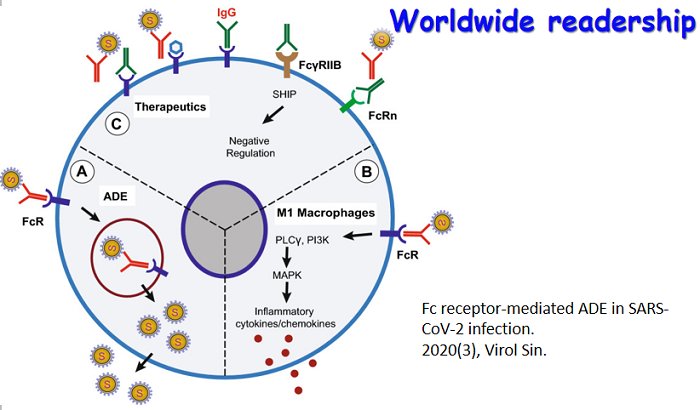
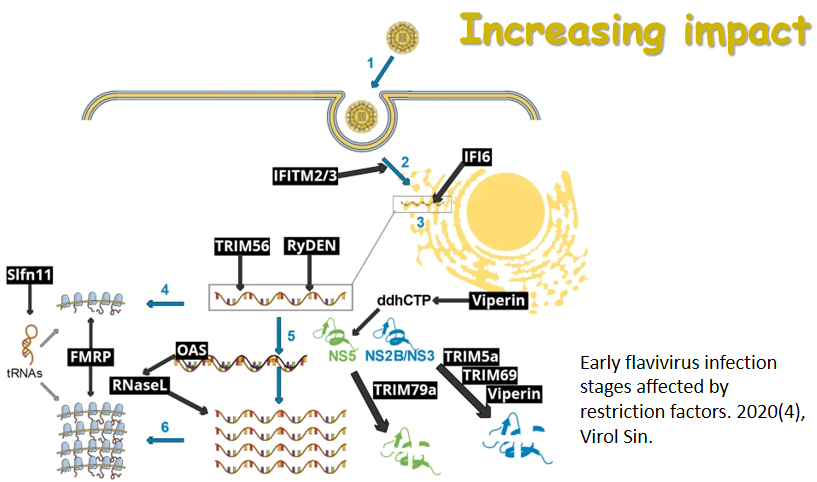
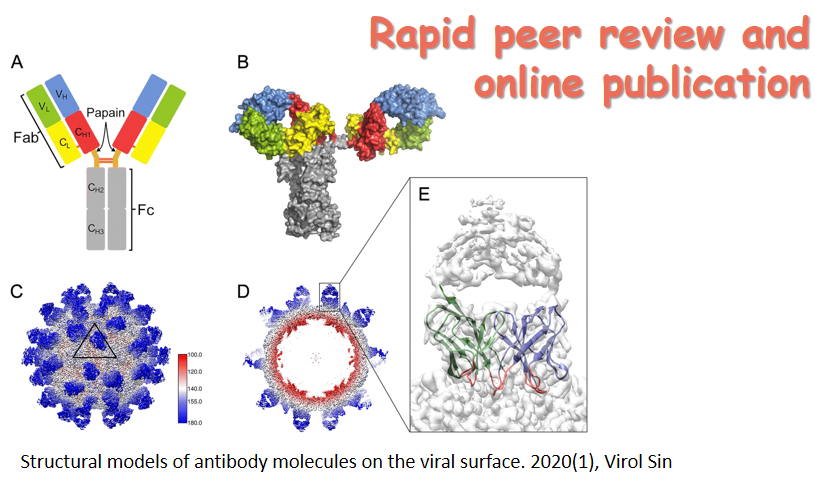
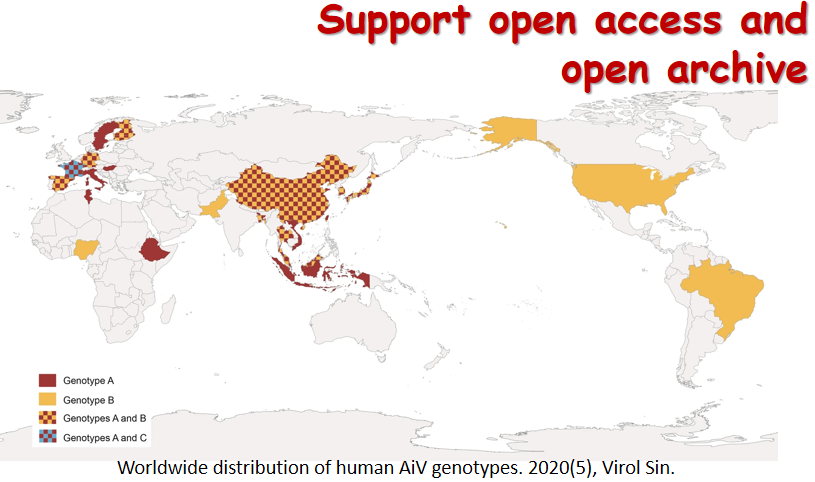
在线优先
显示方式:
GALLERY
会议信息更多+
新闻更多+
- [05/06]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [01/11]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [05/07]Q1区!VS最新影响因子5.5!
- [22/02]2022年VS高被引论文奖发布
- [21/10]第十届新生病毒性疾病控制学术研讨会 | 第一轮通知
- [09/09]肝癌细胞中CK1α上调IFNAR1的表达,从而促进I型IFN抑制HBV复制
- [09/09]一种新的干扰素诱导的长非编码RNA ZAP-IT1阻断寨卡病毒在A549细胞中的复制
- [09/09]首发精神分裂症中,驯化的人内源性逆转录病毒W家族包膜蛋白通过降低5-HT4受体的水平激活SK2
- [09/09]发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒L蛋白功能域和保守残基研究为理解病毒RNA转录/复制机制提供新思路
- [09/09]亲环素A结合AKT1并通过介导AKT/mTOR/NF-κB正反馈环路的激活促进EB病毒的致瘤作用 | VS推荐