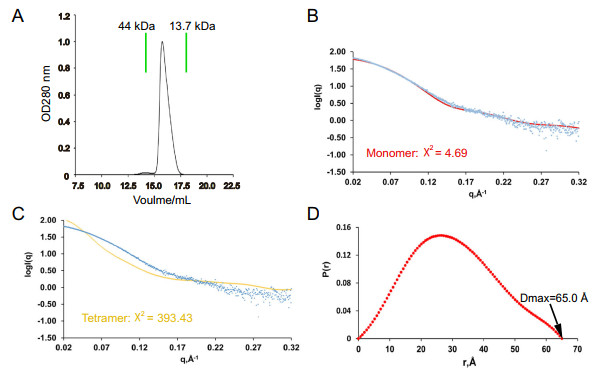
Figure 3. The oligomeric analyses of nsp21-276 in solution. A Size exclusion chromatography of nsp21-276 on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column (GE Healthcare). The theoretical scattering curves of monomer (B, red) and tetramer (C, yellow) are shown. Experimental data are represented by blue dots. D Pair distance distribution P(r) of nsp21-276.
-
Numerous studies have reported that ZnF containing proteins are generally involved in protein–protein, protein-DNA, and protein-RNA interactions (Eom et al. 2016; Sulej 2019). To the best of our knowledge, the biochemical function of nsp2 is unknown. To uncover it, we performed structural analysis. There is a large positively charged region on the electrostatic surface of nsp2 (Fig. 4A). Thus, we hypothesized that the positively charged region on the surface of nsp2 was involved in binding nucleic acids. Since nsp2 may not only participate in the viral replication and transcription, but also affect the host genome to inhibit the synthesis of host protein. We speculated that nsp2 might interact with ssDNA or dsDNA. EMSA assay showed that both full-length and nsp21-276 could bind ssDNA or dsDNA, and the higher the protein concentration, the more obvious the complex band was (Fig. 5A–5D). Interestingly, ZnF1, ZnF2, and ZnF3 are not the most positively charged regions (Fig. 4B). Thus we used different concentrations of EDTA (0–200 mmol/L) to chelate Zn2+ ions to destroy the ZnF structures, and found that 200 mmol/L EDTA still could not affect the interaction of protein and DNA (Fig. 5E). The result shows that the three zinc fingers are not involved in binding nucleic acids directly. Meanwhile, we find three positively charged lysines (K111/K112/K113) located in a prominent position (Fig. 4A). No complex bands were observed when three successive positively charged lysine (K111/K112/K113) were mutated into uncharged alanine (Fig. 5F). Therefore, we can conclude that the interaction of nsp2 and nucleic acid depends on the large region of the positively charged surface, and residues K111, K112, and K113 are key sites.
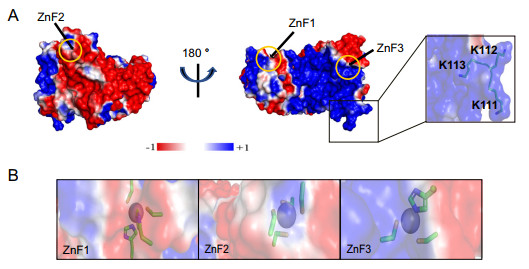
Figure 4. Nsp2 has a large positive surface. A The electrostatic surface of nsp2 (red, negatively charged; white, non-polar; blue, positively charged). Residues K111, K112, and K113 are shown particularly. B Emphasized charged details of three zinc finger structures (ZnF1, ZnF2, and ZnF3) by the electrostatic surface. Residues involved in binding Zn2+ are shown as stick models (C, orange; N, blue; S, yellow; O, red).
