|
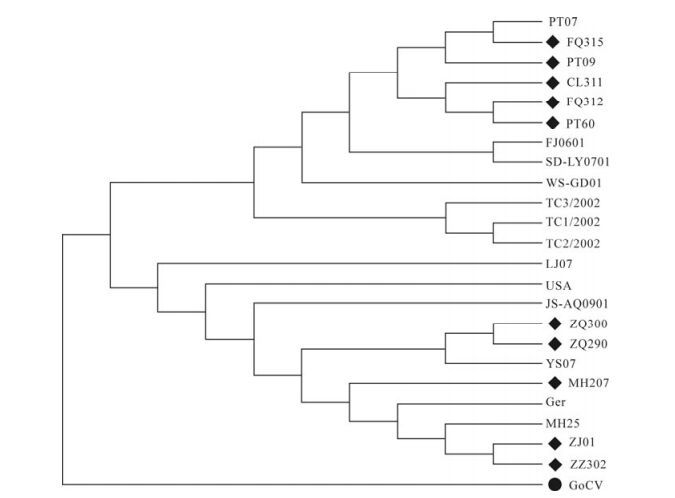
中国南方地区鸭圆环病毒的流行病学调查及其基因组特征
2011, 26(5): 289 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3192-y
为调查鸭圆环病毒——一种潜在的免疫抑制病原在我国南方地区的流行病学情况及其基因组特征。运用PCR方法对来自18个鸭厂的138份现地样品进行分析,其鸭圆环病毒感染率为35.51%,且40~60日龄鸭只易感。通过对各品种鸭蛋、鸭胚进行鸭圆环病毒调查显示其不具备垂直传播的可能性。对调查的鸭圆环病毒阳性鸭厂的鸭只并没有明显的临床症状,如:羽毛凌乱、生长减缓或体重减轻等症状。同时,克隆了10株鸭圆环病毒的全基因,并和GenBank登录的鸭圆环病毒——基因组大小在1988nt和1996nt进行核苷酸同源性比较及遗传进化分析。结果表明,其核苷酸同源性在83.2%~99.8%;遗传进化关系表明,鸭圆环病毒在遗传进化上分为两个明显亚群:欧美亚群和台湾亚群,两个亚群之间核苷酸同源性约有10.0%的差异。对来自不同国家和地区的鸭圆环病毒流行病学调查表明,鸭圆环病毒的感染并没有明显品种特征。
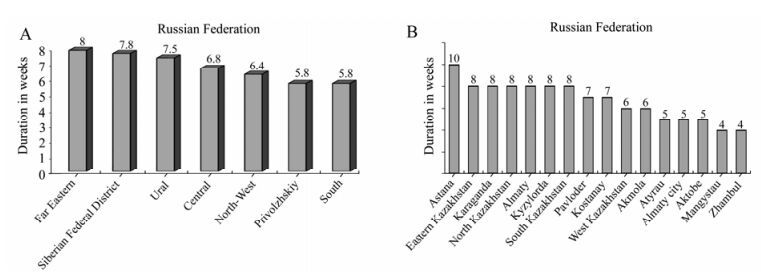
Comparison of Influenza Outbreaks in the Republic of Kazakhstan and Russia Induced by 2009 Yearly New Variant of А(H1N1) Influenza Virus
2011, 26(5): 306 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3203-z
The aim of the work is the comparison of the epidemiology of influenza and acute respiratory virus infections (ARVI) in the Republic of Kazakhstan with the corresponding influenza epidemic in Russia induced by influenza pandemic virus A/California/07/2009 in 2009. Data on influenza and ARVI from the Republic of Kazakhstan and Federal Center of influenza was collected and investigated over the course of several weeks from hospitalized patients with the same diagnosis among all population and in age groups on 16 territories of Kazakhstan and in 49 major cities of Russia. The epidemic in Kazakhstan resembled the Russian epidemic in terms of its abnormally early beginning, expression of monoaetiology, the spread of the epidemic into all territories and start of the epidemics among adult population. High percentage of hospitalized people and lethal outcome were registered in this epidemic. Similarity of epidemic process character in corresponding border-line territories of both countries was found out.

