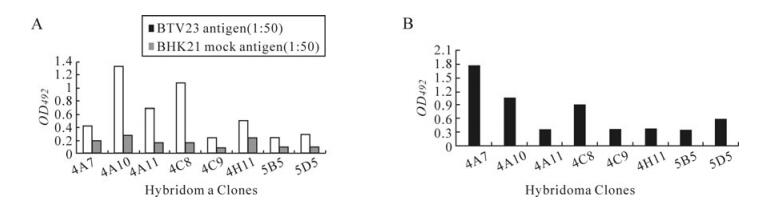
Detection of Bluetongue Virus Group-specific Antigen Using Monoclonal Antibody Based Sandwich ELISA
2010, 25(6): 390 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3160-y
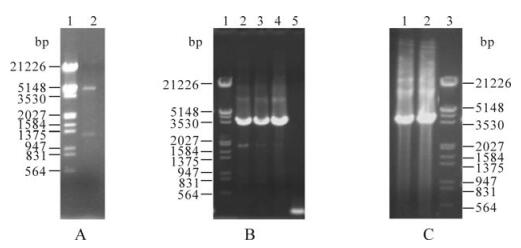
水稻瘤矮病毒外层衣壳蛋白基因S8在昆虫细胞中的表达?
2010, 25(6): 401 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3152-y
为了获得具有生物活性的水稻瘤矮病毒(Rice gall dwarf virus, RGDV)外层衣壳蛋白P8,利用杆状病毒表达系统对其主要外层衣壳蛋白基因S8在草地贪夜蛾(Spodoptera frugiperda, Sf9)昆虫细胞中进行表达。将RGDV外层衣壳蛋白基因S8亚克隆至杆状病毒表达载体pFastBacTM1上,获得重组杆状病毒转移载体pFB-S8,以pFB-S8转化含穿梭质粒Bacmid的E. coli DH10Bac感受态细胞,得到含有目的基因片段的重组杆粒rbpFB-S8。重组病毒rvpFB-S8以不同MOI(Multiplicity of infection, MOI)感染Sf9细胞,不同时间段收集细胞,并进行SDS-PAGE,Western-blotting分析以及免疫荧光显微镜观察。结果表明,S8 基因在昆虫细胞中成功表达,在感染Sf9昆虫细胞48-72 h后RGDV P8蛋白表达量达最高,免疫荧光显微镜观察则显示,RGDV P8蛋白在感染的Sf9昆虫细胞质中形成虚线状结构。
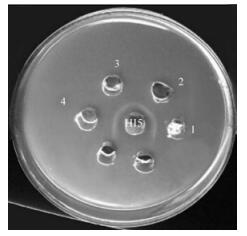
Sequence Analysis of Attachment Gene of Lumpy Skin Disease and Sheep Poxviruses
2010, 25(6): 409 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3150-0
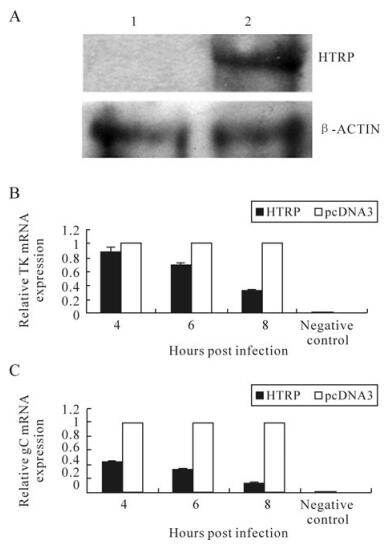
HSV1感染相关细胞分子HTRP通过乙酰化体系对病毒转录调控的影响?
2010, 25(6): 417 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3147-8
Ⅰ型单纯疱疹病毒(HSV-1)感染KMB-17后诱导的差异基因htrp所编码蛋白HTRP可与去乙酰化转移酶HDAC辅抑制因子复合物mSin3A的组成成分之一SAP30之间发生相互作用。为了进一步揭示HTRP与SAP30相互作用的生物学意义,本实验利用实时荧光定量PCR及双荧光素酶检测系统,证明HTRP对病毒启动子的转录具有抑制作用,其和SAP30共同作用对病毒基因的转录抑制具有协同效应,且这种效应与HDAC的酶活性相关。ChIP实验证明其具体机理是HTRP能够促进HDACs酶活性而增加组蛋白H3分子第14和9位赖氨酸的去乙酰化水平。
H5N1感染鸡胚成纤维细胞中标化定量PCR结果的参考基因选择
2010, 25(6): 425 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3114-4
鸡胚成纤维细胞(CEF)是研究H5N1禽流感病毒与宿主之间相互作用时最常用的细胞之一。本研究对H5N1病毒感染CEF细胞后11个持家基因mRNA表达的稳定性进行了比较,旨在获得定量PCR研究中对数据进行标化的可靠内参基因。试验采用100TCID50 H5N1病毒感染CEF,在感染后3、12、24、30小时收获细胞,采用定量PCR技术和GeNorm工具软件,对11个持家基因的表达水平和稳定性进行比较研究。结果表明:在正常CEF和病毒感染的CEF细胞中,11个持家基因表达稳定性不同; RPL4、YWHAZ是研究H5N1病毒感染后宿主细胞基因表达的理想内参基因。对于H5N1禽流感病毒在CEF中复制的相关研究,ACTB以及RPL4则是理想的内参基因。
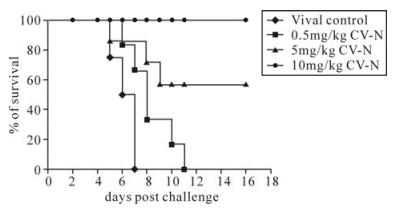
重组蓝藻抗病毒蛋白-N抗HSV-1活性的研究*
2010, 25(6): 432 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3131-3