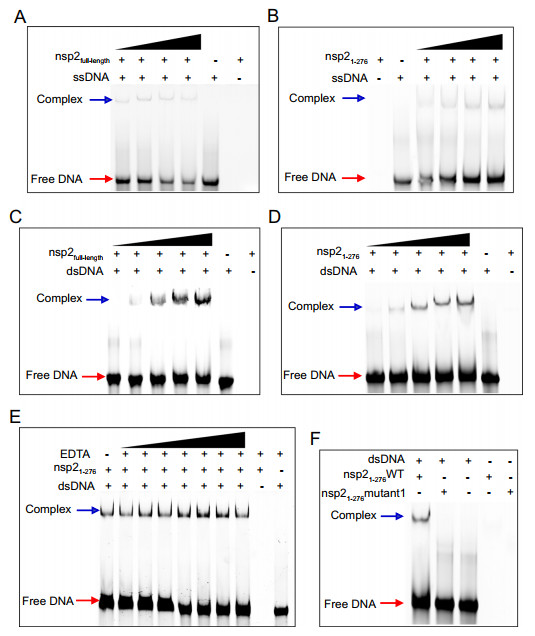
Figure 5. The binding of nsp2 to DNA. 5 μmol/L 65 nt ssDNA binds to nsp2full-length (A) and nsp21-276 (B) with different concentrations (25, 50, 100, and 150 μmol/L). Positions of free DNA and protein-bound DNA are indicated by red and blue arrows, respectively. 5 μmol/L 65 bp dsDNA binds to nsp2full-length (C) and nsp21-276 (D) with different concentration (15, 25, 50, 75, and 100 μmol/L). E 5 μmol/L 65 bp dsDNA binds to 15 μmol/L nsp21-276 in the presence of different concentration of EDTA (5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 150, 200 mmol/L). F 5 μmol/L 65 bp dsDNA binds to 75 μmol/L nsp21-276 wild type (WT) and 75 μmol/L nsp21-276 mutant1 (K111A/K112A/K113A), respectively.
The Overall Structure of nsp2 N-Terminus Reveals a Novel Zinc Finger Domain
The Oligomeric State of nsp21-276 in Solution
K111, K112, and K113 Are Key Residues for Binding Nucleic Acids
-
The continued spread of SARS-CoV-2 has presented a global health challenge confronting the entire international community. Coupled with rapid mutation, it has been a serious threat to human life and health (Shu et al. 2020). In addition to the development and promotion of vaccines, a better understanding of how SARS-CoV-2 reproduces and the discovery of potential antiviral targets are urgently needed. Non-structural proteins, as important targets for drug development, play key roles in the replication and transcription of the virus. Nevertheless, the unknown structure and function of nsp2 impeded our understanding of SARS-CoV-2.
Although we have obtained full-length proteins with high purity, it is regrettable that we have not obtained crystals through a large number of crystallization tests (Fig. 1A). Here we present the first high-resolution crystal structure of nsp21-276 at 1.96 Å resolution. The overall structure has four protein molecules in an asymmetric unit (Fig. 1B). Interestingly, the gel filtration analyses and SAXS experiment indicated that the oligomeric state of nsp21-276 is monomeric in solution (Fig. 3). The superposition of the four chains reveals some slight differences at the ends with a root mean squared deviation (RMSD) of ~ 1.0 Å between each chains (Supplementary Fig. S3). This is mainly due to conformational flexibility in solution.
There is a large positively charged region on the surface (Fig. 4A). Structural analysis and EMSA results confirmed that nsp2full-length and nsp21-276 could bind to ssDNA or dsDNA (Fig. 5A–5D) and high concentrations of EDTA could not destroy this interaction (Fig. 5E). Furthermore, we found three positively charged lysines located in a prominent position (Fig. 4A). Mutation of lysine to alanine completely lost their ability to interact with nucleic acids (Fig. 5F). These results indicate that the interaction of nsp2 and nucleic acid is mainly dependent on the positively charged region on the surface, and K111, K112, K113 are key residues. However, the binding affinity of nsp2 to ssDNA or dsDNA was not high in our experiments. Other substrate RNA, the addition of other SARS-COV-2 or host proteins might improve the binding, and needs further study to confirm.