一种新的用以检测牛泡沫病毒感染的指示细胞系的建立
2011, 26(5): 315 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3204-y
为了改善在细胞水平对牛泡沫病毒 (bovine foamy virus, BFV) 的准确定量,我们建立了一株幼仓鼠肾细胞来源的指示细胞系,此细胞系基因组中整合有BFV长末端重复序列启动子(LTR, 位置在-7 到1012) 控制下的萤火虫荧光素酶报告基因。由于BFV的反式激活因子BTas能激活LTR从而启动下游报告基因的表达,因此可以根据荧光素酶的表达情况对BFV进行定量。从筛选出来的十株亚克隆中,发现一株名为BFVL的指示细胞系具有较低的本底表达水平。实验结果表明,BFVL可特异指示BFV的感染并且荧光素酶的表达对病毒的感染具有时间和剂量的依赖性。尽管在病毒感染84小时后,BFVL中荧光素酶的表达出现峰值,但是在感染后的48小时被感染的细胞和未被感染的细胞已经能够区分开。BFV的感染剂量和BFVL中荧光素酶的活性呈线性关系。除此之外,在病毒感染48小时后,用BFVL测得的病毒滴度要比传统的观察细胞病变的方法灵敏大约一万倍。这些结果表明应用BFVL指示细胞系检测BFV感染是一种快速,简单,灵敏,定量并且特异的方法。
Evaluation of efficacy of stabilizers on the thermostability of live attenuated thermo-adapted peste des petits ruminants vaccines
2011, 26(5): 324 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3205-x
In this study, thermo-adapted (Ta) PPR vaccines were assessed for their stability at 25, 37, 40, 42 and 45°C in lyophilized form using two extrinsic stabilizers {lactalbumin hydrolysate-sucrose (LS) and stabilizer E} and in reconstituted form with the diluents (1M MgSO4 or 0.85% NaCl). The lyophilized vaccines showed an expiry period of 24-26 days at 25°C, 7-8 days at 37°C and 3-4 days at 40°C. LS stabilizer was superior at 42°C with a shelf-life of 44 h, whereas in stabilizer E, a 40 h shelf-life with a comparable half-life was observed. At 45°C, the half-life in stabilizer E was better than LS and lasted for 1 day. Furthermore, the reconstituted vaccine maintained the titre for 48 h both at 4°C and 25°C and for 24-30 h at 37°C. As both the stabilizers performed equally well with regard to shelf-life and half-life, the present study suggests LS as stabilizer as a choice for lyophilization with 0.85% NaCl diluent, because it has better performance at higher temperature. These Ta vaccines can be used as alternatives to existing vaccines for the control of the disease in tropical countries as they are effective in avoiding vaccination failure due to the breakdown in cold-chain maintenance, as this vaccine is considerably more stable at ambient temperatures.
Production of CCHF Virus-Like Particle by a Baculovirus-Insect Cell Expression System
2011, 26(5): 338 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3209-6
克里米亚-刚果出血热病毒属于布尼亚病毒科内罗毕病毒属,是一种全球性分布的蜱传虫媒病毒,具有很高的致死率。克里米亚-刚果出血热病毒核衣壳由该病毒S片段编码的N蛋白组成。本研究利用杆状病毒-昆虫细胞表达系统成功地表达了克里米亚-刚果出血热病毒的N蛋白。通过对重组病毒感染的细胞样品进行电镜观察,发现在胞质的囊泡中包裹有许多形态不均一的病毒样颗粒(VLP)。利用蔗糖密度梯度离心对感染细胞的裂解物进行了分离纯化,发现病毒样颗粒位于~30%(W/V)蔗糖密度区域。进一步通过Western blot和免疫电镜验证了该病毒样颗粒主要由克里米亚-刚果出血热病毒的N蛋白构成。

Molecular Determinants Responsible for the Subcellular Localization of HSV-1 UL4 Protein
2011, 26(5): 347 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3217-6
The function of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) UL4 protein is still elusive. Our objective is to investigate the subcellular transport mechanism of the UL4 protein. In this study, fluorescence microscopy was employed to investigate the subcellular localization of UL4 and characterize the transport mechanism in living cells. By constructing a series of deletion mutants fused with enhanced yellow fluorescent protein (EYFP), the nuclear export signals (NES) of UL4 were for the first time mapped to amino acid residues 178 to 186. In addition, the N-terminal 19 amino acids are identified to be required for the granule-like cytoplasmic pattern of UL4. Furthermore, the UL4 protein was demonstrated to be exported to the cytoplasm through the NES in a chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1)-dependent manner involving RanGTP hydrolysis.