探讨重组蓝藻抗病毒蛋白N 体内外抗单纯疱疹病毒1型(HSV-1) 的作用。选用HSV-1标准株(SM44株)进行了CV-N抗病毒活性的研究。 通过观察细胞病变效应(CPE)、MTT比色法检测细胞增殖判断CV-N在Vero细胞中的抗病毒效果;荧光定量PCR(FQ-PCR)检测病毒DNA的拷贝数。结果显示CV-N对Vero细胞毒性较低,半数毒性浓度CC50为359μg/ml;CV-N对HSV-1无直接灭活作用,在病毒感染前及感染后应用CV-N均可有效地抑制病毒的复制,其IC50分别是2.26 和30.16μg/mL,CV-N还可以明显抑制HSV-DNA的的复制。体内实验通过昆明小鼠脑内局部接种HSV-1,制备疱疹性脑炎模型,分别于病毒接种后2h、3d、5d、7d 以3个不同剂量的的CV-N( 0.5, 5, 10 mg/kg) 腹腔给药治疗,观察记录小鼠的发病时间及存活时间,同时取脑组织标本进行HE染色观察细胞病变。结果表明,与病毒对照组相比,5mg/kg及10mg/kg CV-N治疗组小鼠症状明显减轻,平均存活天数分别超过9天和14天,HE染色显示脑组织仅有轻微的炎症改变。本研究表明CV-N在体内、外均具有良好的抗病毒活性,是治疗HSV感染的潜力药物之一 。
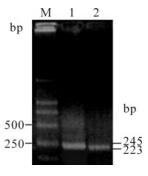
朊蛋白多肽PrP106-126 改变了小鼠小胶质细胞BV-2的 PrP mRNA表达
2010, 25(6): 440 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3134-z
朊病是一种传染性和致死性的神经退行性疾病。朊病病原是一种异常的朊蛋白聚集物。中枢神经系统内的小胶质细胞激活是朊病的一种显著特征。本研究应用实时荧光定量PCR方法检测了朊蛋白多肽PrP106-126对小鼠小胶质细胞BV-2 的PrP mRNA表达影响。结果显示PrP106-126作用BV-2细胞18 h 后PrP mRNA表达水平显著提高,比正常水平提高3倍,作用24 h 后比正常水平提高4.5 倍,且BV-2 细胞的增殖活性在18 h 和24 h 后也相应提高。这些结果首次证明了朊蛋白多肽PrP106-126 提高了小胶质细胞的PrP mRNA 表达水平,表明小胶质细胞在朊病毒致病过程中可能具有关键作用。
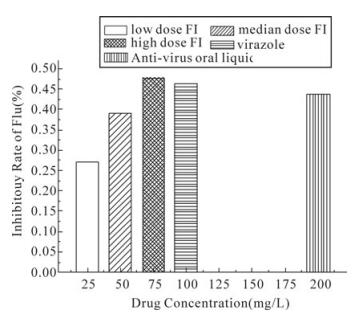
大青叶有效单体体内抗流感病毒活性的研究
2010, 25(6): 445 doi: 10.1007/s12250-010-3142-0
为评价大青叶有效单体在体内抗流感病毒活性,我们建立了病毒性肺炎小鼠模型,分为3个不同剂量(低,中,高)组,然后观察它们的肺指数,肺病变,肺病毒滴度,存活时间和死亡率。结果表明:低,中,高剂量的大青叶单体可降低小鼠肺指数从2.64至1.93,1.63和1.40(P <0.01),病毒血凝滴度可从1.15下降至0.84,0.70和0.59(P <0.01)。此外,不同剂量的大青叶均能将小鼠死亡率由100%降为30%,25%和15%,延长小鼠生存时间从5.1d至6.5d,8.4d和8.9d(P<0.01)。高剂量组(75 mg.kg-1.d-1)与100 mg.kg-1/d病毒唑同效(P> 0.05),优于200 mg.kg-1.d-1抗病毒口服液性(P <0.05)。
- [01/11]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [05/07]Q1区!VS最新影响因子5.5!
- [22/02]2022年VS高被引论文奖发布
- [21/10]第十届新生病毒性疾病控制学术研讨会 | 第一轮通知
- [09/09]肝癌细胞中CK1α上调IFNAR1的表达,从而促进I型IFN抑制HBV复制
- [09/09]一种新的干扰素诱导的长非编码RNA ZAP-IT1阻断寨卡病毒在A549细胞中的复制
- [09/09]首发精神分裂症中,驯化的人内源性逆转录病毒W家族包膜蛋白通过降低5-HT4受体的水平激活SK2
- [09/09]发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒L蛋白功能域和保守残基研究为理解病毒RNA转录/复制机制提供新思路
- [09/09]亲环素A结合AKT1并通过介导AKT/mTOR/NF-κB正反馈环路的激活促进EB病毒的致瘤作用 | VS推荐
- [09/09]转录组分析显示克里米亚刚果出血热病毒调控的关键细胞过程及III型干扰素的抗病毒作用 | VS推荐