-
The genus Capripoxvirus within the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae, family Poxiviridae comprises three closely related viruses, namely lumpy skin disease (LSD), sheeppox (SP) and goatpox (GP) viruses. This nomenclature is based on the animal species from which the virus was first isolated, respectively, cattle, sheep and goat. These viruses are the etiological agents of economically important diseases which collectively constitute the most serious poxvirus diseases of production animals [14]. Lumpy skin disease is an acute, subacute or inapparent viral disease of cattle characterized by pyrexia, generalized skin and internal pox lesions, and generalized lymphadenopathy [10, 23, 28]. The disease is endemic in Central and southern Africa.The first report of LSD outside Africa was from Kuwait in 1986-1988 [1], followed by Israel in 1989 [30]. In Egypt, the LSD was first appeared in the Suez Governorate after cattle were imported from Somalia followed by the Ismailyia Governorate in 1988 [18] and two disease outbreaks were reported in 2005 and 2006 [26, 36]. There were 2 outbreaks of LSD in Israel during 2006 and 2007 and it is believedbe transmitted by yet an unconfirmed insect vector from Egypt [31].
The LSDV genome is a linear dsDNA molecule of 151 kb that consists of a central coding region bounded by identical 2.4 inverted terminal repeats and contains 156 putative genes [32]. Capripoxviruses are antigenically indistinguishable from each other and able to induce heterologous cross protection and the complete nucleotide sequences of the capripoxvirus genomes are 97% similar [5, 9, 10, 33]. Although capripoxviruses are generally considered to be host specific, because disease outbreaks occur in one host species [14], it is known that SPV and GPV strains can naturally or experimentally cross-infect and cause disease in both host species [20, 21]. However, while LSDV can experimentally infect sheep and goats [4, 22], natural infection of sheep and goats with LSDV has not been described previously.
There have been reports of the occurrence of LSD outbreaks in Egypt and Israel and the presence of LSDV circulate in some farms although animals were vaccinated with sheep pox vaccine [2, 3] as well as the appearance of sheep pox cases in areas that are affected by LSD. Therefore we studied the antigenic correlationship between field skin isolates of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV/Ismailyia88 strains, field skin isolates of SPV and the SPV/Kenyan vaccinal strain. We also compared the nucleotide sequence of the attachment gene offield skin isolates of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV/Ismailyia88 strain, field skin isolates of SPV and SPV /Kenyan vaccinal strain to gain new insights into the biology and aid the development of new method of effective control of this disease.
HTML
-
A total of 15 skin nodules from clinically diseased cows that were suspected to be infected with lumpy skin disease (LSD) and 5 scab samples form clinically infected sheep that were suspected to be infected with sheep pox (SP) were collected from Dakahlia Governorate, Egypt. These infected sheep were in close contact with infected cows. Skin biopsies from four normal cows and two normal sheep were included as negative controls. Part of each samples was taken rapidly to the freezing chamber of a cryostat for IF testing. Another part was put in bottles containing neutral buffered formalin 10% for IP testing.
-
Tissue culture adapted LSDV/Ismailyia88 strain was kindly supplied from the Pox Vaccine Production and Research Department, Veterinary Serum and Vaccine Research Institute (VSVRI), Abbasia, Cairo, Egypt. It was prepared in Madian Darby Bovine Kidney (MDBK) and had a titre of 104.5 TCID50/mL. SPV/ Kenyan vaccinal strain was also obtained from the VSVRI, prepared in Vero cell line and had a titre of 104.5 TCID50/mL.
-
Sample preparation was performed as described elsewhere [4, 7] Specifically: LSDV/Ismailyia88 strain and SPV/ Kenyan vaccinal strain were purified through a 40%-60% sucrose gradient; Hyperimmunesera were prepared by the weekly inoculation of rabbits with purified viruses emulsified with equal volume of Freund's incomplete adjuvant subcutaneous, repeated 5 times. Then a final intravenous inoculation of 1 mL of the purified virus was performed. The rabbits were bled out ten days later and the hyperimmune serum was separated by centrifugation at 3000rpm/min for 10 min and kept at -20℃ until use.
-
The collected tissues were taken rapidly to the freezing chamber of a cryostat and left for 15 min at -30℃. Tissues were sectioned at 3 microns thickness using a cryostat knife and then transferred to slides. These sections were left to dry in air for 30 min, fixed with acetone for 10 min and then washed with PBS, pH 7.6. A few drops of 1:100 dilution of the prepared rabbit hyperimmune serum were added to the sections and the slides were kept in a humidified chamber for 1 h at 37℃. The slides were washed with PBS for 15 minutes 3 times then a few drops of 1:200 dilution of antirabbit FITC conjugate was added. After 1 h of incubation at 37℃ in the dark, the slides were thoroughly washed with PBS, and counterstained with Evan's blue stain. They were then mounted with buffered glycerin, covered with a cover slip and examined under a fluorescent microscope.
-
Formalin-fixed, paraffin embedded infected tissues were cut at 5 µm. Slides were heated at 55℃ to melt the paraffin, deparaffinized in xylol, hydrated through graded ethanols and finally rinsed in phosphate buffered saline. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by immersion in 3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 20 min. and then slides were incubated with blocking solution (10% FCS) for 30 min. Sections were incubated with diluted primary antibody (1:100) for 60 min at room temperature in a humid chamber. After washing with PBS 3 times, 10 min for each cycle the sections were incubated with 1:200 dilution of anti-rabbit horseraddish peroxidase (HRP) conjugate and incubated for 60 min at room temperature in a humid chamber. The slides were then washed and drops of diaminobenzidine (DAB) substrate solutions was added for 30 min. Sections were thoroughly washed under tap water and counterstained with hematoxylin. After this the reaction was detected under light microscope.
-
This was studied using prepared hyperimmune rabbit sera to LSDV/Ismailyia88 strain and SPV/ Kenyan vaccine strain against homologous and heterologous viruses by agar gel precipitation test (AGPT) that was performed as described previously [21] and reverse passive haemagglutination (RPHA) that was per-formed as described previously [25, 29]. Also immuno-flourescence test (IF) and immunoperoxidase test (IP) were used.
-
Oligonucleotide primers were designed [19] for amplification of the attachment gene of capripoxvirus. Oligonucleotide primers used in the PCR reactions were synthesized by Mthe etabion International AG Company, Germany. The primers were received in lyophilized form and resuspended in Tris/EDTA (TE) buffer to reach a final concentration of 100 pmol/µL and were designed to amplify a specific segment of 192 bp. The primers sequences for PCR amplification were as follows: forward primer, 5x-TTTCCTGATTT TTCTTACTAT-3x and reverse primer, 5x-AAATTAT ATACG TAAATAAC -3'.
-
DNA extraction was done [34] using0.5 mL of virus suspension digested with 20 µL Proteinase K (final concentration, 100μg/mL) at 56℃ for 2 h. 100 µL Phenol: Chloroform: Isoamylalcohol (25:24:1) was added and mixed by inversion then centrifuged at 13 000 r/min for 5 min then the upper aqueous layer was transferred to a clean microcentrifuge tube and 2.5 volumes absolute ethanol and 1/10 volume of 5 mol/L sodium acetate (pH 5.3) were added and mixed thoroughly. The DNA was precipitated at -20℃ overnight and pelleted by centrifugation at high speed (13 000 r/min) for 15 minutes. The pellet was washed once with 70% ethanol and centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 10 min then air dried and resuspended in 50 µL TE buffer. Normal non-infected skin samples were included as a negative control sample
-
This was carried out as described previously [19]. Briefly, 10 µl sample of extracted genomic DNA was placed in 50 µl of the final volume of 10 × reaction mixture containing 50 mmol/L KCl, 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 1.5 mmol/L MgCl2, 200 mmol/L of each dNTP, 100 pmol of each oligonucleotide primer and 2 U Taq-DNA polymerase. Then 40 μL of mineral oil was added to prevent evaporation of components during thermocycling. The PCR had an initial cycle of 94℃ for 5 min, 50℃ for 30 s, 72℃ for 1 min followed by 34 cycles of 94℃ for 1 min, 50℃ for 30 s, 72℃ for 1 min and a final elongation step of 72℃ for 5 min.
-
This was carried out as described previously [34]. Briefly 10 µL of the PCR product was mixed with 1 μL 10×gel loading buffer and loaded to the individual wells of a 1.5% agarose gel. In addition, 2 µL of a 100 bp DNA molecular weight marker was loaded with 2 µL loading buffer in a single outside well to be used as DNA ladder. The amplified DNA products were detected in comparison with DNA ladder using the U.V. transilluminator. The gel was photographed.
-
Sequencing of the PCR amplicons were performed by JenaGen GmbH Biotechnologie-Gentechnik-Diagnostik (Jena, Germany) using the BigDye® Terminator v1.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit on a 3130 sequencer (Applied Biosystems).
-
The obtained data were analysed using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/), and then the alignment *.aln output file was used for performing the phylogeneticNeighbor-Joining (N-J) analysis with 1000 repeats of bootstrap tests analysis in MEGA 4.0.
Sample collection
Virus strains
Preparation of hyperimmune rabbit sera
Identification of causative agent
Indirect immunofluorescent antibody (IF) technique [13]
Indirect immunoperoxidase (IP) technique [15]
Antigenic correlationship of different strains
Amplification of the attachment gene
Oligonucleotide primers
DNA extraction
PCR amplification
Amplified product analysis
Nucleotide sequencing
Analysis of sequencing data
-
From 15 skin nodules suspected of LSD, 10 showed positive reaction and 3 out of 5 skin scabs suspected of sheeppox were found positive by IF and IP. None of the control samples (normal skin) showed a positive reaction.
-
The obtained results showed that using AGPT, there was identical reactions for field skin isolates of LSDV and LSDV/Imailyia88 strain, field skin isolates of SPV and Kenyan SPV vaccinal strain, and field skin isolates of LSDV and Kenyan SPV vaccinal strain against both LSDV/Ismailyia88 strain and Kenyan SPV hyperimmune sera as shown in Fig. 1. Using RPHA, the titre of LSDV virus was 26 with LSDV hyperimmune sera and 25 with Kenyan sheep poxvirus hyperimmune sera while the titre of SPV was 25with homologous and heterologous hyperimmune sera and the control sample gave a titre of 21. IF and IP tests showed a similar positive reaction with homologous and heterologous hyperimmune sera.
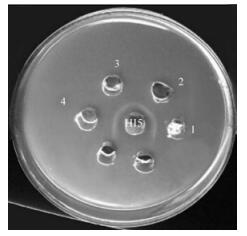
Figure 1. Agar gel precipitation test, showing identical reaction when using tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain) (well 1) and field skin isolate of LSDV (well2), Kenyan sheep poxvirus vaccinal strain (well3) and field skin isolate of sheep poxvirus (well4) against LSDV hyperimmune serum (HIS).
-
Analysis of the PCR products obtained from the amplification reaction of extracted DNA field skin isolate of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV/ Ismailyia88 strain, field skin isolate of SPV and Kenyan SPV vaccinal strain by agarose gel electrophoresis revealed the positive amplification of the attachment gene with correct size (192bp) (Fig. 2)
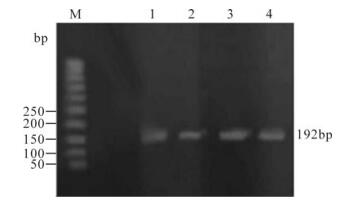
Figure 2. PCR products of the attachment gene (192bp) of different strains in stained agarose gel electrophoresis. M, DNA ladder; Lane 1, The amplified products prepared from tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain); 2, The amplified products prepared from field skin isolate of LSDV; 3, The amplified products prepared from SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain); 4, The amplified products prepared from field skin isolate of SPV.
-
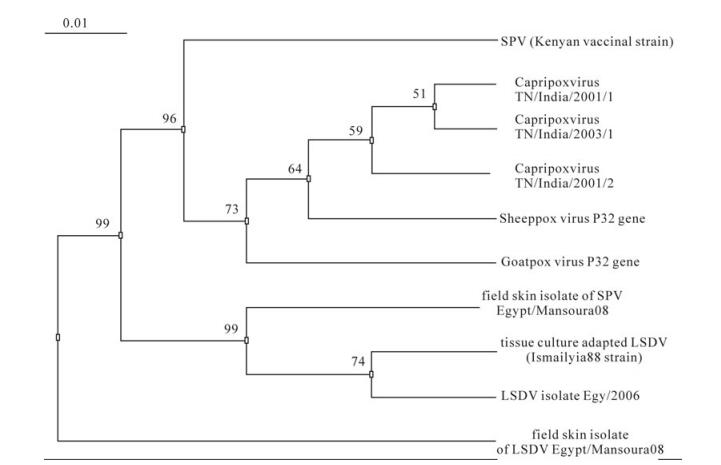
The obtained nucleotide sequence of 192 bp PCR fragments representing the whole attachment gene of LSDV isolate (Egypt/Mansoura08, accession no. GQ202146) and tissue culture adapted strain and SPV isolate (Egypt/Mansoura08, accession no. GQ202147) were analyzed and compared with the published sequences of capripoxviruses: LSDV isolate Egy/2006 attachment gene (accession no. EU807974), Capri-poxvirus TN/India/2001/1 (accession no. AY331145), Capripoxvirus TN/India/ 2001/2 (accession no. AY331146), Capripoxvirus TN/India/2003/1(accession no. AY331147), Sheeppox virus envelope protein P32 gene (accession no. AY368684) and Goatpox virus envelope protein P32 gene gene (accession no. AY382869). The multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences of field skin isolate of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain), SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) and field skin isolate of SPV with published sequences was created using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/).The multiple alignment revealed that field skin isolate of LSDV is found to be different from field skin isolate of LSDV, at 3 positions: 146 (G to T), 158 (A to T) and 159 (A to T), different from field skin isolates of SPV at 6 positions: 28 (C to G), 34 (A to T), 81 (A to T), 89 (G to A), 90 (G to A) and 91 (G to T) and differed from SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) at 44 positions. It was found that field skin isolate of SPV differed from SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) in 42 positions.
The field skin isolate of LSDV was showed to have 98.4% and 98.3% identity at the nucleotide level with tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain) and LSDV isolate Egy/2006, respectively. Also this LSDV isolate showed 96.8% and 83.8% identity with field skin isolate of SPV and SPV vaccinal strain respectively. The field skin isolate of SPV shared an average identity of 96.4% and 77.8% with the LSDV vaccinal strain and SPV vaccinal strain, respectively
The Phylogenetic tree pattern for the alignment is shown in Fig. 3.
Identification of causative agent
Antigenic correlationship of different strains
PCR amplification of attachment gene
Nucleotide sequencing of amplified attachment gene fragments
-
Capripoxviruses cause a severe and highly contagious disease in sheep, goats and cattle. LSDV and SPV belong to the genus Capripoxvirus, classified in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae of the Poxviridae family [6, 14]
LSD and SP need a rapid laboratorydiagnosis after being suspected. Following diagnosis of the disease, rapid performing of control measures such as slaughter, ring vaccination and movement restrictions are required to limit losses [6]. Herein the immunofluorecence and immunoperoxidase techniques used for detection of capripoxvirus in skin lesions serve as a rapid, effective and economic method for laboratory confirmation of disease. The use of these techniques for direct detection of virus reduce the dependence on tissue culture and the time required to isolate the virus which may delay disease control.
Sheep poxvirus (Kenyan strains) vaccination strategy was applied to control LSD in Egypt [24].Egyptian local isolate of LSDV was adapted in MDBK cell lines and used in production of LSD vaccine [8].
In the present study, antigenic correlation of field skin isolate of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain), SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) and field skin isolate of SPV using LSDV/ Ismailyia88 strain and Kenyan sheep pox virus (KSPV) hyperimmune rabbit sera using AGPT, RPHA, IF and IP tests revealed that these virus are antigenically identical and can not differentiated by serological tests. These findings are in agreement with the earlier reports [4, 11, 16, 35]which mentioned that there was an immunological relationship between LSDV and SPV and they can not be serologically distinguished.
Sequence analysis of amplified attachment gene of field skin isolate of LSDV, tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain), SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) and field skin isolate of SPV was carried out. Comparison of the sequences showed that field skin isolate of LSDV is more closely related to tissue culture adapted LSDV (Ismailyia88 strain) than to SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) with reference to attachment gene. This agrees with earlier reported results of the nucleotide sequencing of P32 gene that indicated goat poxvirus (GPV) and LSDV were more closely related than SPV was to LSDV [14]. So further study should be applied on the use of an LSD vaccine prepared from LSDV (rather than sheep pox vaccine) for the protection of cattle against LSD.
It was also found that field skin isolate of SPV is more closely related to the field skin isolate of LSDV than SPV (Kenyan vaccinal strain) with reference to the attachment gene, this may indicate that field skin isolate of SPV may be LSDV that changed its host to infect sheep. This results is in agreement with an earlier report [33] that found sheep and goat poxvirus are probably derived from a common ancestor LSDV, but this point need further study on the whole virus genome.
It is still required to establish a method to differentiate between infectious LSDV and its tissue culture adapted strains that may be used as a vaccine. This problem is particularly urgent because live attenuated vaccine protects animals from the disease but not from infection, therefore, vaccinated animals can be asymptomatic carriers [27].Thus, if a virus is detected in vaccinated animals, it is necessary to determine whether it belongs to a vaccinal or an infectious strain.














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: