专刊
-
 Special Topic on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 In less than two years, SARS-CoV-2 has infected over two hundred million people and caused about 4.8 million deaths worldwide. With global efforts, over 6.3 billion vaccine doses have been administered, which largely reduce the mortality and control the virus spread. Meanwhile, the academia has never stopped the exploration to advance our knowledge in combatting the virus. In this issue, Virologica Sinica presents a collection of original articles that report the latest research progress on SARS-CoV-2, including studies on long COVID-19, development of systems for drugs and vaccines, new strategies on surveillance and counter-measures. The cover shows the basic structure of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles.
Special Topic on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 In less than two years, SARS-CoV-2 has infected over two hundred million people and caused about 4.8 million deaths worldwide. With global efforts, over 6.3 billion vaccine doses have been administered, which largely reduce the mortality and control the virus spread. Meanwhile, the academia has never stopped the exploration to advance our knowledge in combatting the virus. In this issue, Virologica Sinica presents a collection of original articles that report the latest research progress on SARS-CoV-2, including studies on long COVID-19, development of systems for drugs and vaccines, new strategies on surveillance and counter-measures. The cover shows the basic structure of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles. -
 Special Issue: SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 (II) By the end of November 2020, SARS-CoV-2—the new coronavirus behind the disease COVID-19—has infected over 60 million people around the world and caused about one and a half million deaths. Facing the biggest global pandemic of the century, doctors, scientists and the scientific community have been working hard to uncover the pathogenesis and search for effective scientific solutions. Virologica Sinica has online published a series of original articles and reviews on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, covering topics on clinical cohorts/cases and disease features, virus characterization and surveillance, diagnosis and improved methods, antiviral agents and therapeutic treatment, and etc, and they are collectively presented in this special issue. Those researches have greatly advanced our understandings of and empowered our strength to combat the disease. The cover depicts the SARS-CoV-2 virus particle, surrounded by human blood cells.
Special Issue: SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 (II) By the end of November 2020, SARS-CoV-2—the new coronavirus behind the disease COVID-19—has infected over 60 million people around the world and caused about one and a half million deaths. Facing the biggest global pandemic of the century, doctors, scientists and the scientific community have been working hard to uncover the pathogenesis and search for effective scientific solutions. Virologica Sinica has online published a series of original articles and reviews on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, covering topics on clinical cohorts/cases and disease features, virus characterization and surveillance, diagnosis and improved methods, antiviral agents and therapeutic treatment, and etc, and they are collectively presented in this special issue. Those researches have greatly advanced our understandings of and empowered our strength to combat the disease. The cover depicts the SARS-CoV-2 virus particle, surrounded by human blood cells. -
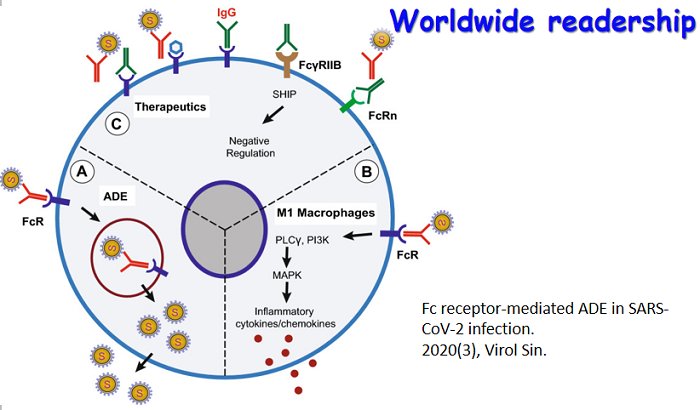
 SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 The ongoing outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a global public health emergency. The causative pathogen of COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), hits the humankind so sudden and brings tremendous challenges to the world. In combating against the COVID-19 pandemic, Virologica Sinica delicates this focused issue to timely present the latest scientific progress. Original reports on virus characterization, clinical features, inflammatory responses, infection models, detection methods, drugs and treatments, etc. are collectively included in the issue. The cover depicts the SARS-CoV-2 virus particle, surrounded by human blood cells.
SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 The ongoing outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has become a global public health emergency. The causative pathogen of COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), hits the humankind so sudden and brings tremendous challenges to the world. In combating against the COVID-19 pandemic, Virologica Sinica delicates this focused issue to timely present the latest scientific progress. Original reports on virus characterization, clinical features, inflammatory responses, infection models, detection methods, drugs and treatments, etc. are collectively included in the issue. The cover depicts the SARS-CoV-2 virus particle, surrounded by human blood cells. -
 Viral Pathogens in Natural Hosts and Vectors Over the past few years, a rising trend of emerging and virulent infectious diseases has been observed. Among the emerging viral infections, more than 75% are natural focal diseases. Natural focal viruses generally recycle in wild animals with relatively large populations as natural hosts, such as bats, rodents, and birds, and are transmitted by vectors such as ticks and mosquitoes that co-exist in the specific natural foci. A program for investigating the main natural hosts and vectors in China has been implemented from 2013 to 2017, which involves a team of researchers across twelve institutions in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Hubei, and Yunnan regions. This special issue collectively presents the interesting results generated from this program. We hope these articles will allow the readers to obtain a better understanding of the importance of investigating pathogen profiles in natural hosts and vectors, and to consider the potential risk of unknown pathogens to the public health. The cover is a gallery of photos which were captured by the team during the field investigation.
Viral Pathogens in Natural Hosts and Vectors Over the past few years, a rising trend of emerging and virulent infectious diseases has been observed. Among the emerging viral infections, more than 75% are natural focal diseases. Natural focal viruses generally recycle in wild animals with relatively large populations as natural hosts, such as bats, rodents, and birds, and are transmitted by vectors such as ticks and mosquitoes that co-exist in the specific natural foci. A program for investigating the main natural hosts and vectors in China has been implemented from 2013 to 2017, which involves a team of researchers across twelve institutions in Xinjiang, Qinghai, Hubei, and Yunnan regions. This special issue collectively presents the interesting results generated from this program. We hope these articles will allow the readers to obtain a better understanding of the importance of investigating pathogen profiles in natural hosts and vectors, and to consider the potential risk of unknown pathogens to the public health. The cover is a gallery of photos which were captured by the team during the field investigation. -
 Herpesviruses and Antiviral Strategies This special issue is dedicated to the recent research progress on human herpesviruses (HHVs). Human herpesviruses are distributed worldwide, and more than 90% of adults are infected by one or multiple HHVs. The HHV family contains three sub-families: the alpha sub-family [herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), HSV-2, and varicella-zoster virus (VZV)], beta sub-family [human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), HHV6, and HHV7)], and gamma sub-family. [Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma–associated herpesvirus (KSHV)]. All the viruses typically establish latent infection in host, and undergo lytic reactivation in certain pathophysiological conditions. In this issue, we collectively present ten articles focusing on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and interventions of HSV-1, VZV, HCMV, EBV and KSHV respectively, and these high-quality review and research articles are contributed by experts on those specific viruses.
Herpesviruses and Antiviral Strategies This special issue is dedicated to the recent research progress on human herpesviruses (HHVs). Human herpesviruses are distributed worldwide, and more than 90% of adults are infected by one or multiple HHVs. The HHV family contains three sub-families: the alpha sub-family [herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), HSV-2, and varicella-zoster virus (VZV)], beta sub-family [human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), HHV6, and HHV7)], and gamma sub-family. [Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma–associated herpesvirus (KSHV)]. All the viruses typically establish latent infection in host, and undergo lytic reactivation in certain pathophysiological conditions. In this issue, we collectively present ten articles focusing on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, and interventions of HSV-1, VZV, HCMV, EBV and KSHV respectively, and these high-quality review and research articles are contributed by experts on those specific viruses. -
 Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses Viral hemorrhagic fevers are caused by several distinct families of RNA and DNA viruses that can cause devastating disease in humans and other animals. Hemorrhagic fever viruses usually reside in animal or arthropod hosts and transmit to humans, resulting in human outbreak. Four major families of HFVs are Arenaviridae, Filoviridae, Bunyaviridae, and Flaviviridae. This special Issue presents the recent progress on Ebola virus, dengue virus, hantavirus, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, and covers topics on viral epidemiology, viral pathogenesis, and virus-host cell interaction of those hemorrhagic fever viruses. The cover depicts the hemorrhagic fever viruses and their major hosts.
Hemorrhagic Fever Viruses Viral hemorrhagic fevers are caused by several distinct families of RNA and DNA viruses that can cause devastating disease in humans and other animals. Hemorrhagic fever viruses usually reside in animal or arthropod hosts and transmit to humans, resulting in human outbreak. Four major families of HFVs are Arenaviridae, Filoviridae, Bunyaviridae, and Flaviviridae. This special Issue presents the recent progress on Ebola virus, dengue virus, hantavirus, Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus, and covers topics on viral epidemiology, viral pathogenesis, and virus-host cell interaction of those hemorrhagic fever viruses. The cover depicts the hemorrhagic fever viruses and their major hosts. -
 Coronaviruses Coronaviruses (CoVs) infect a wide range of vertebrates, including humans. They can cause respiratory, gastrointestinal, hepatic and central nervous system diseases. Some CoVs have managed to across the species barrier, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV. This special issue of Virologica Sinica is dedicated to the recent progress on coronaviruses and covers topics on viral epidemiology, virus replication and the interactions between the coronaviruses and their hosts. This updated information would provide new insights in the control of CoV infections, and in the development of effective antivirals. The cover depicts the modes of transmission of coronavirus from animals to humans.
Coronaviruses Coronaviruses (CoVs) infect a wide range of vertebrates, including humans. They can cause respiratory, gastrointestinal, hepatic and central nervous system diseases. Some CoVs have managed to across the species barrier, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)-CoV. This special issue of Virologica Sinica is dedicated to the recent progress on coronaviruses and covers topics on viral epidemiology, virus replication and the interactions between the coronaviruses and their hosts. This updated information would provide new insights in the control of CoV infections, and in the development of effective antivirals. The cover depicts the modes of transmission of coronavirus from animals to humans. -
 Oncogenic Viruses and Cancer Viruses are leading causes of different types of human cancers, accounting for about 20% of total cases. Seven viruses are currently considered oncogenic viruses, including hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein Barr virus (EBV), human herpes virus 8 (HHP8), Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV), and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1). The molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis are complex and may involve the induction of chronic inflammation, disruption of host genetic and epigenetic integrity and homeostasis, interference with cellular DNA repair mechanisms resulting in genome instability and cell cycle dysregulation. Genetic and epigenetic alterations induced by infection and replication of oncogenic viruses may lead to the appearance and proliferation of cancer stem cells, which are important for the initiation, progression, metastasis, relapse, and chemotherapy resistance of cancers. The cover illustrates the seven oncoviruses that could lead to human cancer.
Oncogenic Viruses and Cancer Viruses are leading causes of different types of human cancers, accounting for about 20% of total cases. Seven viruses are currently considered oncogenic viruses, including hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein Barr virus (EBV), human herpes virus 8 (HHP8), Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV), and human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1). The molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis are complex and may involve the induction of chronic inflammation, disruption of host genetic and epigenetic integrity and homeostasis, interference with cellular DNA repair mechanisms resulting in genome instability and cell cycle dysregulation. Genetic and epigenetic alterations induced by infection and replication of oncogenic viruses may lead to the appearance and proliferation of cancer stem cells, which are important for the initiation, progression, metastasis, relapse, and chemotherapy resistance of cancers. The cover illustrates the seven oncoviruses that could lead to human cancer. -
 Phage and Therapy This issue of Virologica Sinica is to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the discovery of “fi lterable lytic factor” or “bacteriophage” (1915-2015). During the past 100 years, both basic knowledge and applications of bacteriophages have been substantially explored and developed. In recent years, bacteriophage research is booming and holding the hope to tackle the rise of antimicrobial resistance in the post-antibiotic era. In this issue, new phages are introduced, phage lytic enzymes are described, phage and host interactions are discussed, and successful experiences of phage therapy are shared. The cover illustrates the phages in this issue: ΦVMY22 (golden yellow), ΦCASbig (orange red), ΦKAZ14(magenta). And the phage in blue color is the courtesy of the Core Facility of Wuhan Institute of Virology.
Phage and Therapy This issue of Virologica Sinica is to celebrate the 100th anniversary of the discovery of “fi lterable lytic factor” or “bacteriophage” (1915-2015). During the past 100 years, both basic knowledge and applications of bacteriophages have been substantially explored and developed. In recent years, bacteriophage research is booming and holding the hope to tackle the rise of antimicrobial resistance in the post-antibiotic era. In this issue, new phages are introduced, phage lytic enzymes are described, phage and host interactions are discussed, and successful experiences of phage therapy are shared. The cover illustrates the phages in this issue: ΦVMY22 (golden yellow), ΦCASbig (orange red), ΦKAZ14(magenta). And the phage in blue color is the courtesy of the Core Facility of Wuhan Institute of Virology. -
 Herpesviruses The special issue included perspectives, minireviews, research articles, and brief communications. All manuscripts accepted will be waived for publication charge. And all submitted manuscripts will be processed following the standard journal procedure such as being screened by editors and peer-reviewing.
Herpesviruses The special issue included perspectives, minireviews, research articles, and brief communications. All manuscripts accepted will be waived for publication charge. And all submitted manuscripts will be processed following the standard journal procedure such as being screened by editors and peer-reviewing. -
 Chronic Viral Infections and Immunomodulation Viral infection in human induces various levels of host immune response, through which the host aims to eliminate those intruders. However, some viruses could often evade immune system and result in chronic infections. Almost 500 million people world-wide are chronically infected with hepatitis B and C viruses and human immune deficiency virus. Thus, a special issue focusing on the interaction of the host immune system with HBC, HCV, and HIV, and new immunomodulations of these chronic viral diseases is presented as the first issue of 2014 in Virologica Sinica. The cover depicts hepatitis C viruses approaching the B lymphocyte.
Chronic Viral Infections and Immunomodulation Viral infection in human induces various levels of host immune response, through which the host aims to eliminate those intruders. However, some viruses could often evade immune system and result in chronic infections. Almost 500 million people world-wide are chronically infected with hepatitis B and C viruses and human immune deficiency virus. Thus, a special issue focusing on the interaction of the host immune system with HBC, HCV, and HIV, and new immunomodulations of these chronic viral diseases is presented as the first issue of 2014 in Virologica Sinica. The cover depicts hepatitis C viruses approaching the B lymphocyte. -
 Structural Virology A special topic section on Structural Virology is included in this issue. The section contains three review articles, which cover the recent research advancement on the structures of reovirus particle, flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease, and enterophage T7 RNA polymerase. The issue cover presents: i) Crystal structure of a late initiation complex of T7 RNA Polymerase; ii) Crystal structure of the NS2B-NS3 protease with a peptide-based inhibitor; iii) Cryo-EM structure of the turreted reovirus core.
Structural Virology A special topic section on Structural Virology is included in this issue. The section contains three review articles, which cover the recent research advancement on the structures of reovirus particle, flavivirus NS2B-NS3 protease, and enterophage T7 RNA polymerase. The issue cover presents: i) Crystal structure of a late initiation complex of T7 RNA Polymerase; ii) Crystal structure of the NS2B-NS3 protease with a peptide-based inhibitor; iii) Cryo-EM structure of the turreted reovirus core. -
 Cyanophage and Algal Virus Electron microscopy images of three types of cyanophages: 1) upper left: AsGV-L cyanophage particles, showing geminivirus-like morphology with two incomplete icosahedra joined together; 2) lower left: MaCV-L cyanophage particles,showing corticovirus-like and round shape with icosahedral symmetry and a non-enveloped capsid; 3) right: cyanophage PP virions , with short and stubby tail structures. Images painted with pseudo-colors. (Cover designed by Meng Wang, Wuhan IOV.)
Cyanophage and Algal Virus Electron microscopy images of three types of cyanophages: 1) upper left: AsGV-L cyanophage particles, showing geminivirus-like morphology with two incomplete icosahedra joined together; 2) lower left: MaCV-L cyanophage particles,showing corticovirus-like and round shape with icosahedral symmetry and a non-enveloped capsid; 3) right: cyanophage PP virions , with short and stubby tail structures. Images painted with pseudo-colors. (Cover designed by Meng Wang, Wuhan IOV.)
GALLERY
会议信息更多+
新闻更多+
- [05/06]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [01/11]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [05/07]Q1区!VS最新影响因子5.5!
- [22/02]2022年VS高被引论文奖发布
- [21/10]第十届新生病毒性疾病控制学术研讨会 | 第一轮通知
- [09/09]肝癌细胞中CK1α上调IFNAR1的表达,从而促进I型IFN抑制HBV复制
- [09/09]一种新的干扰素诱导的长非编码RNA ZAP-IT1阻断寨卡病毒在A549细胞中的复制
- [09/09]首发精神分裂症中,驯化的人内源性逆转录病毒W家族包膜蛋白通过降低5-HT4受体的水平激活SK2
- [09/09]发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒L蛋白功能域和保守残基研究为理解病毒RNA转录/复制机制提供新思路
- [09/09]亲环素A结合AKT1并通过介导AKT/mTOR/NF-κB正反馈环路的激活促进EB病毒的致瘤作用 | VS推荐