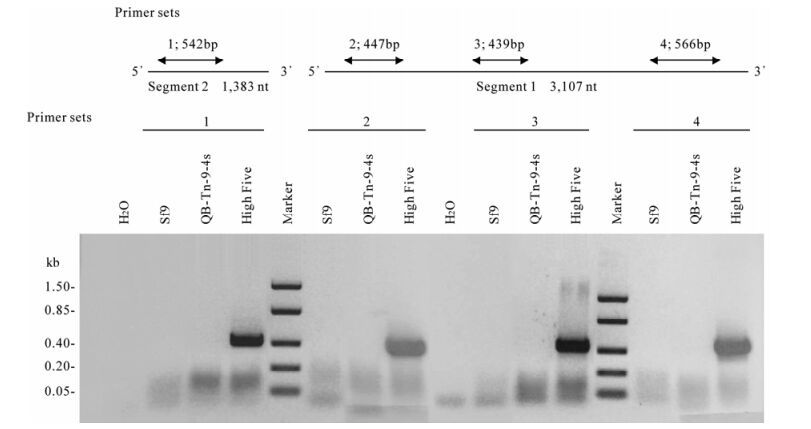
粉纹夜蛾细胞系QAU-BTI-Tn9-4s新克隆株的病毒感染和重组蛋白表达研究
2011, 26(5): 297 doi: 10.1007/s12250-011-3201-1
众所周知,Tn5B1-4细胞系(注册名为High Five)是对杆状病毒高度敏感的细胞,同时,与目前报道过的其他细胞系比较,其重组蛋白也是超高表达。但细胞系的生物学特性不是永远不变的,特别是经多次传代后可能发生改变。最近就在High5细胞中发现一种TNCL病毒(Alphanoda病毒),为此我们利用粉纹夜蛾重新建立了一个细胞系,QB-Tn9-4s,经RT-PCR分析确定无TNCL病毒存在。该文报道来自QB-Tn9-4s细胞的新克隆株QB-CL-B的建立、病毒敏感性和重组蛋白表达。结果表明,该细胞克隆在形态、生长速率及对病毒敏感性等都与其亲代细胞QB-Tn9-4s和High5细胞相似,但其重组蛋白表达水平要明显高于QB-Tn9-4s和High5细胞,是一个有应用潜力的新克隆株。
- [01/11]《中国病毒学(英文)》期刊编辑部招聘启事
- [05/07]Q1区!VS最新影响因子5.5!
- [22/02]2022年VS高被引论文奖发布
- [21/10]第十届新生病毒性疾病控制学术研讨会 | 第一轮通知
- [09/09]肝癌细胞中CK1α上调IFNAR1的表达,从而促进I型IFN抑制HBV复制
- [09/09]一种新的干扰素诱导的长非编码RNA ZAP-IT1阻断寨卡病毒在A549细胞中的复制
- [09/09]首发精神分裂症中,驯化的人内源性逆转录病毒W家族包膜蛋白通过降低5-HT4受体的水平激活SK2
- [09/09]发热伴血小板减少综合征病毒L蛋白功能域和保守残基研究为理解病毒RNA转录/复制机制提供新思路
- [09/09]亲环素A结合AKT1并通过介导AKT/mTOR/NF-κB正反馈环路的激活促进EB病毒的致瘤作用 | VS推荐
- [09/09]转录组分析显示克里米亚刚果出血热病毒调控的关键细胞过程及III型干扰素的抗病毒作用 | VS推荐