When we were submitting our manuscript, another group released two Cryo-EM structures (PDB: 7MSW and 7MSX) at 3.76 Å and 3.15 Å, respectively (Gupta et al. 2021). A quick comparison with our structure indicates that the N-terminal ZnF is similar with a RMSD of 1.3 (Supplementary Fig. S4A). In addition, the RMSD of ZnF1, ZnF2, and ZnF3 between these two structures are 0.7 Å, 0.5 Å, and 1.1 Å, respectively (Supplementary Fig. S4B-S4D). But there are some differences. Our high-resolution X-ray structure might provide more details, such as the geometry, coordination and distance of ZnFs. A DALI search (Holm and Rosenström 2010) of the overall X-ray nsp21-276 structure found no similar structure in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) except for the EM structure of nsp2, indicating that overall nsp21-276 structure appeared to be a novel folding type.
Then these three ZnF structures of nsp21-276 caught our attention, and they belonged to C2H2, C4, and C2HC types, respectively. Structural analysis and mutagenesis results indicated that they did not play important roles in binding nucleic acids. These three ZnF domains may play other unknown functions. To explore the function, we submitted three ZnFs to the DALI server to search for structurally similar proteins. ZnF1 is similar to the protein serine/threonine phosphatase 2C (PDB: 1A6Q) with an RMSD of 2.6 Å, which is essential for regulating cellular stress responses in eukaryotes (Das et al. 1996) (Supplementary Fig. S5A). This ZnF fold is also similar to the eukaryotic DNA transposase (PDB: 2BW3) with an RMSD of 3.0 Å (Hickman et al. 2005) (Supplementary Fig. S5B). These indicated that nsp2 might interact with host genomes to be involved in regulating intracellular signaling pathways. These two structures are similar to ZnF1 of nsp2, but both lack zinc ions. Furthermore, ZnF2 is similar to the 50S ribosomal protein L44E (PDB: 1S72) with a RMSD of 1.8 Å, and four cysteines are highly conserved (Klein et al. 2004) (Supplementary Fig. S5C). Recently, it has been reported that nsp1 and nsp2 prevent the entry of cellular mRNA into ribosomes, and accelerate cellular mRNA degradation to inhibit the synthesis of host protein in cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 (Finkel et al. 2021). This process may be related to the ZnF2 of nsp2. In addition, ZnF3 is similar to the RNAi polymerase from Neurospora crassa (PDB: 2J7N) with RMSD of 2.4 Å, which is related to RNA silencing and regulation of gene expression (Salgado et al. 2006) (Supplementary Fig. S5D). Moreover, cysteines and histidines that coordinated ZnF2 and ZnF3 are highly conserved according to sequence alignment of nsp21-276 between SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV (Supplementary Fig. S1). This indicated that these two ZnFs are important in the evolution of viruses.
Previous studies have reported that the deletion of SARS-CoV nsp2 leads to attenuation of viral growth and RNA synthesis. By analysis of protein-protein interactions and involvement of viral proteins in SARS-CoV replication, nsp2 can interact with nsp7, nsp8, and other viral non-structural proteins (von Brunn et al. 2007; Pan et al. 2008). It is speculated that nsp2 can assist the formation of replication-transcription complex (RTC) and participate in viral replication and transcription, which needs further study to confirm. The structures of N-terminal nsp2 are the first step to a comprehensive understanding of the structure-function relationship of SARS-CoV-2 nsp2. Our findings, responding to the global pandemic, SARS-CoV-2, are significant to make full use of nsp2 as further research and development of antiviral targets and drug design.
-
We would like to thank the staff of beamlines BL17U1 and BL19U2 at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility for the excellent technical assistance. We thank Prof. Dr. Bo Zhang for generously providing SARS-CoV-2 nsp2 gene. This work was supported financially by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFE0113100) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872713).
-
JM and ZC designed the experiments. JM, YC, WW, and ZC carried out the experiments. JM and ZC analyzed the data. JM wrote the paper. JM, YC, and ZC checked and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
-
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
-
Final refined coordinates and structure factors have been deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) under accession code 7EXM.
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: